Showing 1–10 of 22 results
Chemokines
Chemokines are small signaling proteins that play a crucial role in the immune system by directing the movement of immune cells towards sites of inflammation, infection, and injury. In research, chemokines are widely studied for their involvement in various diseases, including cancer, autoimmune disorders, and chronic inflammatory conditions. Understanding chemokine signaling pathways and their receptors can lead to the development of targeted therapies that modulate immune responses. For instance, blocking specific chemokine receptors has shown promise in preventing the spread of cancer cells and in treating autoimmune diseases by reducing inappropriate immune cell activation.
Reagents related to chemokines are essential tools in research for studying these proteins functions and interactions. These reagents include recombinant chemokines, antibodies, and inhibitors, which are used in various assays to analyze chemokine activity, receptor binding, and signaling pathways. The availability of high-quality chemokine reagents enables researchers to dissect complex immune responses and develop new therapeutic strategies. Additionally, chemokine reagents are used in drug screening processes to identify potential compounds that can modulate chemokine signaling, furthering the advancement of treatments for diseases linked to immune system dysfunction.
Reagents related to chemokines are essential tools in research for studying these proteins functions and interactions. These reagents include recombinant chemokines, antibodies, and inhibitors, which are used in various assays to analyze chemokine activity, receptor binding, and signaling pathways. The availability of high-quality chemokine reagents enables researchers to dissect complex immune responses and develop new therapeutic strategies. Additionally, chemokine reagents are used in drug screening processes to identify potential compounds that can modulate chemokine signaling, furthering the advancement of treatments for diseases linked to immune system dysfunction.
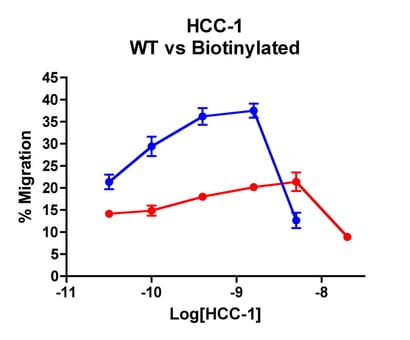
Migration assay with [8021] : Migration Assay: Cells expressing recombinant CCR1 were assayed for migration through a transwell filter at various concentrations of WT or Biotinylated HCC-1. Responses are expressed as the % of total input cells (Blue: wild type; Red: biotinylated).
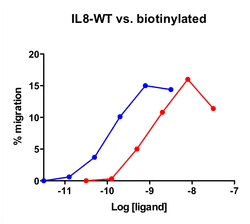
Migration assay with [8024] : Chemokine Induced Migration
Cells expressing recombinant CXCR1 were assayed for migration through the transwell bare filter at various concentrations of IL-8. The response is expressed as the % of total input cells (Blue: wild type; Red: biotinylated).

Migration assay with [8023] : Migration Assay: Cells expressing recombinant CCR10 were assayed for migration through a transwell filter at various concentrations of WT or Biotinylated MEC. Responses are expressed as the % of total input cells (Blue: wild type; Red: biotinylated).










