Showing all 3 results
GFAP antibodies
Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein (GFAP) is an intermediate filament protein primarily expressed in astrocytes, a type of glial cell in the central nervous system (CNS). GFAP plays a key role in maintaining the structural integrity of astrocytes and supporting their essential functions, including nutrient supply to neurons, maintenance of the blood-brain barrier, and response to CNS injuries. Due to its specific expression in astrocytes, GFAP serves as a widely used marker for astroglial cells and is particularly valuable in studies of neuroinflammation, gliosis, and CNS trauma.
In Western blotting (WB), GFAP is commonly used to monitor astrocyte activation and gliosis, which occurs in response to CNS injuries or neurodegenerative diseases. The GFAP antibodies available on your website can also be used in immunofluorescence (IF) and immunohistochemistry (IHC) to visualize astrocyte distribution and reactivity in brain and spinal cord tissues. These techniques are especially useful in studying conditions such as multiple sclerosis, Alzheimer's disease, and brain injuries, where astrocyte activation plays a significant role in disease progression and repair mechanisms.
Given its central role in astrocyte function and its specific upregulation during CNS damage or disease, GFAP is an essential marker in research focused on neuroinflammation, astrocyte biology, and the brain�s response to injury. Its expression provides valuable insights into both normal CNS function and pathological conditions involving glial activation and scar formation.
| target | type | reactivity | applications | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6193 | GFAP | rabbit monoclonal (ZR356) | human | IHC | |||
| 6194 | GFAP | mouse monoclonal (GA-5) | human | IHC | |||
| 9024 | GFAP | mouse monoclonal | human mouse rat | WB ICC IHC | |||
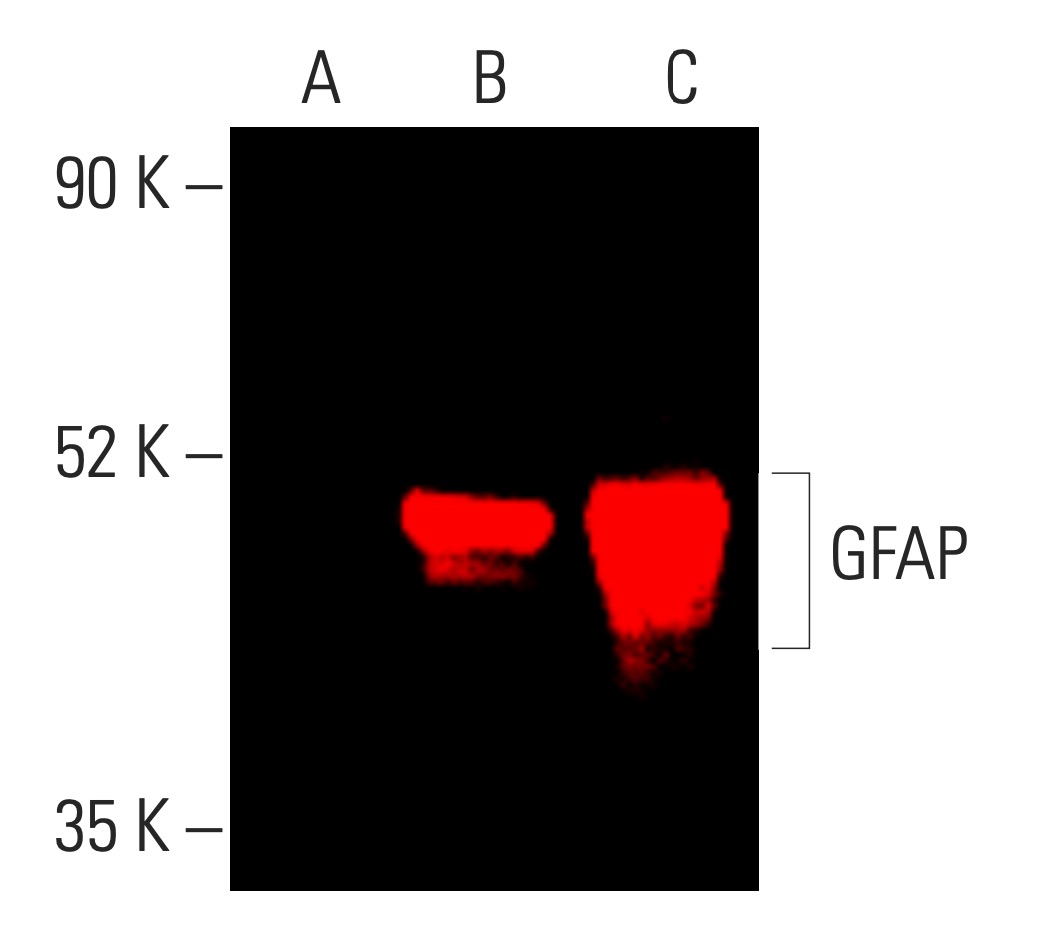
WB with antibody [9024] : Near-Infrared western blot analysis of GFAP expression in non-transfected (A) human GFAP transfected 293T (B) and human GFAP transfected 293T (C) whole cell lysates.
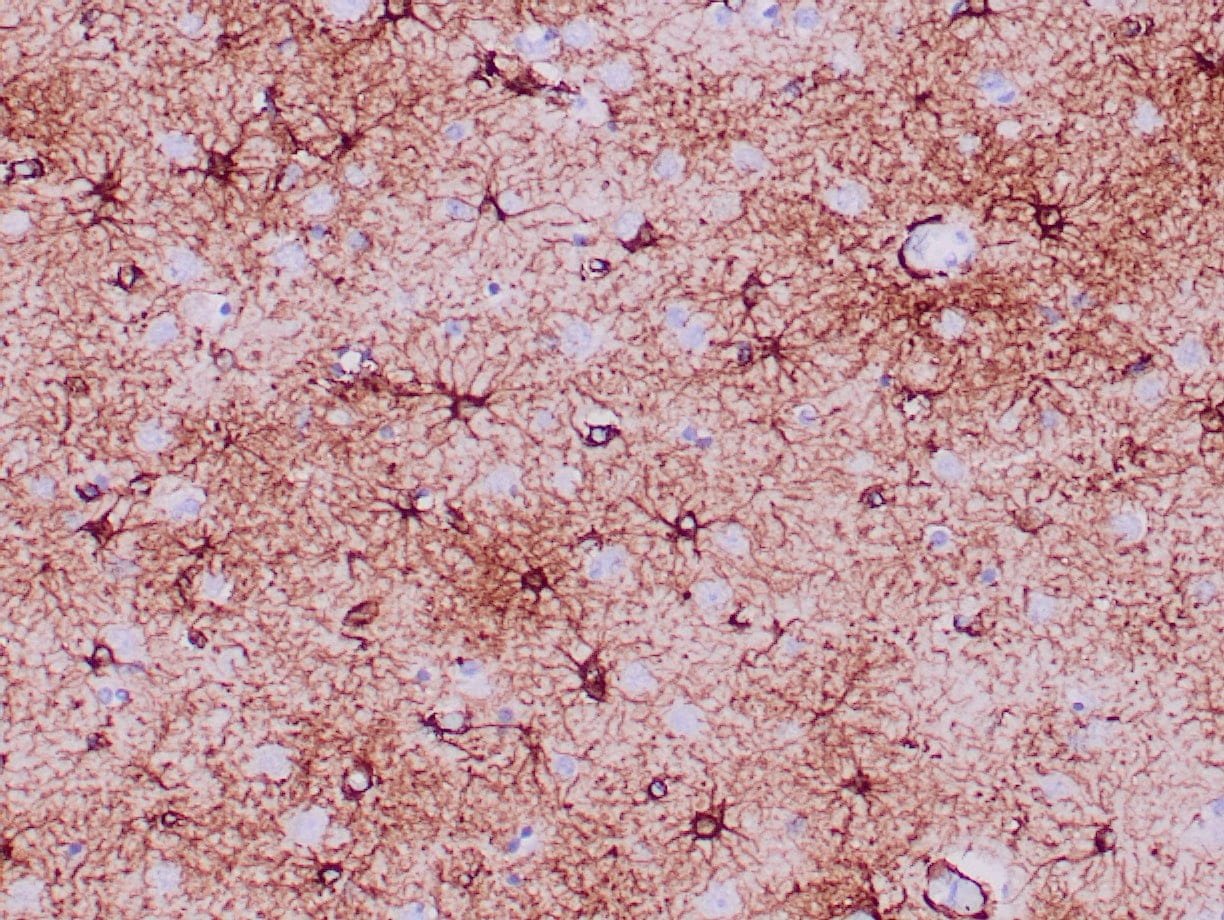
IHC with antibody [6193] : Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human brain stained with anti-GFAP antibody using peroxidase-conjugate and DAB chromogen. Note positive staining of astrocytic processes
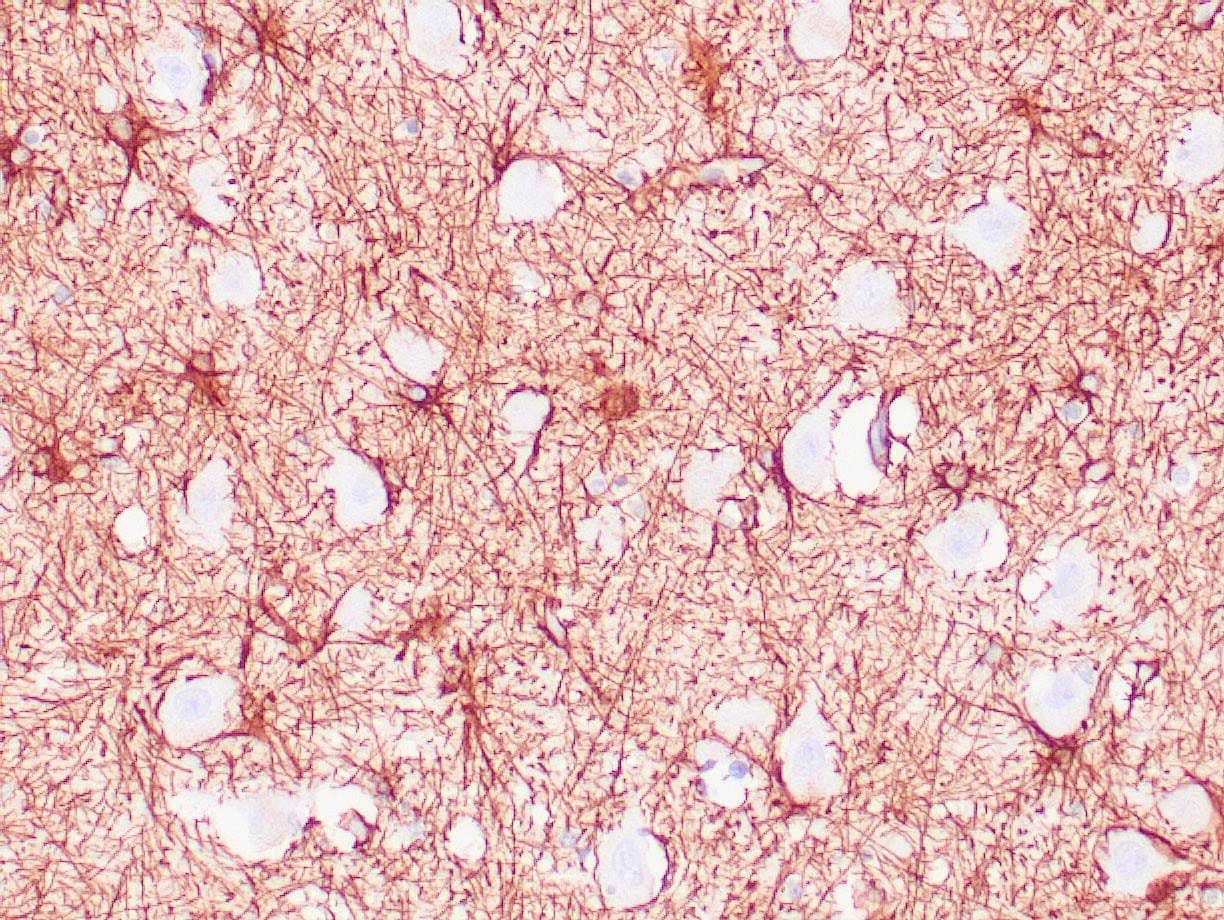
IHC with antibody [6194] : Human brain stained with anti-GFAP antibody using peroxidase-conjugate and DAB chromogen. Note positive staining of astrocytic processes.



