Showing all 2 results
Ubiquitin antibodies
Ubiquitin is a small regulatory protein that plays a fundamental role in cellular protein degradation through the ubiquitin-proteasome system. By attaching to target proteins, ubiquitin tags them for degradation, ensuring proper turnover of damaged, misfolded, or unneeded proteins. This process is critical for maintaining cellular homeostasis, regulating key biological processes such as cell cycle progression, DNA repair, and response to stress. As a result, ubiquitin is a central player in cellular quality control mechanisms.
In Western blotting (WB), ubiquitin is commonly used to study protein degradation, ubiquitination pathways, and the cellular response to stress or disease. The antibodies for ubiquitin offered on your website can also be applied in immunofluorescence (IF) and immunohistochemistry (IHC) to visualize ubiquitinated proteins and their distribution within cells and tissues. This enables researchers to investigate alterations in protein turnover, particularly in conditions like cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, and inflammatory disorders, where the ubiquitin-proteasome system is often dysregulated.
Given its role in tagging proteins for degradation and its involvement in diverse cellular processes, ubiquitin serves as an essential marker for studying proteostasis and cellular stress responses. Its significance in research spans many areas, from understanding disease mechanisms to exploring therapeutic targets aimed at modulating protein degradation.
| target | type | reactivity | applications | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6399 | Ubiquitin | mouse monoclonal (ZM191) | human | IHC | |||
| 9044 | Ubiquitin | rabbit polyclonal (BLR100G) | human mouse rat rabbit goat cat sheep hamster cow dog guinea pig pig h pylori other | WB ICC IHC | |||
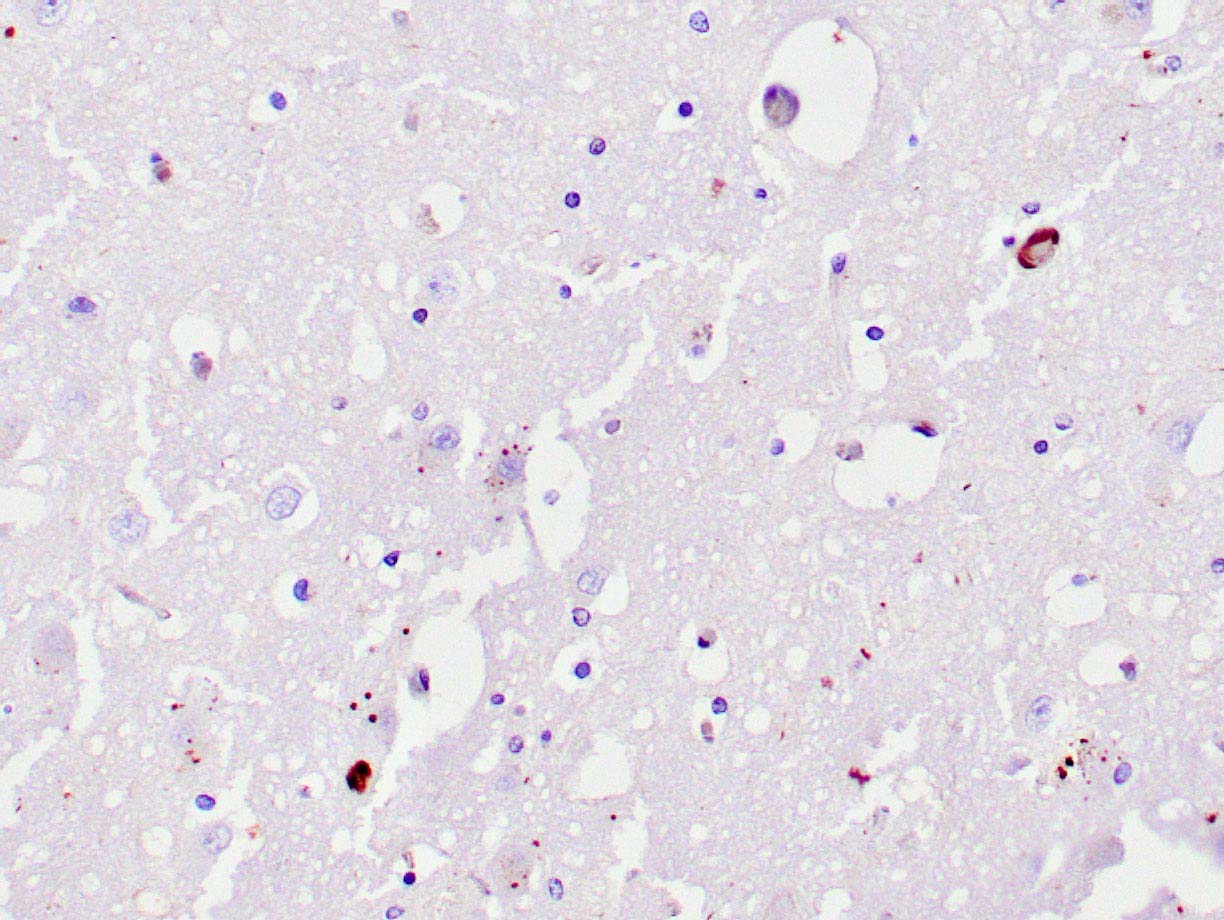
IHC with antibody [6399] : Human brain hippocampus stained with anti-ubiquitin antibody using peroxidase-conjugate and DAB chromogen. Note the cytoplasmic staining of few neurons..
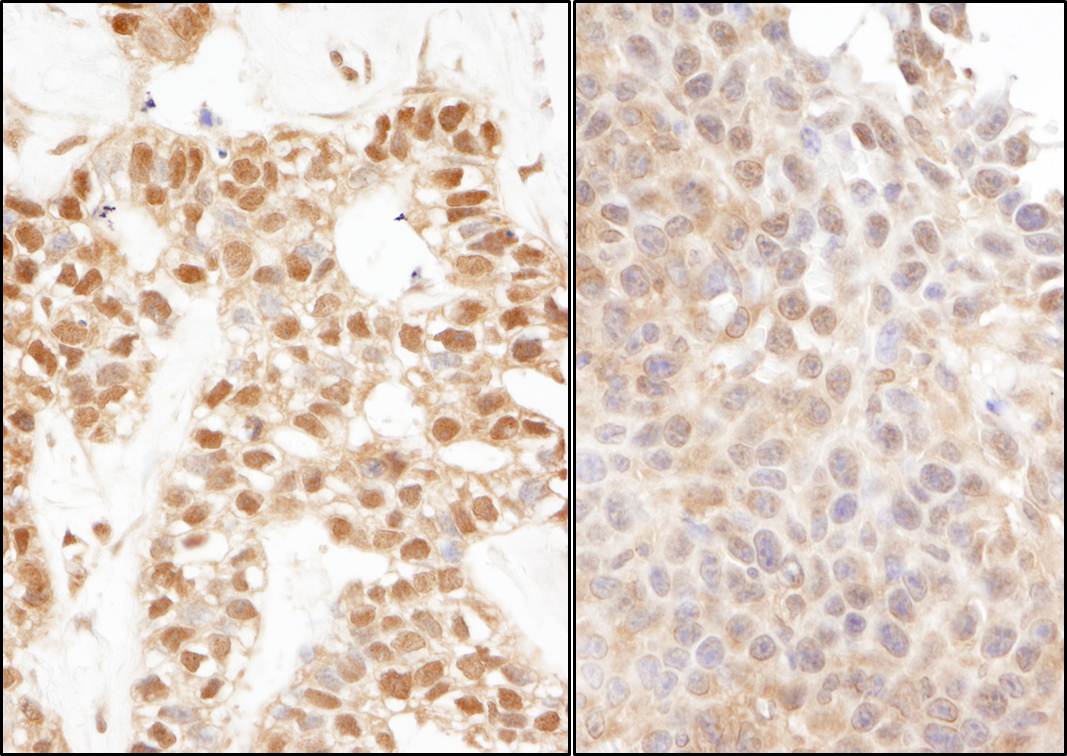
IHC with antibody [9044] : Detection of human and mouse Ubiquitin by immunohistochemistry. Sample: FFPE sections of human breast carcinoma (left) and mouse teratoma (right). Antibody: Affinity purified rabbit anti-Ubiquitin used at a dilution of 1:1,000 (1µg/ml). Detection: DAB
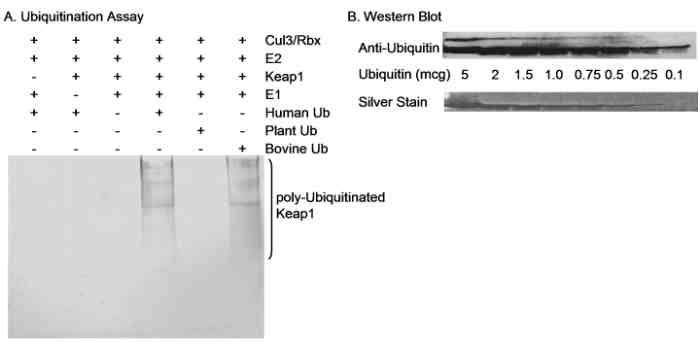
WB with antibody [9044] : Detection of Ubiquitin by western blotting of Products from an Ubiquitination Assay and Purified Ubiquitin. Samples: A) Ubiquitination assay was performed as described in Zhang et al., 2004, Mol. Cell. Biol. 24(24):10941-10953. B) Purified ubiquitin applied in decreasing amounts from 5 to 0.1 µg. Antibody: Affinity purified rabbit anti-Ubiquitin antibody used at 0.4 µg/ml for western blot. Detection: Alkaline phosphatase conjugated secondary antibody and development with NBT/BCIP for 10 minutes (A and B).


