Showing the single result
Tyrosine Hydroxylase
Actin is widely used as a reliable loading control in Western blotting (WB) due to its consistent expression levels across different cell types and conditions. Its stable and ubiquitous presence in cells ensures that variations in protein loading are accurately normalized, making actin ideal for comparative analysis in WB experiments.
Beyond WB, actin antibodies offered by your website are also available for use in immunofluorescence (IF) and immunohistochemistry (IHC). These antibodies can detect actin structures in a variety of tissues and cell types, helping visualize cytoskeletal dynamics. Actin is a key component of the cytoskeleton, playing an essential role in maintaining cell shape, facilitating cell movement, and organizing intracellular structures. It forms dynamic structures such as filaments and microfilaments, which are crucial for many cellular processes, including division and signaling.
| target | type | reactivity | applications | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9009 | Tyrosine Hydroxylase | rabbit monoclonal | human mouse rat | WB ICC | |||
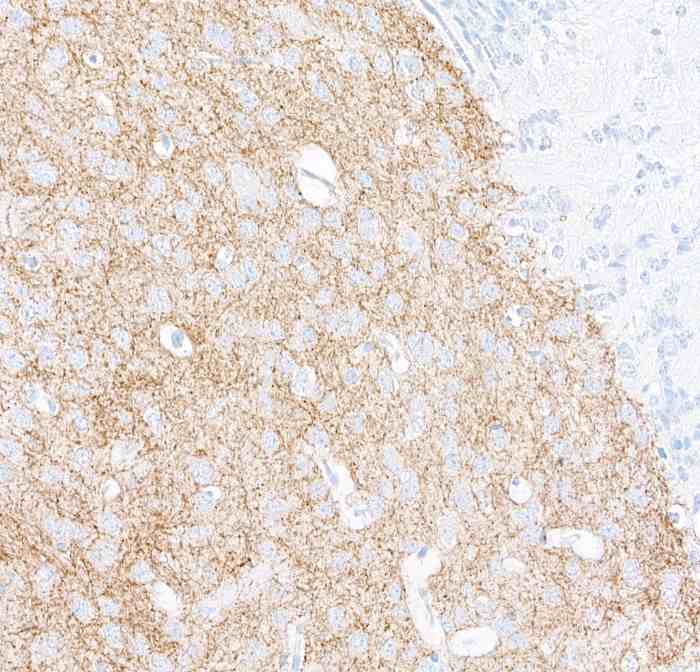
IHC with antibody [9009] : Detection of human Tyrosine Hydroxylase in FFPE mouse brain by immunohistochemistry.
Antibody: Rabbit anti-Tyrosine Hydroxylase recombinant monoclonal antibody. Secondary: HRP-conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG. Substrate: DAB.
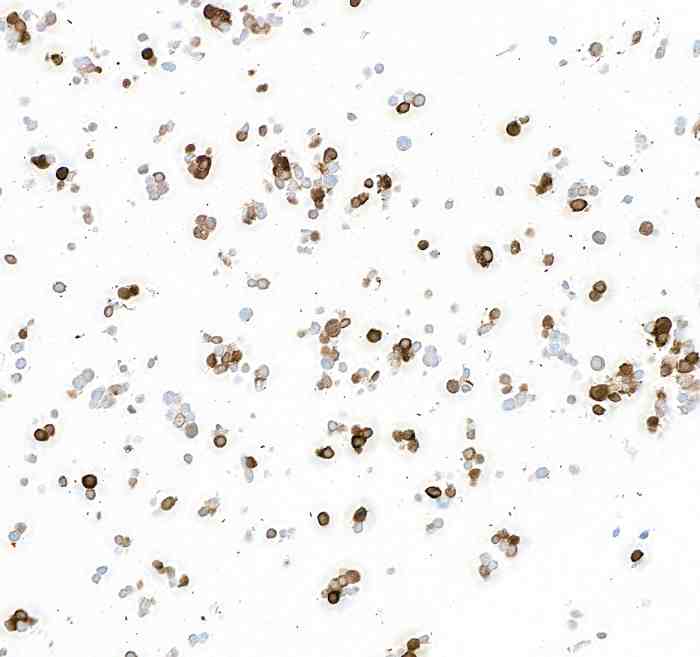
IHC with antibody [9009] : Detection of human Tyrosine Hydroxylase in FFPE SK-N-BE(2) cells by immunocytochemistry.
Antibody: Rabbit anti-Tyrosine Hydroxylase recombinant monoclonal antibody. Secondary: HRP-conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG. Substrate: DAB.

WB with antibody [9009] : Detection of human Tyrosine Hydroxylase by Western blot. Samples: Whole cell lysate (10 �g) from HEK293T, SK-N-SH, SK-N-BE(2), Jurkat, and SK-N-MC cells prepared using NETN lysis buffer. Antibody: Rabbit anti-Tyrosine Hydroxylase recombinant monoclonal antibody used at 1:1000. Secondary: HRP-conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG. Detection: Chemiluminescence with an exposure time of 30 seconds. Lower Panel: Rabbit anti-COPB2 antibody.
