| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| accession | P48061-2 |
| express system | E.coli |
| product tag | biotin at C-terminal |
| purity | > 97% by SDS PAGE |
| molecular weight | Predicted Molecular Mass: 10.381kDa Extinction Coefficient: 14,180 M-1 cm-1 Actual Molecular Mass: 10.381kDa by ESI Mass Spec |
| available size | 100 µg, 20 µg, 5 µg, 50 µg |
| endotoxin | <0.01 EU per 1μg of the protein by the LAL method |
Biotinylated Stromal-Cell Derived Factor-1a (SDF-1a/CXCL12) 8026
Price range: $134.00 through $2,862.00
Summary
- Expression: E.coli
- Amino Acid Range: 22-89
Biotinylated Stromal-Cell Derived Factor-1a (SDF-1a/CXCL12) 8026
| protein |
|---|
| Database link: human P48061-2 |
| Size and concentration 2, 10, 50, 100µg and lyophilized |
| Form Lyophilized |
| Storage Instructions Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles: • 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied. • 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution. • 3 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution |
| Storage buffer ​Reconstitution: Spin sample prior to reconstitution. Recommended concentration of 100µg/mL in sterile water. Shipping: Room Temp |
| Purity > 97% by SDS PAGE and HPLC |
| target relevance |
|---|
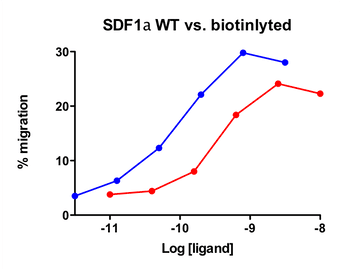
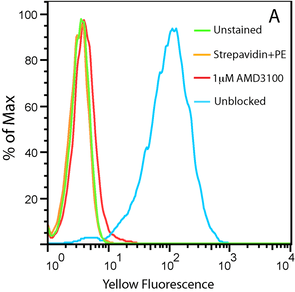
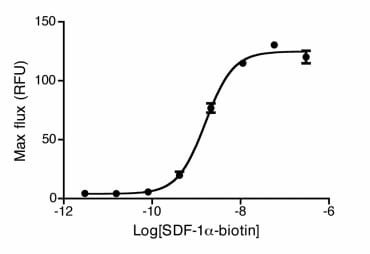
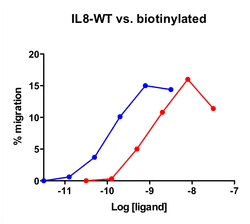
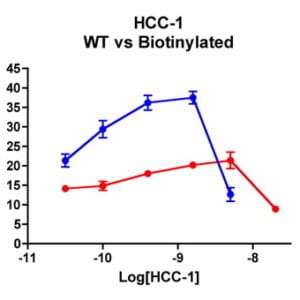
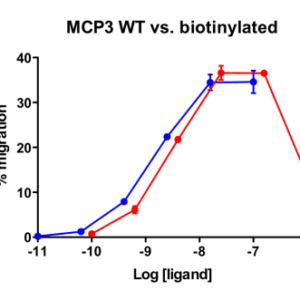
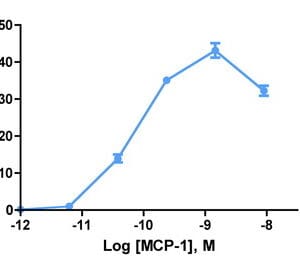
| Stromal-Cell Derived Factor-1α (SDF-1α) (CXCL12) attracts lymphocytes and plays important roles in embryogenesis and angiogenesis with implications in tumor metastasis. By binding to CXCR4, one of the co-receptors for HIV viral entry, SDF-1α can suppress HIV. Besides CXCR4, SDF-1 α also binds to the “decoy†receptor CXCR7, and activates the downstream β-arrestin- rather than G protein-mediated signaling pathway. Biotinylated CXCL12 is made using an enzymatic method, which has several advantages over chemical biotinylation methods. The attachment of biotin at a specific lysine residue is nearly 100% complete, and leads to a modified chemokine with functionalities comparable to those of the unmodified CXCL12 in calcium flux and migration assay. Combining with avidin analogues conjugated to various fluorescent labels, biotinylated CXCL12 is useful in studies on receptor identification, distribution, chemokine binding, and other cellular assays. They serve as great tools in visualization and quantification, and replace the needs for radioactively labeled chemokines. |
| Protein names Stromal cell-derived factor 1 (SDF-1) (hSDF-1) (C-X-C motif chemokine 12) (Intercrine reduced in hepatomas) (IRH) (hIRH) (Pre-B cell growth-stimulating factor) (PBSF) [Cleaved into: SDF-1-beta(3-72); SDF-1-alpha(3-67)] |
| Gene names CXCL12,CXCL12 SDF1 SDF1A SDF1B |
| Protein family Intercrine alpha (chemokine CxC) family |
| Mass 10666Da |
| Function FUNCTION: Chemoattractant active on T-lymphocytes and monocytes but not neutrophils. Activates the C-X-C chemokine receptor CXCR4 to induce a rapid and transient rise in the level of intracellular calcium ions and chemotaxis. SDF-1-beta(3-72) and SDF-1-alpha(3-67) show a reduced chemotactic activity. Binding to cell surface proteoglycans seems to inhibit formation of SDF-1-alpha(3-67) and thus to preserve activity on local sites. Also binds to atypical chemokine receptor ACKR3, which activates the beta-arrestin pathway and acts as a scavenger receptor for SDF-1. Binds to the allosteric site (site 2) of integrins and activates integrins ITGAV:ITGB3, ITGA4:ITGB1 and ITGA5:ITGB1 in a CXCR4-independent manner (PubMed:29301984). Acts as a positive regulator of monocyte migration and a negative regulator of monocyte adhesion via the LYN kinase. Stimulates migration of monocytes and T-lymphocytes through its receptors, CXCR4 and ACKR3, and decreases monocyte adherence to surfaces coated with ICAM-1, a ligand for beta-2 integrins. SDF1A/CXCR4 signaling axis inhibits beta-2 integrin LFA-1 mediated adhesion of monocytes to ICAM-1 through LYN kinase. Inhibits CXCR4-mediated infection by T-cell line-adapted HIV-1. Plays a protective role after myocardial infarction. Induces down-regulation and internalization of ACKR3 expressed in various cells. Has several critical functions during embryonic development; required for B-cell lymphopoiesis, myelopoiesis in bone marrow and heart ventricular septum formation. Stimulates the proliferation of bone marrow-derived B-cell progenitors in the presence of IL7 as well as growth of stromal cell-dependent pre-B-cells (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P40224, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11069075, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11859124, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16107333, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18802065, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19255243, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29301984, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8752281}. |
| Subellular location SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: Secreted. |
| Tissues TISSUE SPECIFICITY: Isoform Alpha and isoform Beta are ubiquitously expressed, with highest levels detected in liver, pancreas and spleen. Isoform Gamma is mainly expressed in heart, with weak expression detected in several other tissues. Isoform Delta, isoform Epsilon and isoform Theta have highest expression levels in pancreas, with lower levels detected in heart, kidney, liver and spleen. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16626895}. |
| Structure SUBUNIT: Monomer or homodimer; in equilibrium. Dimer formation is induced by non acidic pH and the presence of multivalent anions, and by binding to CXCR4 or heparin. Monomeric form is required for full chemotactic activity and resistance to ischemia/reperfusion injury, whereas the dimeric form acts as a partial agonist of CXCR4, stimulating Ca2+ mobilization but with no chemotactic activity and instead acts as a selective antagonist that blocks chemotaxis induced by the monomeric form. Interacts with the N-terminus of ACKR3. Interacts with integrin subunit ITGB3 (via the allosteric site (site 2)) (PubMed:29301984). Interacts with TNFAIP6 (via Link domain). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10446158, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16107333, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16725153, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17264079, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18799424, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19255243, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27044744, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29301984, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9427609}.; SUBUNIT: (Microbial infection) Interacts with molluscum contagiosum virus protein MC148. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21802105}. |
| Post-translational modification PTM: Processed forms SDF-1-beta(3-72) and SDF-1-alpha(3-67) are produced after secretion by proteolytic cleavage of isoforms Beta and Alpha, respectively. The N-terminal processing is probably achieved by DPP4. Isoform Alpha is first cleaved at the C-terminus to yield a SDF-1-alpha(1-67) intermediate before being processed at the N-terminus. The C-terminal processing of isoform Alpha is reduced by binding to heparin and, probably, cell surface proteoglycans. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:14525775}. |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: P48061 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
| Migration assay |
Documents
| # | ||
|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | ||
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.
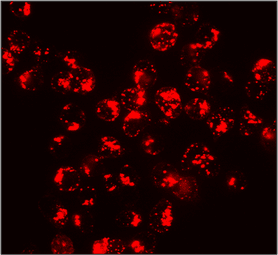

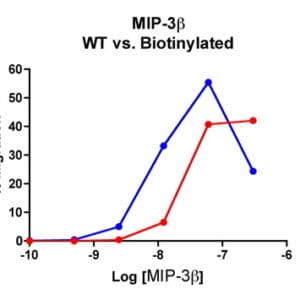
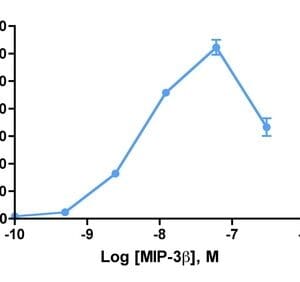
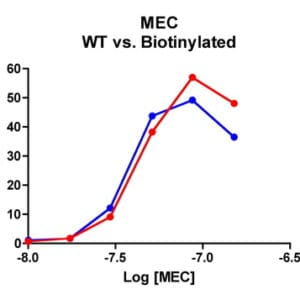


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.