| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| host | rabbit |
| isotype | IgG |
| clonality | monoclonal |
| concentration | 1 mg/mL |
| applications | ELISA, ICC/IF, WB |
| available sizes | 100 µg |
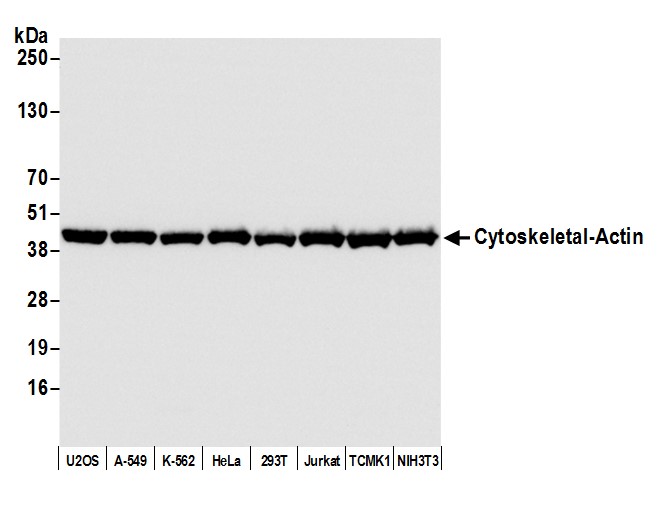
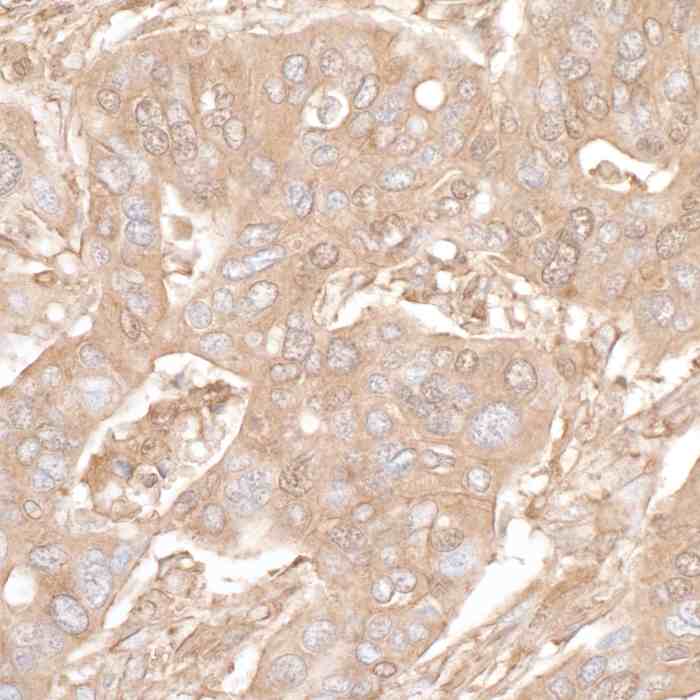
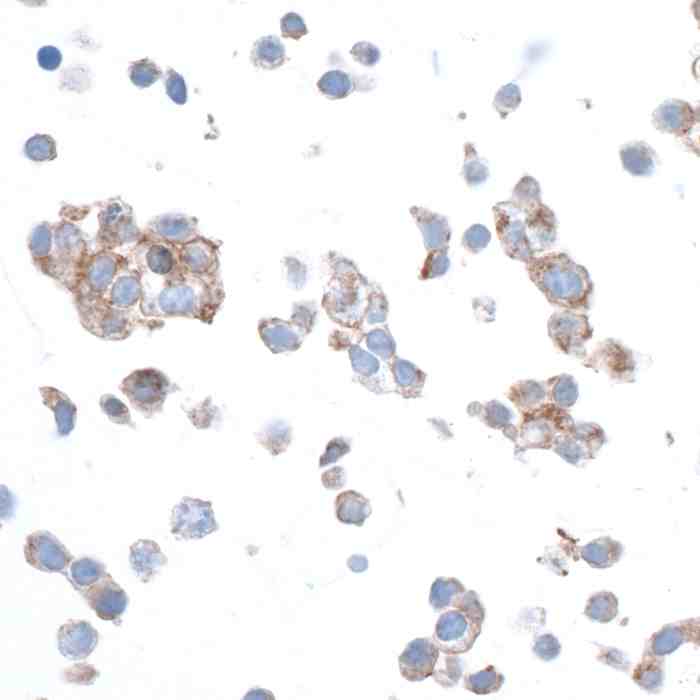
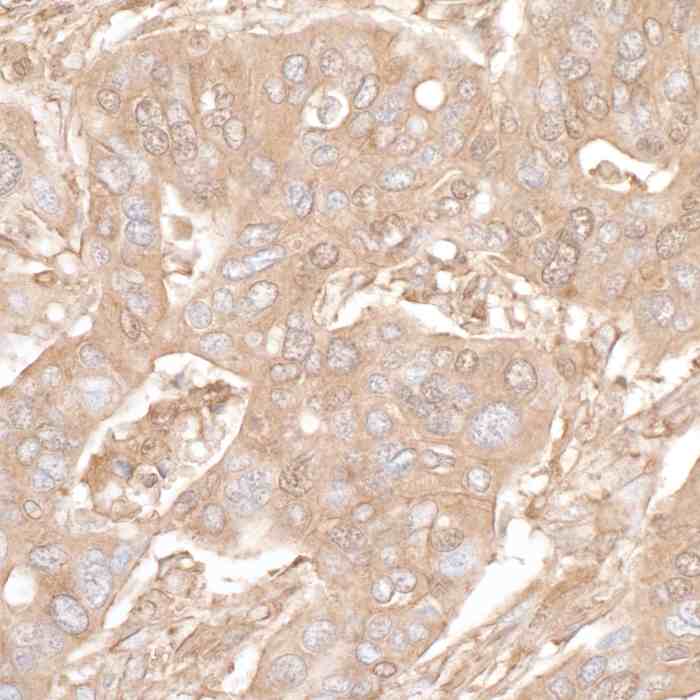
rabbit anti-beta actin monoclonal antibody 9038
$409.00
Antibody summary
- Rabbit monoclonal to beta actin
- Suitable for: WB,ICC/IF,ELISA
- Reacts with: human, mouse, rat
- Isotype: IgG
- 100 µg
rabbit anti-beta actin monoclonal antibody 9038
| antibody |
|---|
| Database link: human P60709 mouse P60710 rat P60711 |
| Tested applications WB,ICC/IF,ELISA |
| Recommended dilutions WB: 1:1000-5000 |
| Immunogen β-Actin N-terminal peptide-KLH conjugates. |
| Size and concentration 100µg and 1 mg/mL |
| Form liquid |
| Storage Instructions -20°C for 2 years or more. °Centrifuge after first thaw to maximize product recovery. Aliquot to avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. Store aliquots at 4°C for several days to weeks. |
| Storage buffer PBS, pH 7.2, 0.05% NaN3 |
| Purity affinity purified |
| Clonality monoclonal |
| Isotype IgG |
| Compatible secondaries goat anti-rabbit IgG, H&L chain specific, peroxidase conjugated, conjugated polyclonal antibody 9512 goat anti-rabbit IgG, H&L chain specific, biotin conjugated polyclonal antibody 2079 goat anti-rabbit IgG, H&L chain specific, FITC conjugated polyclonal antibody 7863 goat anti-rabbit IgG, H&L chain specific, Cross Absorbed polyclonal antibody 2371 goat anti-rabbit IgG, H&L chain specific, biotin conjugated polyclonal antibody, crossabsorbed 1715 goat anti-rabbit IgG, H&L chain specific, FITC conjugated polyclonal antibody, crossabsorbed 1720 |
| Isotype control Rabbit monocolonal IgG - Isotype Control |
| target relevance |
|---|
| Actin, a highly conserved protein, is widely recognized as an essential loading control in scientific research, particularly in the field of cell biology and molecular biology. As a structural component of the cytoskeleton, actin is present in virtually all eukaryotic cells. Actin participates in many important cellular processes, including muscle contraction, cell motility, cell division and cytokinesis, vesicle and organelle movement, cell signaling, and the establishment and maintenance of cell junctions and cell shape. Many of these processes are mediated by extensive and intimate interactions of actin with cellular membranes. Its ubiquitous expression and relatively stable levels make it an ideal reference protein for normalizing protein loading in Western blotting and other protein analysis techniques. Actin' abundance and consistent expression ensure that its quantity remains relatively constant across different experimental conditions and sample variations. Actin isoforms are distinct variants of the actin protein found in eukaryotic cells, and they play crucial roles in various cellular processes. One of the primary differences between actin isoforms lies in their tissue-specific distribution. For instance, skeletal muscle cells predominantly express the α-actin isoform, while smooth muscle cells mainly contain the γ-actin isoform. These tissue-specific distributions are essential for the specialized functions of muscle cells. Moreover, actin isoforms can also differ in their post-translational modifications. For example, γ-actin is more prone to undergo acetylation than α-actin. Additionally, actin isoforms can exhibit variations in their kinetic properties, such as rates of polymerization and depolymerization, which can influence their roles in processes like cell motility or cytoskeletal stability. Furthermore, some actin isoforms may interact with different binding partners or regulatory proteins, further diversifying their functions within the cell. These differences in tissue distribution, post-translational modifications, kinetic properties, and protein interactions contribute to the versatility and specificity of actin isoforms in various cellular processes and underline their importance in maintaining cellular structure and function. This antibody recognizes the beta actin isoform and can be used as a loading control when run alongside proteins of interest with different and resolvable molecular weights and ideally in combination with antibodies of same host and when using a secondary antibody. Click for more on: loading controls and beta Actin |
| Protein names Actin, cytoplasmic 1 (EC 3.6.4.-) (Beta-actin) [Cleaved into: Actin, cytoplasmic 1, N-terminally processed] |
| Gene names ACTB,ACTB |
| Protein family Actin family |
| Mass 41737Da |
| Function FUNCTION: Actin is a highly conserved protein that polymerizes to produce filaments that form cross-linked networks in the cytoplasm of cells (PubMed:25255767, PubMed:29581253). Actin exists in both monomeric (G-actin) and polymeric (F-actin) forms, both forms playing key functions, such as cell motility and contraction (PubMed:29581253). In addition to their role in the cytoplasmic cytoskeleton, G- and F-actin also localize in the nucleus, and regulate gene transcription and motility and repair of damaged DNA (PubMed:29925947). Part of the ACTR1A/ACTB filament around which the dynactin complex is built. The dynactin multiprotein complex activates the molecular motor dynein for ultra-processive transport along microtubules (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q6QAQ1, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25255767, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29581253, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29925947}. |
| Catalytic activity CATALYTIC ACTIVITY: Reaction=ATP + H2O = ADP + phosphate + H(+); Xref=Rhea:RHEA:13065, ChEBI:CHEBI:15377, ChEBI:CHEBI:15378, ChEBI:CHEBI:30616, ChEBI:CHEBI:43474, ChEBI:CHEBI:456216; Evidence={ECO:0000269|PubMed:25255767}; |
| Subellular location SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11687588, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17289661}. Nucleus {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11687588, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29925947}. Note=Localized in cytoplasmic mRNP granules containing untranslated mRNAs. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17289661}. |
| Structure SUBUNIT: Polymerization of globular actin (G-actin) leads to a structural filament (F-actin) in the form of a two-stranded helix (PubMed:16685646, PubMed:28604741). Each actin can bind to 4 others (PubMed:16685646, PubMed:28604741). Identified in a IGF2BP1-dependent mRNP granule complex containing untranslated mRNAs (PubMed:17289661). Component of the BAF complex, which includes at least actin (ACTB), ARID1A, ARID1B/BAF250, SMARCA2, SMARCA4/BRG1, ACTL6A/BAF53, ACTL6B/BAF53B, SMARCE1/BAF57 SMARCC1/BAF155, SMARCC2/BAF170, SMARCB1/SNF5/INI1, and one or more of SMARCD1/BAF60A, SMARCD2/BAF60B, or SMARCD3/BAF60C (PubMed:18765789). In muscle cells, the BAF complex also contains DPF3 (PubMed:18765789). Found in a complex with XPO6, Ran, ACTB and PFN1 (PubMed:14592989). Interacts with PFN1 (PubMed:10411937, PubMed:25255767). Interacts with XPO6 and EMD (PubMed:15328537). Interacts with ERBB2 (PubMed:21555369). Interacts with GCSAM (PubMed:17823310). Interacts with TBC1D21 (By similarity). Interacts with CPNE1 (via VWFA domain) and CPNE4 (via VWFA domain) (By similarity). Interacts with DHX9 (via C-terminus); this interaction is direct and mediates the attachment to nuclear ribonucleoprotein complexes (PubMed:11687588). Interacts with FAM107A (PubMed:21969592, PubMed:28604741). Part of the ACTR1A/ACTB filament around which the dynactin complex is built. The filament contains 8 copies of ACTR1A and 1 ACTB (By similarity). Interacts with TPRN which forms ring-like structures in the stereocilium taper region; the interaction may stabilize stereocilia in inner ear hair cells (By similarity). Interacts with AMOTL2 (via N-terminus), the interaction facilitates binding of cell junction complexes to actin fibers in endothelial cells (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P60710, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q6QAQ1, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10411937, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11687588, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14592989, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15328537, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16685646, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17289661, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17823310, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18765789, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21555369, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21969592, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25255767, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28604741}. |
| Post-translational modification PTM: ISGylated. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16139798}.; PTM: Oxidation of Met-44 and Met-47 by MICALs (MICAL1, MICAL2 or MICAL3) to form methionine sulfoxide promotes actin filament depolymerization. MICAL1 and MICAL2 produce the (R)-S-oxide form. The (R)-S-oxide form is reverted by MSRB1 and MSRB2, which promote actin repolymerization. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:29343822}.; PTM: Monomethylation at Lys-84 (K84me1) regulates actin-myosin interaction and actomyosin-dependent processes (PubMed:23673617). Demethylation by ALKBH4 is required for maintaining actomyosin dynamics supporting normal cleavage furrow ingression during cytokinesis and cell migration (PubMed:23673617). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23673617}.; PTM: Methylated at His-73 by SETD3 (PubMed:30526847, PubMed:30626964, PubMed:30785395, PubMed:31388018). Methylation at His-73 is required for smooth muscle contraction of the laboring uterus during delivery (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P60710, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30526847, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30626964, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30785395, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31388018}.; PTM: [Actin, cytoplasmic 1]: N-terminal cleavage of acetylated methionine of immature cytoplasmic actin by ACTMAP. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:36173861}.; PTM: [Actin, cytoplasmic 1, N-terminally processed]: N-terminal acetylation by NAA80 affects actin filament depolymerization and elongation, including elongation driven by formins (PubMed:29581253). In contrast, filament nucleation by the Arp2/3 complex is not affected (PubMed:29581253). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:29581253}.; PTM: (Microbial infection) Monomeric actin is cross-linked by V.cholerae toxins RtxA and VgrG1 in case of infection: bacterial toxins mediate the cross-link between Lys-50 of one monomer and Glu-270 of another actin monomer, resulting in formation of highly toxic actin oligomers that cause cell rounding (PubMed:19015515). The toxin can be highly efficient at very low concentrations by acting on formin homology family proteins: toxic actin oligomers bind with high affinity to formins and adversely affect both nucleation and elongation abilities of formins, causing their potent inhibition in both profilin-dependent and independent manners (PubMed:26228148). {ECO:0000305|PubMed:19015515, ECO:0000305|PubMed:26228148}. |
| Involvement in disease DISEASE: Dystonia-deafness syndrome 1 (DDS1) [MIM:607371]: An autosomal dominant form of dystonia with juvenile onset, associated with congenital or childhood-onset sensorineural deafness. Dystonia is defined by the presence of sustained involuntary muscle contraction, often leading to abnormal postures. Some DDS1 patients have dysmorphic features, skeletal anomalies, and/or mild developmental delay with impaired intellectual development. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16685646, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25255767, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28487785, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29788902, ECO:0000269|PubMed:35005077}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Baraitser-Winter syndrome 1 (BRWS1) [MIM:243310]: A rare developmental disorder characterized by the combination of congenital ptosis, high-arched eyebrows, hypertelorism, ocular colobomata, and a brain malformation consisting of anterior-predominant lissencephaly. Other typical features include postnatal short stature and microcephaly, intellectual disability, seizures, and hearing loss. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22366783, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30733661}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Thrombocytopenia 8, with dysmorphic features and developmental delay (THC8) [MIM:620475]: A form of thrombocytopenia, a hematologic disorder defined by a decrease in the number of platelets in circulating blood, resulting in the potential for increased bleeding and decreased ability for clotting. THC8 is an autosomal dominant form characterized by early-childhood onset of thrombocytopenia with platelet anisotropy. Affected individuals also have dysmorphic facial features and variable developmental delay with speech delay and mildly impaired intellectual development. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10411937, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25255767, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30315159, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30733661}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Becker nevus syndrome (BNS) [MIM:604919]: A syndrome characterized by the association of Becker nevi with musculoskeletal abnormalities, unilateral breast hypoplasia, intellectual disability, developmental delay, and cardiomyopathy. Becker nevus is a cutaneous hamartoma that appears in childhood as a unilateral tan patch and increases in thickness, pigmentation, and hair growth during adolescence. Histologically, epidermal acanthosis is accompanied by irregularly dispersed ectopic smooth muscle bundles and increased terminal hair follicles. Most cases are sporadic. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28347698}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Congenital smooth muscle hamartoma, with or without hemihypertrophy (CSMH) [MIM:620470]: A benign skin lesion that usually presents as an indurated, slightly pigmented or flesh-colored plaque with perifollicular papules or coarse hair. Histopathologically, there is excessive proliferation of ectopic smooth muscle within the dermis. Hair follicles are normal in number and hyperkeratosis, acanthosis and hyperpigmentation of the basal cell layer can sometimes be seen. Rarely, CSMH is associated with hemihypertrophy. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:32170967}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: P60709 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
| Western blot ICC |
Documents
| # | SDS | Certificate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | |||
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.




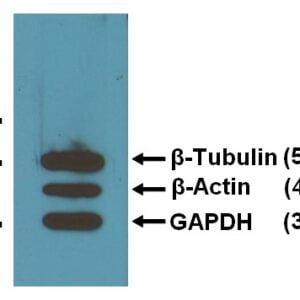
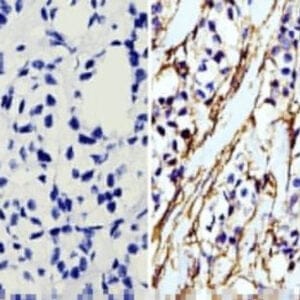
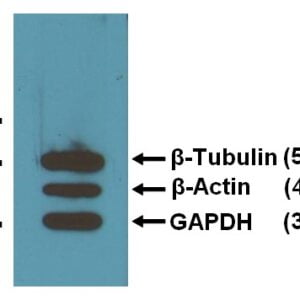
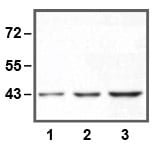


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.