| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| host | rabbit |
| isotype | IgG |
| clonality | polyclonal |
| concentration | 1 mg/mL |
| applications | ICC/IF, IHC, WB |
| available sizes | 100 µg |
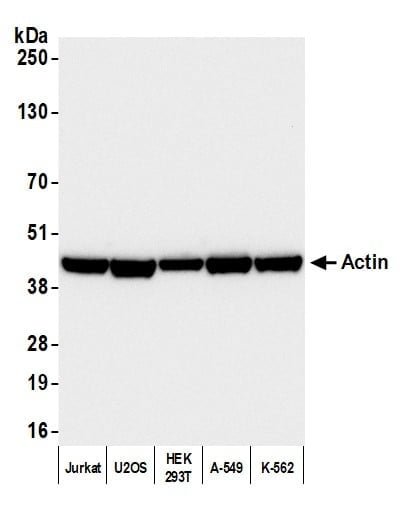
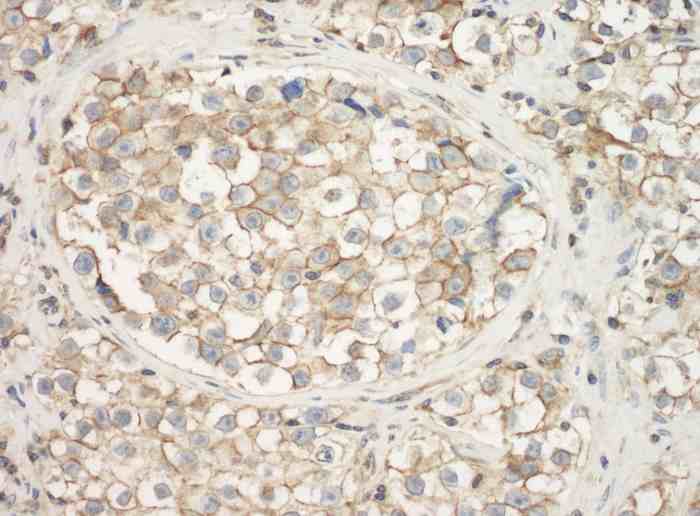
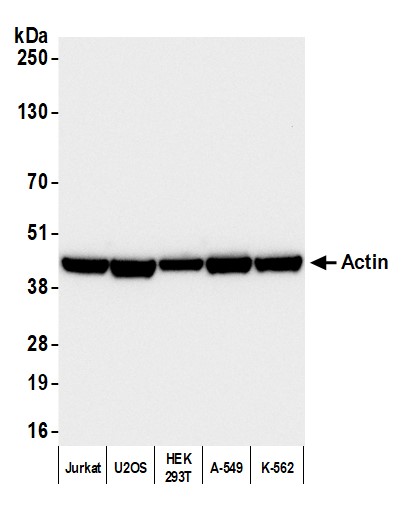
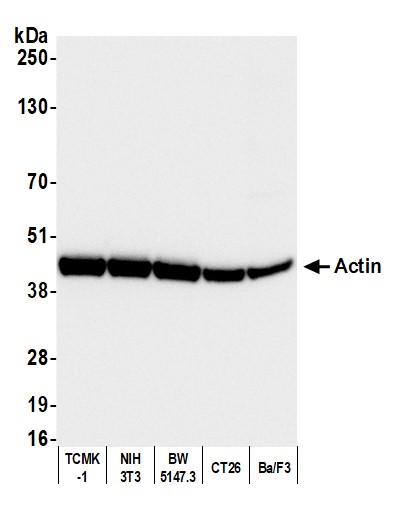
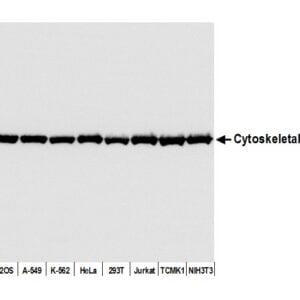
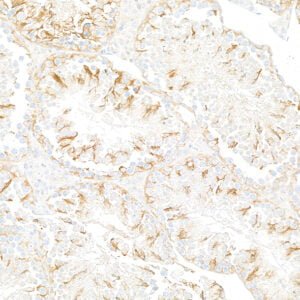
rabbit anti-Actin (pan) polyclonal antibody 9052
$409.00
Antibody summary
- Rabbit polyclonal to Actin (pan)
- Suitable for: WB, ICC/IF, IHC
- Reacts with: human, mouse, rat, cow, pig
- Isotype: IgG1
- 100 µg
rabbit anti-Actin (pan) polyclonal antibody 9052
| target relevance |
|---|
| Actin, a highly conserved protein, is widely recognized as an essential loading control in scientific research, particularly in the field of cell biology and molecular biology. As a structural component of the cytoskeleton, actin is present in virtually all eukaryotic cells. Actin participates in many important cellular processes, including muscle contraction, cell motility, cell division and cytokinesis, vesicle and organelle movement, cell signaling, and the establishment and maintenance of cell junctions and cell shape. Many of these processes are mediated by extensive and intimate interactions of actin with cellular membranes. Its ubiquitous expression and relatively stable levels make it an ideal reference protein for normalizing protein loading in Western blotting and other protein analysis techniques. Actin's abundance and consistent expression ensure that its quantity remains relatively constant across different experimental conditions and sample variations. Actin isoforms are distinct variants of the actin protein found in eukaryotic cells, and they play crucial roles in various cellular processes. One of the primary differences between actin isoforms lies in their tissue-specific distribution. For instance, skeletal muscle cells predominantly express the α-actin isoform, while smooth muscle cells mainly contain the γ-actin isoform. These tissue-specific distributions are essential for the specialized functions of muscle cells. Moreover, actin isoforms can also differ in their post-translational modifications. For example, γ-actin is more prone to undergo acetylation than α-actin. Additionally, actin isoforms can exhibit variations in their kinetic properties, such as rates of polymerization and depolymerization, which can influence their roles in processes like cell motility or cytoskeletal stability. Furthermore, some actin isoforms may interact with different binding partners or regulatory proteins, further diversifying their functions within the cell. These differences in tissue distribution, post-translational modifications, kinetic properties, and protein interactions contribute to the versatility and specificity of actin isoforms in various cellular processes and underline their importance in maintaining cellular structure and function. This antibody recognizes multiple actin isoforms and can be used as a loading control when run alongside proteins of interest with different and resolvable molecular weights and ideally in combination with antibodies of same host and when using a secondary antibody. Click for more on: loading controls and Actin |
| Protein names PANACT |
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
| Western blot IHC ICC |
Documents
| # | SDS | Certificate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | |||
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.


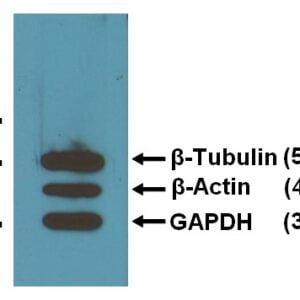
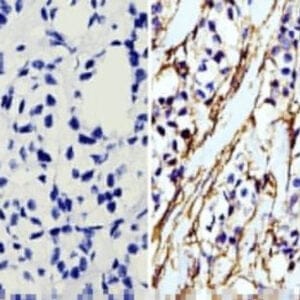
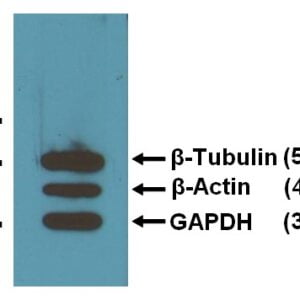
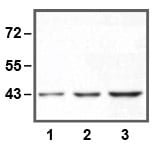


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.