| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| host | mouse |
| isotype | IgG |
| clonality | monoclonal |
| concentration | concentrate, predilute |
| applications | IHC |
| reactivity | human |
| available size | 0.1 mL, 0.5 mL, 1 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted |
rabbit anti-PTEN monoclonal antibody (ZR235) 6351
Price range: $160.00 through $528.00
Antibody summary
- Rabbit monoclonal to PTEN
- Suitable for: Immunohistochemistry (formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues)
- Reacts with: Human
- Isotype:IgG
- Control: Endometrial adenocarcinoma
- Visualization: Cytoplasmic and nuclear
- 0.1, 0.5, 1.0 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted
rabbit anti-PTEN monoclonal antibody ZR235 6351
| target relevance |
|---|
| Protein names Phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate 3-phosphatase and dual-specificity protein phosphatase PTEN (EC 3.1.3.16) (EC 3.1.3.48) (EC 3.1.3.67) (Inositol polyphosphate 3-phosphatase) (EC 3.1.3.-) (Mutated in multiple advanced cancers 1) (Phosphatase and tensin homolog) |
| Gene names PTEN,PTEN MMAC1 TEP1 |
| Protein family PTEN phosphatase protein family |
| Mass 47166Da |
| Function FUNCTION: Dual-specificity protein phosphatase, dephosphorylating tyrosine-, serine- and threonine-phosphorylated proteins (PubMed:9187108, PubMed:9256433, PubMed:9616126). Also functions as a lipid phosphatase, removing the phosphate in the D3 position of the inositol ring of PtdIns(3,4,5)P3/phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate, PtdIns(3,4)P2/phosphatidylinositol 3,4-diphosphate and PtdIns3P/phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate with a preference for PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 (PubMed:16824732, PubMed:26504226, PubMed:9593664, PubMed:9811831). Furthermore, this enzyme can also act as a cytosolic inositol 3-phosphatase acting on Ins(1,3,4,5,6)P5/inositol 1,3,4,5,6 pentakisphosphate and possibly Ins(1,3,4,5)P4/1D-myo-inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate (PubMed:11418101, PubMed:15979280). Antagonizes the PI3K-AKT/PKB signaling pathway by dephosphorylating phosphoinositides and thereby modulating cell cycle progression and cell survival (PubMed:31492966, PubMed:37279284). The unphosphorylated form cooperates with MAGI2 to suppress AKT1 activation (PubMed:11707428). In motile cells, suppresses the formation of lateral pseudopods and thereby promotes cell polarization and directed movement (PubMed:22279049). Dephosphorylates tyrosine-phosphorylated focal adhesion kinase and inhibits cell migration and integrin-mediated cell spreading and focal adhesion formation (PubMed:22279049). Required for growth factor-induced epithelial cell migration; growth factor stimulation induces PTEN phosphorylation which changes its binding preference from the p85 regulatory subunit of the PI3K kinase complex to DLC1 and results in translocation of the PTEN-DLC1 complex to the posterior of migrating cells to promote RHOA activation (PubMed:26166433). Meanwhile, TNS3 switches binding preference from DLC1 to p85 and the TNS3-p85 complex translocates to the leading edge of migrating cells to activate RAC1 activation (PubMed:26166433). Plays a role as a key modulator of the AKT-mTOR signaling pathway controlling the tempo of the process of newborn neurons integration during adult neurogenesis, including correct neuron positioning, dendritic development and synapse formation (By similarity). Involved in the regulation of synaptic function in excitatory hippocampal synapses. Recruited to the postsynaptic membrane upon NMDA receptor activation, is required for the modulation of synaptic activity during plasticity. Enhancement of lipid phosphatase activity is able to drive depression of AMPA receptor-mediated synaptic responses, activity required for NMDA receptor-dependent long-term depression (LTD) (By similarity). May be a negative regulator of insulin signaling and glucose metabolism in adipose tissue. The nuclear monoubiquitinated form possesses greater apoptotic potential, whereas the cytoplasmic nonubiquitinated form induces less tumor suppressive ability (PubMed:10468583, PubMed:18716620). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O08586, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O54857, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10468583, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11418101, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11707428, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15979280, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16824732, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18716620, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22279049, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26166433, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26504226, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31492966, ECO:0000269|PubMed:37279284, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9187108, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9256433, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9593664, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9616126, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9811831}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform alpha]: Functional kinase, like isoform 1 it antagonizes the PI3K-AKT/PKB signaling pathway. Plays a role in mitochondrial energetic metabolism by promoting COX activity and ATP production, via collaboration with isoform 1 in increasing protein levels of PINK1. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23744781}. |
| Catalytic activity CATALYTIC ACTIVITY: Reaction=a 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phospho-(1D-myo-inositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate) + H2O = a 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phospho-(1D-myo-inositol-4,5-bisphosphate) + phosphate; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:25017, ChEBI:CHEBI:15377, ChEBI:CHEBI:43474, ChEBI:CHEBI:57836, ChEBI:CHEBI:58456; EC=3.1.3.67; Evidence={ECO:0000269|PubMed:16824732, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9811831}; PhysiologicalDirection=left-to-right; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:25018; Evidence={ECO:0000305|PubMed:16824732}; CATALYTIC ACTIVITY: Reaction=O-phospho-L-seryl-[protein] + H2O = L-seryl-[protein] + phosphate; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:20629, Rhea:RHEA-COMP:9863, Rhea:RHEA-COMP:11604, ChEBI:CHEBI:15377, ChEBI:CHEBI:29999, ChEBI:CHEBI:43474, ChEBI:CHEBI:83421; EC=3.1.3.16; Evidence={ECO:0000269|PubMed:9256433}; PhysiologicalDirection=left-to-right; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:20630; Evidence={ECO:0000305|PubMed:9256433}; CATALYTIC ACTIVITY: Reaction=O-phospho-L-threonyl-[protein] + H2O = L-threonyl-[protein] + phosphate; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:47004, Rhea:RHEA-COMP:11060, Rhea:RHEA-COMP:11605, ChEBI:CHEBI:15377, ChEBI:CHEBI:30013, ChEBI:CHEBI:43474, ChEBI:CHEBI:61977; EC=3.1.3.16; Evidence={ECO:0000269|PubMed:9256433}; PhysiologicalDirection=left-to-right; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:47005; Evidence={ECO:0000305|PubMed:9256433}; CATALYTIC ACTIVITY: Reaction=O-phospho-L-tyrosyl-[protein] + H2O = L-tyrosyl-[protein] + phosphate; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:10684, Rhea:RHEA-COMP:10136, Rhea:RHEA-COMP:20101, ChEBI:CHEBI:15377, ChEBI:CHEBI:43474, ChEBI:CHEBI:46858, ChEBI:CHEBI:61978; EC=3.1.3.48; Evidence={ECO:0000269|PubMed:9187108, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9256433}; PhysiologicalDirection=left-to-right; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:10685; Evidence={ECO:0000305|PubMed:9256433}; CATALYTIC ACTIVITY: Reaction=1,2-dioctanoyl-sn-glycero-3-phospho-(1D-myo-inositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate) + H2O = 1,2-dioctanoyl-sn-glycero-3-phospho-(1D-myo-inositol-4,5-bisphosphate) + phosphate; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:43552, ChEBI:CHEBI:15377, ChEBI:CHEBI:43474, ChEBI:CHEBI:83416, ChEBI:CHEBI:83419; Evidence={ECO:0000269|PubMed:16824732, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9593664}; PhysiologicalDirection=left-to-right; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:43553; Evidence={ECO:0000305|PubMed:16824732}; CATALYTIC ACTIVITY: Reaction=1,2-dihexadecanoyl-sn-glycero-3-phospho-(1D-myo-inositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate) + H2O = 1,2-dihexadecanoyl-sn-glycero-3-phospho-(1D-myo-inositol-4,5-bisphosphate) + phosphate; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:43560, ChEBI:CHEBI:15377, ChEBI:CHEBI:43474, ChEBI:CHEBI:83420, ChEBI:CHEBI:83423; Evidence={ECO:0000269|PubMed:16824732, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9593664}; PhysiologicalDirection=left-to-right; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:43561; Evidence={ECO:0000305|PubMed:16824732}; CATALYTIC ACTIVITY: Reaction=1D-myo-inositol 1,3,4,5,6-pentakisphosphate + H2O = 1D-myo-inositol 1,4,5,6-tetrakisphosphate + phosphate; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:77143, ChEBI:CHEBI:15377, ChEBI:CHEBI:43474, ChEBI:CHEBI:57627, ChEBI:CHEBI:57733; Evidence={ECO:0000269|PubMed:11418101}; PhysiologicalDirection=left-to-right; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:77144; Evidence={ECO:0000269|PubMed:11418101}; CATALYTIC ACTIVITY: Reaction=1D-myo-inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate + H2O = 1D-myo-inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate + phosphate; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:77155, ChEBI:CHEBI:15377, ChEBI:CHEBI:43474, ChEBI:CHEBI:57895, ChEBI:CHEBI:203600; Evidence={ECO:0000269|PubMed:9593664}; PhysiologicalDirection=left-to-right; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:77156; Evidence={ECO:0000305|PubMed:9593664}; |
| Subellular location SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: Cytoplasm {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15987703, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18716620, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19473982, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25801959, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9187108}. Nucleus {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15987703, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18716620, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19473982, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25801959}. Nucleus, PML body {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18716620}. Cell projection, dendritic spine {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O54857}. Postsynaptic density {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O54857}. Note=Monoubiquitinated form is nuclear. Nonubiquitinated form is cytoplasmic. Colocalized with PML and USP7 in PML nuclear bodies (PubMed:18716620). XIAP/BIRC4 promotes its nuclear localization (PubMed:19473982). Associares with the postsynaptic density in response to NMDAR activation (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O54857, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18716620, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19473982}.; SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: [Isoform alpha]: Secreted {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23744781, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24768297}. Note=May be secreted via a classical signal peptide and reenter into cells with the help of a poly-Arg motif. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23744781, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24768297}. |
| Tissues TISSUE SPECIFICITY: Expressed at a relatively high level in all adult tissues, including heart, brain, placenta, lung, liver, muscle, kidney and pancreas. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9090379}. |
| Structure SUBUNIT: Monomer. The unphosphorylated form interacts with the second PDZ domain of MAGI2 and with DLG1 and MAST2 in vitro (PubMed:10646847, PubMed:10760291, PubMed:11707428). Interacts with MAGI2, MAGI3, MAST1 and MAST3, but neither with MAST4 nor with DLG5; interaction with MAGI2 increases protein stability (PubMed:10748157, PubMed:15951562). Interacts with NEDD4 (PubMed:17218260). Interacts with NDFIP1 and NDFIP2; in the presence of NEDD4 or ITCH, this interaction promotes PTEN ubiquitination (PubMed:20534535, PubMed:25801959). Interacts (via C2 domain) with FRK (PubMed:19345329). Interacts with USP7; the interaction is direct (PubMed:18716620). Interacts with ROCK1 (By similarity). Interacts with XIAP/BIRC4 (PubMed:19473982). Interacts with STK11; the interaction phosphorylates PTEN (PubMed:15987703). Interacts with PPP1R16B (PubMed:25007873). Interacts with NOP53; regulates PTEN phosphorylation and increases its stability (PubMed:15355975). Interacts (via PDZ domain-binding motif) with DLG4; the interaction is induced by NMDA and is required for PTEN location at postsynaptic density (By similarity). Interacts with the regulatory p85 subunit of the PI3K kinase complex and with Rho GTPase-activating protein DLC1; in resting cells, interacts (via C2 tensin-type domain) with p85 but, following growth factor stimulation, PTEN is phosphorylated which leads to weakened interaction with p85 and enhanced interaction (via C2 tensin-type domain) with DLC1 while p85 interaction with TNS3 increases (PubMed:26166433). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O08586, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O54857, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10555148, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10646847, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10748157, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10760291, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11707428, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15355975, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15951562, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15987703, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17218260, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18716620, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19345329, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19473982, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20534535, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25007873, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25801959, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26166433}. |
| Post-translational modification PTM: Constitutively phosphorylated by CK2 under normal conditions. Phosphorylated in vitro by MAST1, MAST2, MAST3 and STK11. Phosphorylation results in an inhibited activity towards PIP3. Phosphorylation can both inhibit or promote PDZ-binding. Phosphorylation at Tyr-336 by FRK/PTK5 protects this protein from ubiquitin-mediated degradation probably by inhibiting its binding to NEDD4. Phosphorylation by ROCK1 is essential for its stability and activity. Phosphorylation by PLK3 promotes its stability and prevents its degradation by the proteasome. Phosphorylated on Thr-319 and Thr-321 in the C2-type tensin domain following EGF stimulation which changes its binding preference from the p85 regulatory subunit of the PI3K kinase complex to DLC1 (PubMed:26166433). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10646847, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11035045, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11707428, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12297295, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15951562, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15987703, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18716620, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19345329, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20940307, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26166433}.; PTM: Monoubiquitinated; monoubiquitination is increased in presence of retinoic acid. Deubiquitinated by USP7; leading to its nuclear exclusion. Monoubiquitination of one of either Lys-13 and Lys-289 amino acid is sufficient to modulate PTEN compartmentalization. Ubiquitinated by XIAP/BIRC4. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18716620, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19473982}.; PTM: Ubiquitinated by the DCX(DCAF13) E3 ubiquitin ligase complex, leading to its degradation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:31492966}.; PTM: ISGylated. ISGylation promotes PTEN degradation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:37279284}. |
| Domain DOMAIN: The C2 domain binds phospholipid membranes in vitro in a Ca(2+)-independent manner; this binding is important for its tumor suppressor function. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10468583, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10555148}. |
| Involvement in disease DISEASE: Cowden syndrome 1 (CWS1) [MIM:158350]: An autosomal dominant hamartomatous polyposis syndrome with age-related penetrance. Cowden syndrome is characterized by hamartomatous lesions affecting derivatives of ectodermal, mesodermal and endodermal layers, macrocephaly, facial trichilemmomas (benign tumors of the hair follicle infundibulum), acral keratoses, papillomatous papules, and elevated risk for development of several types of malignancy, particularly breast carcinoma in women and thyroid carcinoma in both men and women. Colon cancer and renal cell carcinoma have also been reported. Hamartomas can be found in virtually every organ, but most commonly in the skin, gastrointestinal tract, breast and thyroid. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10051160, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10234502, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10400993, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10772390, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10866302, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11230179, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11494117, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15355975, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18716620, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21659347, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24778394, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9140396, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9241266, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9259288, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9345101, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9399897, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9425889, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9467011, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9593664, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9600246, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9735393, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9797362, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9811831, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9832031, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9915974}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Lhermitte-Duclos disease (LDD) [MIM:158350]: A rare disease characterized by the occurrence of a slowly enlarging mass within the cerebellar cortex corresponding histologically to a cerebellar hamartoma. It manifests, most commonly in the third and fourth decades of life, with increased intracranial pressure, headache, nausea, cerebellar dysfunction, occlusive hydrocephalus, ataxia, visual disturbances and other cranial nerve palsies. Various associated abnormalities may be present such as megalencephaly, microgyria, hydromyelia, polydactyly, partial gigantism, macroglossia. LDD is part of the PTEN hamartoma tumor syndromes spectrum that also includes Cowden syndrome. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (HNSCC) [MIM:275355]: A non-melanoma skin cancer affecting the head and neck. The hallmark of cutaneous SCC is malignant transformation of normal epidermal keratinocytes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11801303}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Endometrial cancer (ENDMC) [MIM:608089]: A malignancy of endometrium, the mucous lining of the uterus. Most endometrial cancers are adenocarcinomas, cancers that begin in cells that make and release mucus and other fluids. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16506206}. Note=Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Note=PTEN mutations are found in a subset of patients with Proteus syndrome, a genetically heterogeneous condition. The molecular diagnosis of PTEN mutation positive cases classifies Proteus syndrome patients as part of the PTEN hamartoma syndrome spectrum. As such, patients surviving the early years of Proteus syndrome are likely at a greater risk of developing malignancies.; DISEASE: Glioma 2 (GLM2) [MIM:613028]: Gliomas are benign or malignant central nervous system neoplasms derived from glial cells. They comprise astrocytomas and glioblastoma multiforme that are derived from astrocytes, oligodendrogliomas derived from oligodendrocytes and ependymomas derived from ependymocytes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12085208}. Note=Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Prostate cancer (PC) [MIM:176807]: A malignancy originating in tissues of the prostate. Most prostate cancers are adenocarcinomas that develop in the acini of the prostatic ducts. Other rare histopathologic types of prostate cancer that occur in approximately 5% of patients include small cell carcinoma, mucinous carcinoma, prostatic ductal carcinoma, transitional cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, basal cell carcinoma, adenoid cystic carcinoma (basaloid), signet-ring cell carcinoma and neuroendocrine carcinoma. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26504226, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9072974}. Note=Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Macrocephaly/autism syndrome (MCEPHAS) [MIM:605309]: Patients have autism spectrum disorders and macrocephaly, with head circumferences ranging from +2.5 to +8 SD for age and sex (average head circumference +4.0 SD). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15805158, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23160955, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26637798}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Note=A microdeletion of chromosome 10q23 involving BMPR1A and PTEN is a cause of chromosome 10q23 deletion syndrome, which shows overlapping features of the following three disorders: Bannayan-Zonana syndrome, Cowden disease and juvenile polyposis syndrome. |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: P60484 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
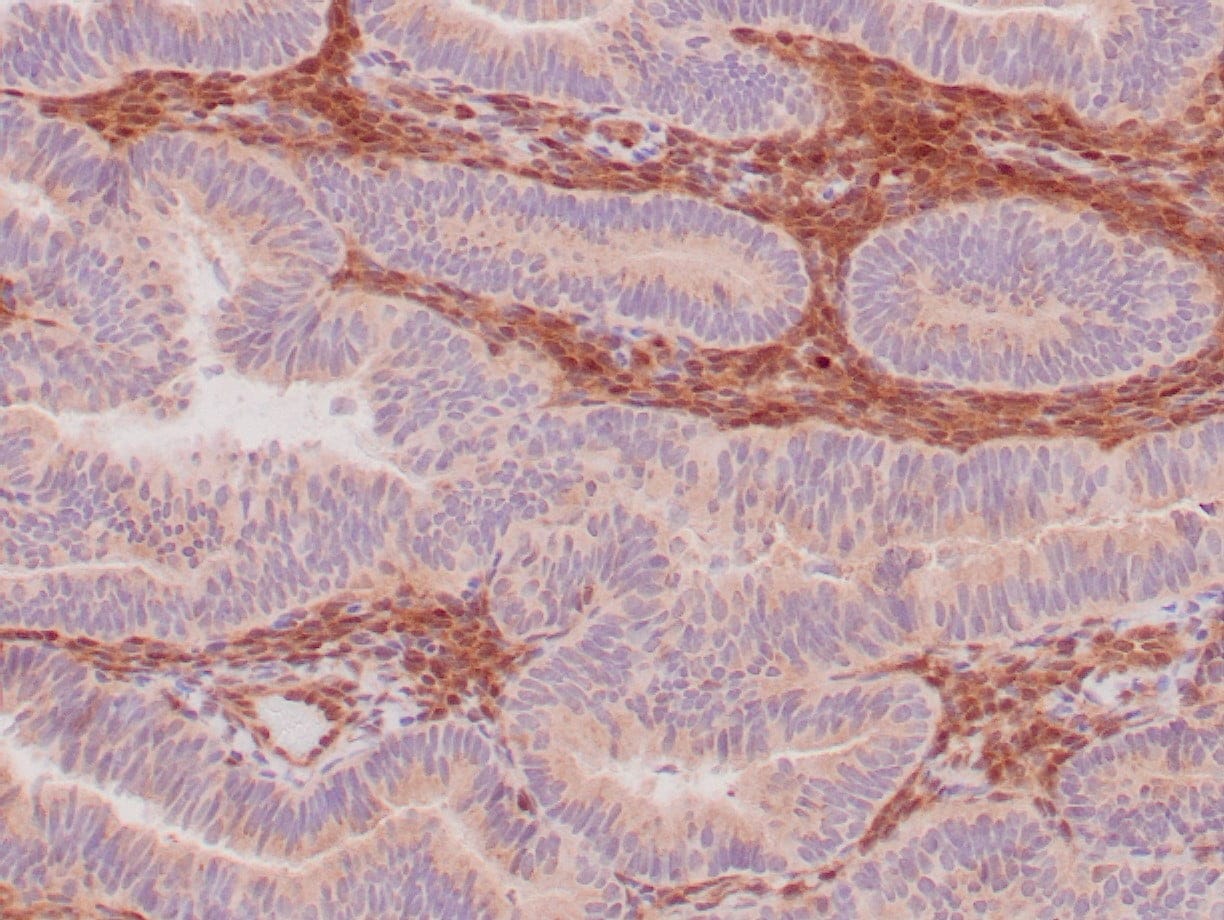 |
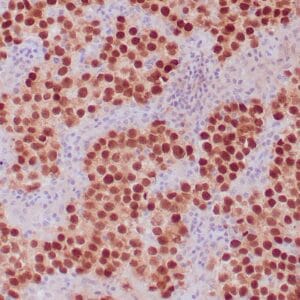
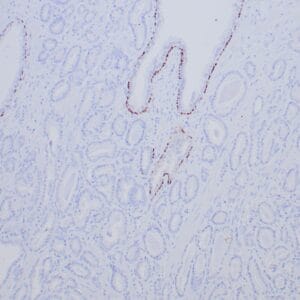
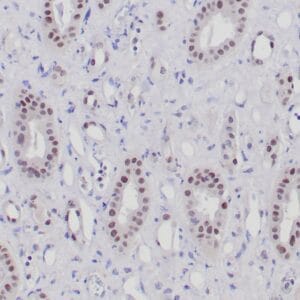
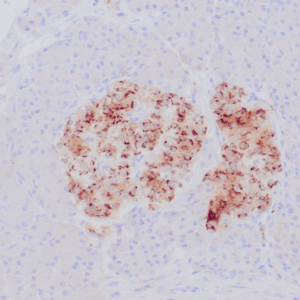
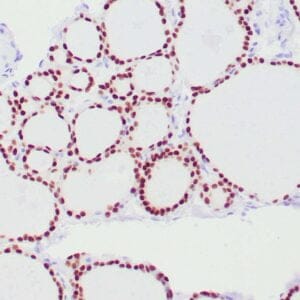
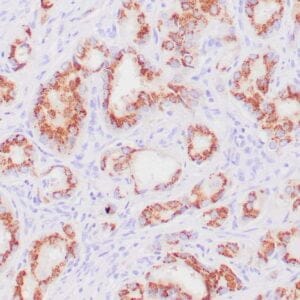
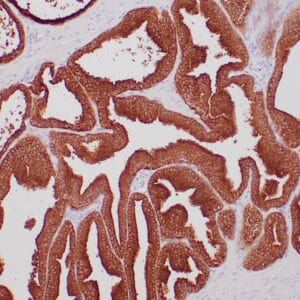
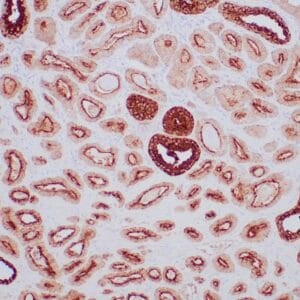
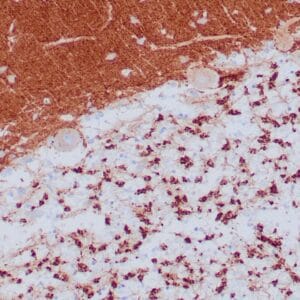
| Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human endometrioid adenocarcinoma stained with anti-PTEN using peroxidase-conjugate and DAB chromogen. Note carcinoma is negative whereas stromal cells are positive |
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
| IHC |
Documents
| # | SDS | Certificate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | |||
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.