| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| host | mouse |
| isotype | IgG |
| clonality | monoclonal |
| concentration | concentrate, predilute |
| applications | IHC |
| reactivity | human |
| available size | 0.1 mL, 0.5 mL, 1 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted |
rabbit anti-CTLA-4 monoclonal antibody (ZR452) 6130
Price range: $160.00 through $528.00
Antibody summary
- Rabbit monoclonal to CTLA-4
- Suitable for: Immunohistochemistry (formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues)
- Reacts with: Human
- Isotype:IgG
- Control: Lymph node or tonsil
- Visualization: Secreted and cell surface
- 0.1, 0.5, 1.0 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted
rabbit anti-CTLA-4 monoclonal antibody ZR452 6130
| target relevance |
|---|
| Protein names Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte protein 4 (Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated antigen 4) (CTLA-4) (CD antigen CD152) |
| Gene names CTLA4,CTLA4 CD152 |
| Mass 24656Da |
| Function FUNCTION: Inhibitory receptor acting as a major negative regulator of T-cell responses. The affinity of CTLA4 for its natural B7 family ligands, CD80 and CD86, is considerably stronger than the affinity of their cognate stimulatory coreceptor CD28. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16551244, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1714933}. |
| Subellular location SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: Cell membrane {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18468488, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28484017}; Single-pass type I membrane protein {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18468488, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28484017}. Note=Exists primarily an intracellular antigen whose surface expression is tightly regulated by restricted trafficking to the cell surface and rapid internalization. |
| Tissues TISSUE SPECIFICITY: Widely expressed with highest levels in lymphoid tissues. Detected in activated T-cells where expression levels are 30- to 50-fold less than CD28, the stimulatory coreceptor, on the cell surface following activation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10493833, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16551244, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1713603}. |
| Structure SUBUNIT: Homodimer; disulfide-linked (PubMed:11279501, PubMed:11279502, PubMed:21156796, PubMed:28484017, Ref.23). Binds to CD80/B7-1 and CD86/B7.2 (PubMed:11279501, PubMed:11279502, PubMed:28484017). Interacts with ICOSLG (PubMed:28484017). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11279501, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11279502, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21156796, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28484017, ECO:0000269|Ref.23}. |
| Post-translational modification PTM: N-glycosylation is important for dimerization. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11279502, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16002699, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21156796}.; PTM: Phosphorylation at Tyr-201 prevents binding to the AP-2 adapter complex, blocks endocytosis, and leads to retention of CTLA4 on the cell surface. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10842319, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9175836, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9813138}. |
| Involvement in disease DISEASE: Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) [MIM:152700]: A chronic, relapsing, inflammatory, and often febrile multisystemic disorder of connective tissue, characterized principally by involvement of the skin, joints, kidneys and serosal membranes. It is of unknown etiology, but is thought to represent a failure of the regulatory mechanisms of the autoimmune system. The disease is marked by a wide range of system dysfunctions, an elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate, and the formation of LE cells in the blood or bone marrow. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15138458, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15688186}. Note=Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Note=Genetic variations in CTLA4 may influence susceptibility to Graves disease, an autoimmune disorder associated with overactivity of the thyroid gland and hyperthyroidism. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10924276}.; DISEASE: Type 1 diabetes mellitus 12 (T1D12) [MIM:601388]: A multifactorial disorder of glucose homeostasis that is characterized by susceptibility to ketoacidosis in the absence of insulin therapy. Clinical features are polydipsia, polyphagia and polyuria which result from hyperglycemia-induced osmotic diuresis and secondary thirst. These derangements result in long-term complications that affect the eyes, kidneys, nerves, and blood vessels. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9259273}. Note=Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Celiac disease 3 (CELIAC3) [MIM:609755]: A multifactorial, chronic disorder of the small intestine caused by intolerance to gluten. It is characterized by immune-mediated enteropathy associated with failed intestinal absorption, and malnutrition. In predisposed individuals, the ingestion of gluten-containing food such as wheat and rye induces a flat jejunal mucosa with infiltration of lymphocytes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10189842, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15657618}. Note=Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Immune dysregulation with autoimmunity, immunodeficiency, and lymphoproliferation (IDAIL) [MIM:616100]: An autosomal dominant primary immunodeficiency characterized by severe autoimmunity, infiltration of non-lymphoid organs, such as the intestine, lungs and brain, by hyperactive T cells and B cells, autoimmune cytopenias, and hypogammaglobulinemia in early childhood. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25213377, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25329329}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: P16410 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
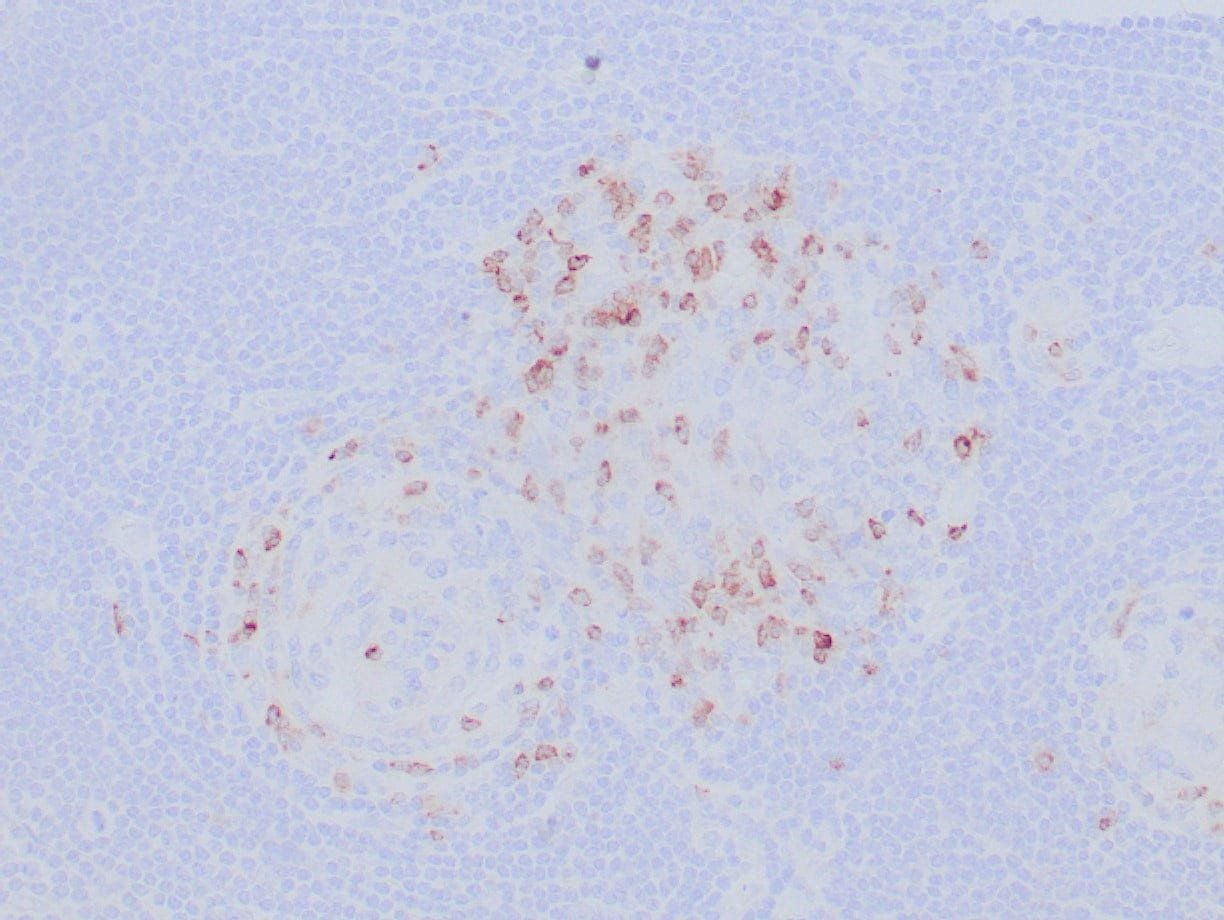 |
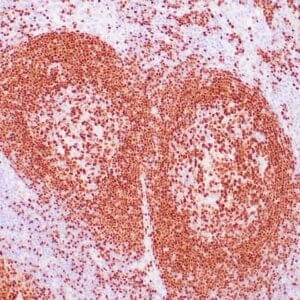
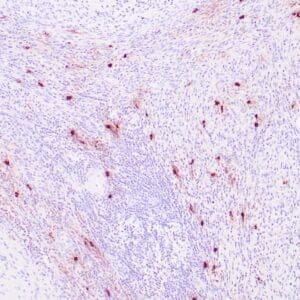
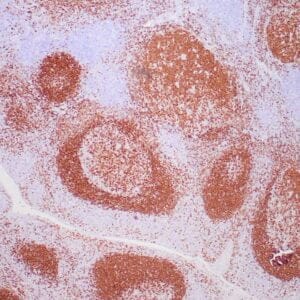
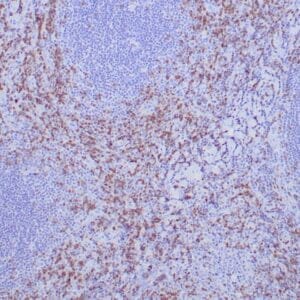
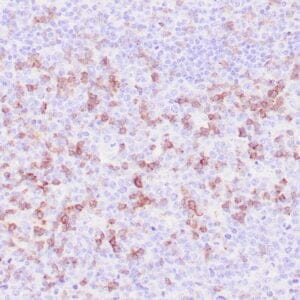
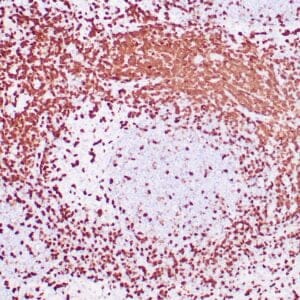
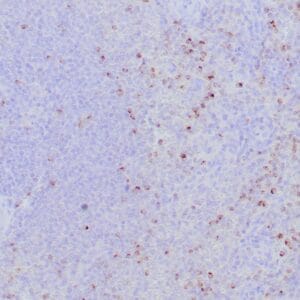
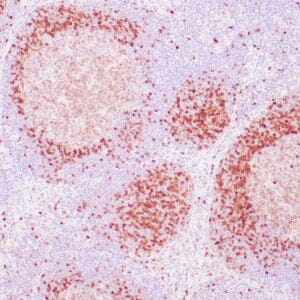
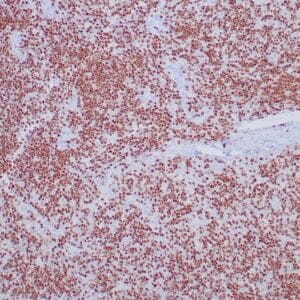
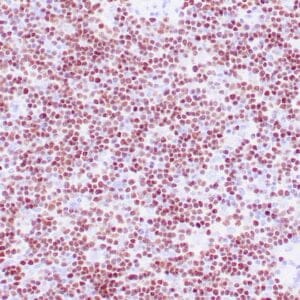
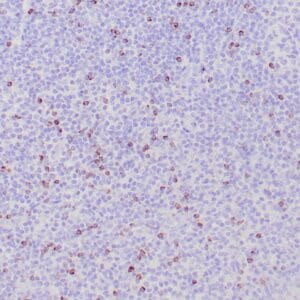
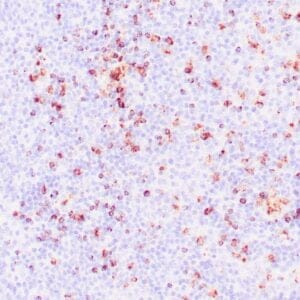
| Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human tonsil stained with anti-CTLA4 antibody using peroxidase-conjugate and DAB chromogen. Note the cytoplasmic staining of cytotoxic T-cells |
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
| IHC |
Documents
| # | SDS | Certificate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | |||
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.