| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| host | mouse |
| isotype | IgG |
| clonality | monoclonal |
| concentration | concentrate, predilute |
| applications | IHC |
| reactivity | human |
| available size | 0.1 mL, 0.5 mL, 1 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted |
rabbit anti-BAP1 monoclonal antibody (ZR454) 6026
Price range: $160.00 through $528.00
Antibody summary
- Rabbit monoclonal to BAP1
- Suitable for: Immunohistochemistry (formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues)
- Reacts with: Human
- Isotype:IgG
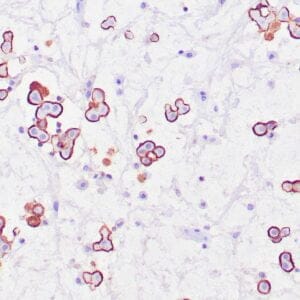
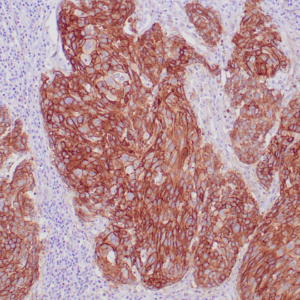
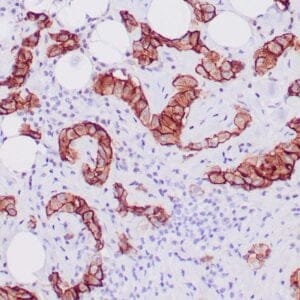
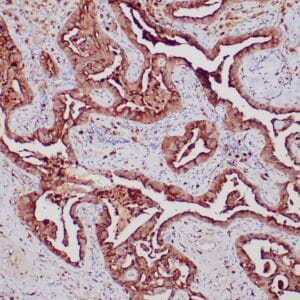
- Control: Malignant Mesothelioma
- Visualization: Nuclear
- 0.1, 0.5, 1.0 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted
rabbit anti-BAP1 monoclonal antibody ZR454 6026
| target relevance |
|---|
| Protein names Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase BAP1 (EC 3.4.19.12) (BRCA1-associated protein 1) (Cerebral protein 6) |
| Gene names BAP1,BAP1 KIAA0272 hucep-6 |
| Protein family Peptidase C12 family, BAP1 subfamily |
| Mass 80362Da |
| Function FUNCTION: Deubiquitinating enzyme that plays a key role in chromatin by mediating deubiquitination of histone H2A and HCFC1 (PubMed:12485996, PubMed:18757409, PubMed:20436459, PubMed:25451922, PubMed:35051358). Catalytic component of the polycomb repressive deubiquitinase (PR-DUB) complex, a complex that specifically mediates deubiquitination of histone H2A monoubiquitinated at 'Lys-120' (H2AK119ub1) (PubMed:20436459, PubMed:25451922, PubMed:30664650, PubMed:35051358). Does not deubiquitinate monoubiquitinated histone H2B (PubMed:20436459, PubMed:30664650). The PR-DUB complex is an epigenetic regulator of gene expression and acts as a transcriptional coactivator, affecting genes involved in development, cell communication, signaling, cell proliferation and cell viability (PubMed:20805357, PubMed:30664650, PubMed:36180891). Antagonizes PRC1 mediated H2AK119ub1 monoubiquitination (PubMed:30664650). As part of the PR-DUB complex, associates with chromatin enriched in histone marks H3K4me1, H3K4me3, and H3K27Ac, but not in H3K27me3 (PubMed:36180891). Recruited to specific gene-regulatory regions by YY1 (PubMed:20805357). Acts as a regulator of cell growth by mediating deubiquitination of HCFC1 N-terminal and C-terminal chains, with some specificity toward 'Lys-48'-linked polyubiquitin chains compared to 'Lys-63'-linked polyubiquitin chains (PubMed:19188440, PubMed:19815555). Deubiquitination of HCFC1 does not lead to increase stability of HCFC1 (PubMed:19188440, PubMed:19815555). Interferes with the BRCA1 and BARD1 heterodimer activity by inhibiting their ability to mediate ubiquitination and autoubiquitination (PubMed:19117993). It however does not mediate deubiquitination of BRCA1 and BARD1 (PubMed:19117993). Able to mediate autodeubiquitination via intramolecular interactions to counteract monoubiquitination at the nuclear localization signal (NLS), thereby protecting it from cytoplasmic sequestration (PubMed:24703950). Negatively regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) of trophoblast stem cells during placental development by regulating genes involved in epithelial cell integrity, cell adhesion and cytoskeletal organization (PubMed:34170818). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12485996, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18757409, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19117993, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19188440, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19815555, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20436459, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20805357, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24703950, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25451922, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30664650, ECO:0000269|PubMed:34170818, ECO:0000269|PubMed:35051358, ECO:0000269|PubMed:36180891}. |
| Catalytic activity CATALYTIC ACTIVITY: Reaction=Thiol-dependent hydrolysis of ester, thioester, amide, peptide and isopeptide bonds formed by the C-terminal Gly of ubiquitin (a 76-residue protein attached to proteins as an intracellular targeting signal).; EC=3.4.19.12; Evidence={ECO:0000269|PubMed:20436459, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30258054, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9528852}; |
| Subellular location SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: Cytoplasm {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18757409, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19188440, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19815555, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24703950}. Nucleus {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18757409, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19188440, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19815555, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24703950, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24748658, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30664650, ECO:0000269|PubMed:35051358, ECO:0000269|PubMed:35446349, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9528852}. Chromosome {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30664650}. Note=Mainly nuclear (PubMed:24703950, PubMed:30664650). Binds to chromatin (PubMed:30664650). Localizes to the cytoplasm when monoubiquitinated by the E2/E3 hybrid ubiquitin-protein ligase UBE2O (PubMed:24703950). Recruitment to chromatin is dependent on ASXL1/2/3 and recruitment to specific genes on FOXK1/2 (By similarity). Nuclear localization is redundantly mediated by the importin and transportin systems; TNPO1/transportin-1 is the major mediator of nuclear localization (PubMed:35446349). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q99PU7, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24703950, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30664650, ECO:0000269|PubMed:35446349}. |
| Tissues TISSUE SPECIFICITY: Highly expressed in testis, placenta and ovary (PubMed:9528852). Expressed in breast (PubMed:9528852). levels in the placenta increase over the course of pregnancy (PubMed:34170818). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:34170818, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9528852}. |
| Structure SUBUNIT: Core component of the polycomb repressive deubiquitinase (PR-DUB) complex, at least composed of BAP1, one of ASXL1, ASXL2 or (probably) ASXL3, and one of MBD5 or MBD6 (PubMed:20436459, PubMed:24634419, PubMed:30664650, PubMed:36180891). The PR-DUB core associates with a number of accessory proteins, including FOXK1, FOXK2, KDM1B, HCFC1, YY1 and OGT; KDM1B specifically associates with ASXL2 PR-DUB complexes (Probable) (PubMed:20805357, PubMed:30664650). The BAP1 deubiquitinase activity is not required for PR-DUB assembly (PubMed:20805357). Homodimerizes (via coiled-coil hinge-region between the UCH and ULD domains) to mediate assembly of 2 copies of the BAP1-ASXL heterodimer into a bisymmetric tetramer; dimerization enhances association with nucleosomes (PubMed:30258054, PubMed:35446349). The PR-DUB complex associates with nucleosomes to mediate deubiquitination of 'lys-120' of histone H2AK118ub1 substrates; the association requires the positively charged C-terminal tail of BAP1 (PubMed:30258054, PubMed:36991118, PubMed:37556531). Interacts (via ULD domain) with ASXL1 (via DEUBAD domain); the interaction is direct and forms a ubiquitin binding cleft (PubMed:36180891, PubMed:36991118, PubMed:37556531). The interaction with ASXL1 stabilizes BAP1 but is not required for nucleosome binding (PubMed:36180891). Associates (via C-terminus) with nucleosome and chromatosome complexes through direct interaction with DNA and the histone3/4 dimer; this association displaces the histone-2A C-terminal tail, extending and orienting the H2AK118ub1 substrate towards the BAP1 deubiquitinase active site (PubMed:36991118, PubMed:37556531). Also interacts (via arginine finger) directly with the histone H2A-H2B acidic patch; this interaction is not critical for nucleosome-chromatosome association but may play a role in orienting the H2AK118ub1 substrate towards the PR-DUB complex active site (PubMed:36991118). Interacts with BRCA1 (via the RING finger) (PubMed:19117993, PubMed:9528852). Interacts (via HBM-like motif) with HCFC1 (PubMed:19188440, PubMed:19815555, PubMed:20805357). Interacts (via a C-terminal region overlapping the ULD domain) with YY1; the interaction is direct and requires the interaction with HCFC1 (PubMed:20805357). Interacts (when phosphorylated at Thr-493) with FOXK1 (PubMed:25451922). Interacts (when phosphorylated at Thr-493) with FOXK2; leading to recruitment of the PR-DUB complex and repression of FOXK2 target genes (PubMed:24748658, PubMed:25451922). Interacts (via non-classical PY-NLS) with TNPO1/transportin-1 (via HEAT repeats 8-12); the interaction is direct, mediates BAP1 nuclear localization and disrupts BAP1 homodimerization (PubMed:35446349). Interacts (via C-terminus) with KPNA1/importin alpha5 and KPNA2/importin alpha1; these interactions can contribute to BAP1 nuclear localization but are less important than the interaction with TNPO1/transportin-1 (PubMed:35446349). The interaction with TNPO1/transportin-1 disrupts homodimerization and blocks ubiquitination by UBE2O (PubMed:35446349). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19117993, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19188440, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19815555, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20436459, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20805357, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24634419, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24748658, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25451922, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30258054, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30664650, ECO:0000269|PubMed:35446349, ECO:0000269|PubMed:36180891, ECO:0000269|PubMed:36991118, ECO:0000269|PubMed:37556531, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9528852, ECO:0000305|PubMed:24634419}. |
| Post-translational modification PTM: Ubiquitinated: monoubiquitinated at multiple sites within its nuclear localization signal (NLS) BY UBE2O, leading to cytoplasmic retention (PubMed:24703950). Able to mediate autodeubiquitination via intramolecular interactions to counteract cytoplasmic retention (PubMed:24703950). Monoubiquitinated on at least 4 sites near or within its PY-NLS (PubMed:35446349). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24703950, ECO:0000269|PubMed:35446349}. |
| Domain DOMAIN: Possesses 2 overlapping nuclear localization sequences (NLS), a classic bipartite NLS and a non-classical PY-NLS (PubMed:35446349). The classical NLS probably mediates import via the importin alpha/beta system while the PY-NLS mediates nuclear import via the transportin system (PubMed:35446349). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:35446349}.; DOMAIN: The positively charged C-terminal tail stabilizes the interaction with nucleosomes/chromatosomes through interaction with the DNA backbone (PubMed:30258054, PubMed:36991118). Binding of ASXL1 just upstream of the positively charged C-terminal tail may stabilize its orientation to align the PR-DUB with its H2AK118ub1 substrate (PubMed:36991118). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30258054, ECO:0000269|PubMed:36991118}.; DOMAIN: The ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase (UCH) domain, together with the DEUBAD domain of ASXL1, forms the ubiquitin binding cleft of the PR-DUB complex. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:36991118, ECO:0000269|PubMed:37556531}.; DOMAIN: The positively charged Arg-finger motif mediates interaction with the histone H2A-H2B acidic patch; this interaction is critical for nucleosomal H2AK119ub1 deubiquitination activity but not nucleosomal binding. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:37556531}. |
| Involvement in disease DISEASE: Mesothelioma, malignant (MESOM) [MIM:156240]: An aggressive neoplasm of the serosal lining of the chest. It appears as broad sheets of cells, with some regions containing spindle-shaped, sarcoma-like cells and other regions showing adenomatous patterns. Pleural mesotheliomas have been linked to exposure to asbestos. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21642991, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21874000}. Note=The gene represented in this entry is involved in disease pathogenesis.; DISEASE: Tumor predisposition syndrome 1 (TPDS1) [MIM:614327]: An autosomal dominant condition characterized by predisposition to develop a variety of tumors, including benign melanocytic tumors as well as several malignant tumors, including uveal melanoma, cutaneous melanoma, malignant mesothelioma on exposure to asbestos, lung adenocarcinoma and meningioma. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21874000, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21874003, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21941004, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23684012}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Melanoma, uveal, 2 (UVM2) [MIM:606661]: Most common intraocular malignancy, arising from melanocytes in the iris, ciliary body, or choroid. Metastases develop in more than 30% of case patients, almost invariably in the liver, with poor prognosis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25687217, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32002398}. Note=Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Kury-Isidor syndrome (KURIS) [MIM:619762]: An autosomal dominant neurodevelopmental disorder characterized mainly by mild global developmental delay apparent from infancy or early childhood, and behavioral problems, including autism in most patients. Intellectual development may be mildly delayed, borderline, or even normal. Additional variable systemic features may include poor overall growth, hypotonia, distal skeletal anomalies, seizures, and non-specific dysmorphic facial features. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19117993, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19815555, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20805357, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25451922, ECO:0000269|PubMed:35051358}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: Q92560 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
| IHC |
Documents
| # | SDS | Certificate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | |||
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.
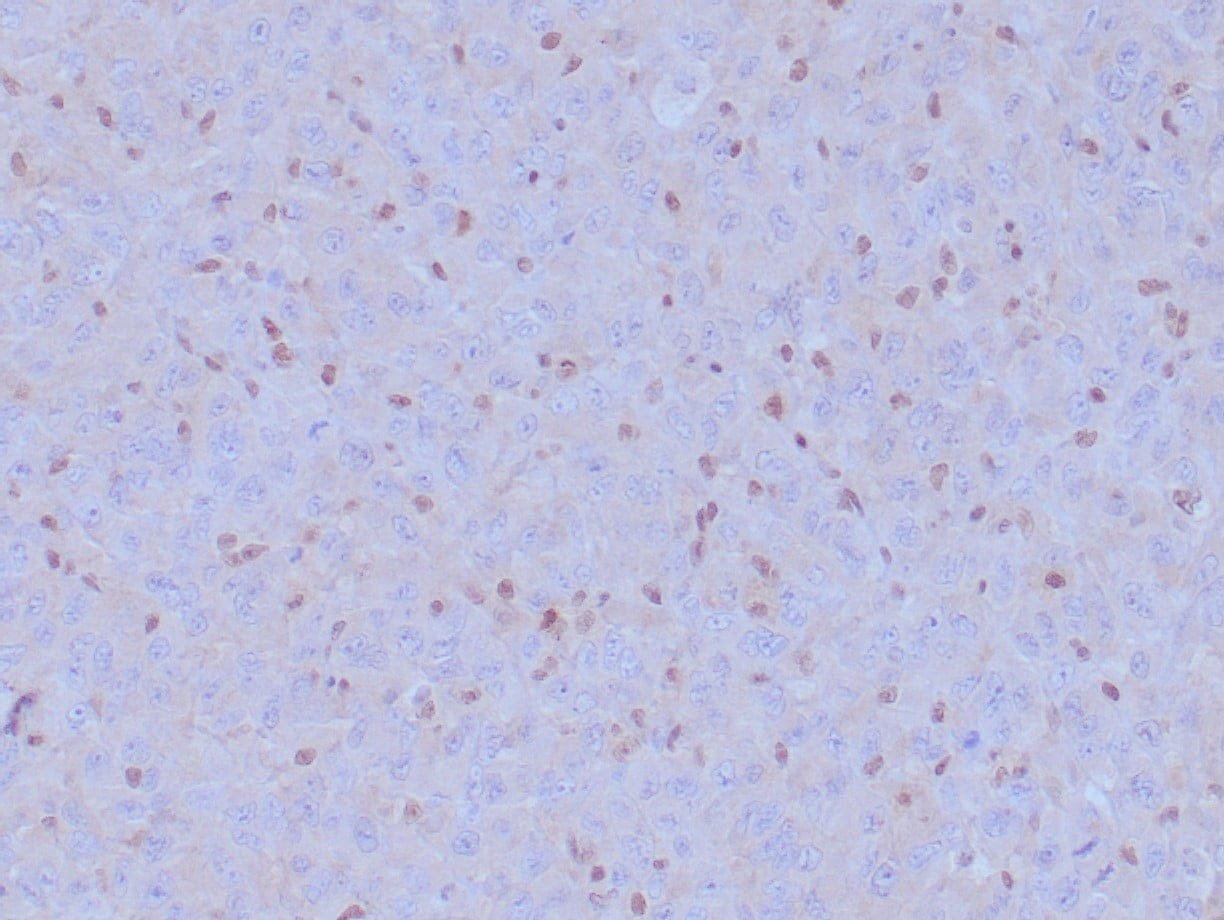
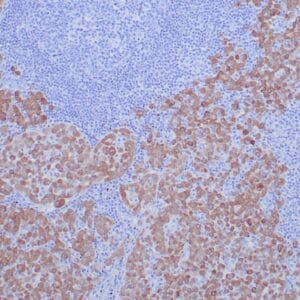
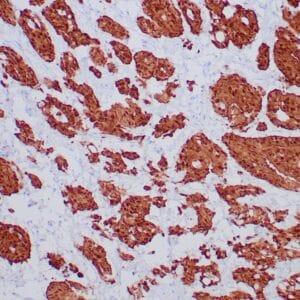
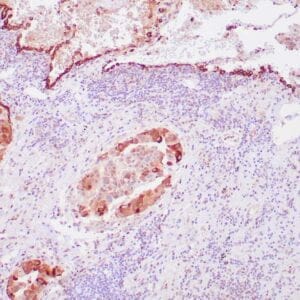
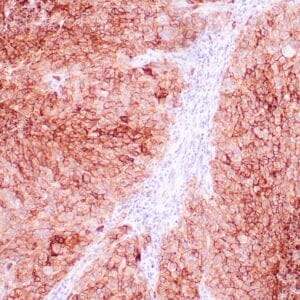
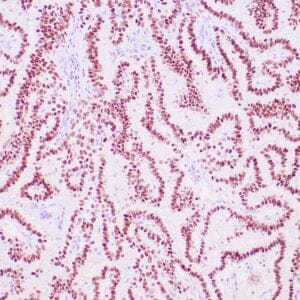
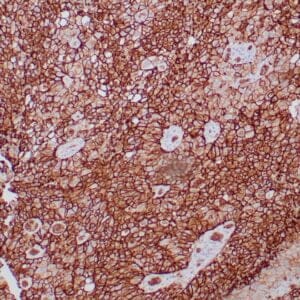
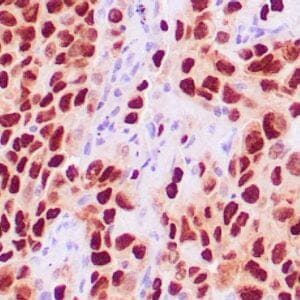

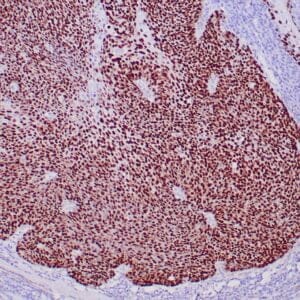
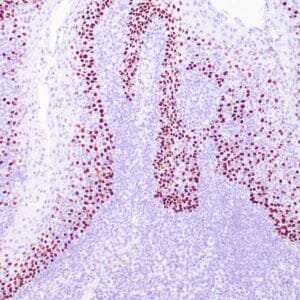
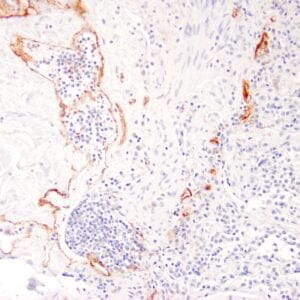
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.