| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| host | mouse |
| isotype | IgG1 |
| clonality | monoclonal |
| concentration | concentrate, predilute |
| applications | IHC |
| reactivity | human |
| available size | 0.1 mL, 0.5 mL, 1 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted |
mouse anti-ZAP-70 monoclonal antibody (ZM97) 6406
Price range: $160.00 through $528.00
Antibody summary
- Mouse monoclonal to ZAP-70
- Suitable for: Immunohistochemistry (formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues)
- Reacts with: Human
- Isotype:IgG1
- Control: Tonsil, CLL/SLL
- Visualization: Cytoplasmic
- 0.1, 0.5, 1.0 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted
mouse anti-ZAP-70 monoclonal antibody ZM97 6406
| target relevance |
|---|
| Protein names Tyrosine-protein kinase ZAP-70 (EC 2.7.10.2) (70 kDa zeta-chain associated protein) (Syk-related tyrosine kinase) |
| Gene names ZAP70,ZAP70 SRK |
| Protein family Protein kinase superfamily, Tyr protein kinase family, SYK/ZAP-70 subfamily |
| Mass 69872Da |
| Function FUNCTION: Tyrosine kinase that plays an essential role in regulation of the adaptive immune response. Regulates motility, adhesion and cytokine expression of mature T-cells, as well as thymocyte development. Also contributes to the development and activation of primary B-lymphocytes. When antigen presenting cells (APC) activate T-cell receptor (TCR), a serie of phosphorylations lead to the recruitment of ZAP70 to the doubly phosphorylated TCR component CD247/CD3Z through ITAM motif at the plasma membrane. This recruitment serves to localization to the stimulated TCR and to relieve its autoinhibited conformation. Release of ZAP70 active conformation is further stabilized by phosphorylation mediated by LCK. Subsequently, ZAP70 phosphorylates at least 2 essential adapter proteins: LAT and LCP2. In turn, a large number of signaling molecules are recruited and ultimately lead to lymphokine production, T-cell proliferation and differentiation. Furthermore, ZAP70 controls cytoskeleton modifications, adhesion and mobility of T-lymphocytes, thus ensuring correct delivery of effectors to the APC. ZAP70 is also required for TCR-CD247/CD3Z internalization and degradation through interaction with the E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase CBL and adapter proteins SLA and SLA2. Thus, ZAP70 regulates both T-cell activation switch on and switch off by modulating TCR expression at the T-cell surface. During thymocyte development, ZAP70 promotes survival and cell-cycle progression of developing thymocytes before positive selection (when cells are still CD4/CD8 double negative). Additionally, ZAP70-dependent signaling pathway may also contribute to primary B-cells formation and activation through B-cell receptor (BCR). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11353765, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12051764, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1423621, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20135127, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26903241, ECO:0000269|PubMed:38614099, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8124727, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8702662, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9489702}. |
| Catalytic activity CATALYTIC ACTIVITY: Reaction=L-tyrosyl-[protein] + ATP = O-phospho-L-tyrosyl-[protein] + ADP + H(+); Xref=Rhea:RHEA:10596, Rhea:RHEA-COMP:10136, Rhea:RHEA-COMP:20101, ChEBI:CHEBI:15378, ChEBI:CHEBI:30616, ChEBI:CHEBI:46858, ChEBI:CHEBI:61978, ChEBI:CHEBI:456216; EC=2.7.10.2; Evidence={ECO:0000255|PROSITE-ProRule:PRU10028, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15292186}; |
| Subellular location SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: Cytoplasm {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9813084}. Cell membrane {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9813084}; Peripheral membrane protein {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9813084}. Note=In quiescent T-lymphocytes, it is cytoplasmic. Upon TCR activation, it is recruited at the plasma membrane by interacting with CD247/CD3Z. Colocalizes together with RHOH in the immunological synapse. RHOH is required for its proper localization to the cell membrane and cytoskeleton fractions in the thymocytes (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
| Tissues TISSUE SPECIFICITY: Expressed in T- and natural killer cells. Also present in early thymocytes and pro/pre B-cells. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:1423621, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16467082, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9378960}. |
| Structure SUBUNIT: Interacts with CD247/CD3Z; this interaction docks ZAP70 at the stimulated TCR (PubMed:1423621, PubMed:26783323, PubMed:7659156). Interacts with NFAM1 (PubMed:15143214). Interacts with adapter protein SLA; this interaction negatively regulates T-cell receptor signaling (PubMed:10449770). Interacts with FCRL3 (PubMed:12051764, PubMed:19843936). Interacts with VAV1 (PubMed:9151714). Interacts with CBL; this interaction promotes ubiquitination, internalization and subsequent degradation of CD247/CD3Z (PubMed:10078535, PubMed:10449770). Identified in a complex with CBL and UBE2L3 (PubMed:10966114). Interacts with SHB (PubMed:12084069). Interacts with adapter protein SLA2; this interaction negatively regulates T-cell receptor signaling. Interacts with CBLB. Interacts (via SH2 domains) with RHOH; this interaction regulates ZAP70 subcellular localization. Interacts with DEF6 (By similarity). Interacts (ubiquitinated form) with OTUD7B and UBASH3B (PubMed:26903241). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P43404, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10078535, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10449770, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10966114, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12051764, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12084069, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1423621, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15143214, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19843936, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26783323, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26903241, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7659156, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9151714}. |
| Post-translational modification PTM: Phosphorylated on tyrosine residues upon T-cell antigen receptor (TCR) stimulation. Phosphorylation of Tyr-315 and Tyr-319 are essential for ZAP70 positive function on T-lymphocyte activation whereas Tyr-292 has a negative regulatory role. Within the C-terminal kinase domain, Tyr-492 and Tyr-493 are phosphorylated after TCR induction, Tyr-492 playing a negative regulatory role and Tyr-493 a positive. Tyr-493 is dephosphorylated by PTN22. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10037717, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1423621, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16339550, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8943331}.; PTM: Ubiquitinated in response to T cell activation. Deubiquitinated by OTUD7B. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26903241}. |
| Domain DOMAIN: Composed of 2 N-terminal SH2 domains and a C-terminal kinase domain. The tandem SH2 domains bind to the doubly phosphorylated tyrosine-based activation motif (ITAM) of CD247/CD3Z and the non-canonical phosphorylated tyrosine-based activation motif (TAM) of RHOH (By similarity). The interdomain B located between the second SH2 and the kinase domain contains 3 tyrosines (Tyr-292, Tyr-315, Tyr-319) that are phosphorylated following TCR activation. These sites have been implicated in binding to other signaling molecules including CBL or VAV1. Thus, ZAP70 can also function as a scaffold by recruiting additional factors to the stimulated TCR complex. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20135127}. |
| Involvement in disease DISEASE: Immunodeficiency 48 (IMD48) [MIM:269840]: A form of severe immunodeficiency characterized by a selective absence of CD8+ T-cells. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11123350, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11412303, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18509675, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8124727, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8202713}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Autoimmune disease, multisystem, infantile-onset, 2 (ADMIO2) [MIM:617006]: An autosomal recessive, autoimmune disorder characterized by systemic manifestations including blistering skin disease, uncontrollable bullous pemphigoid, inflammatory colitis, autoimmune hypothyroidism, proteinuria and nephrotic syndrome. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26783323}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: P43403 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
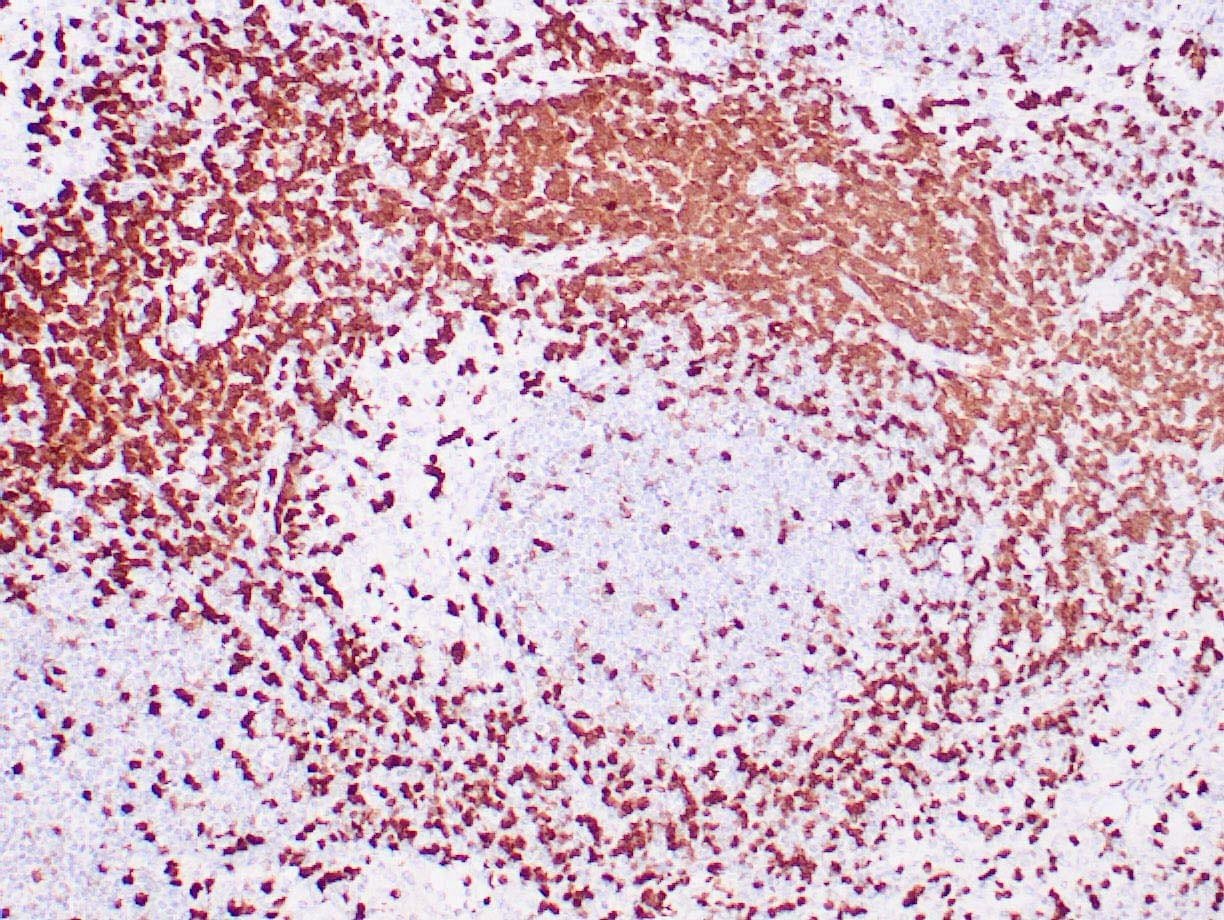 |
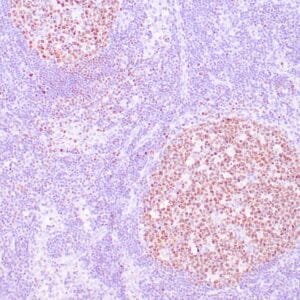
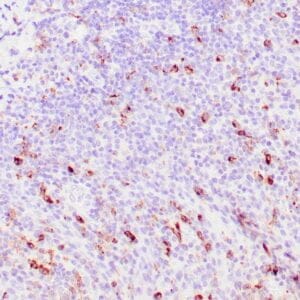
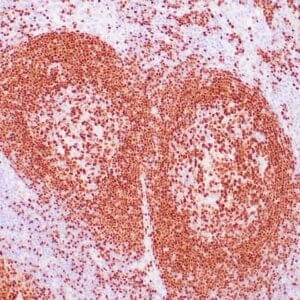
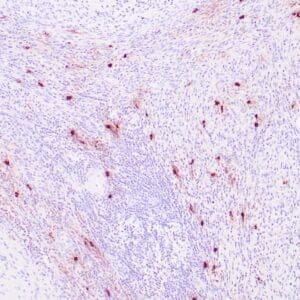
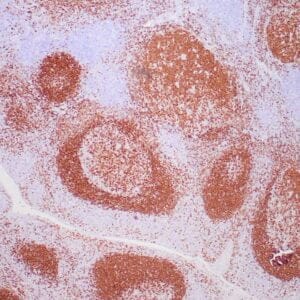
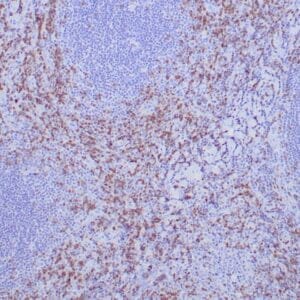
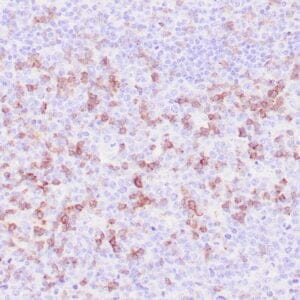
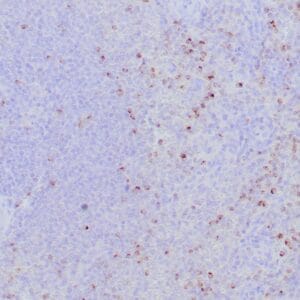
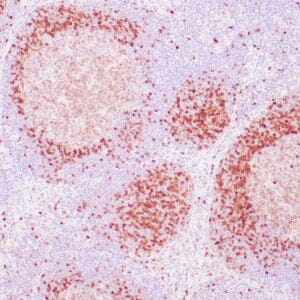
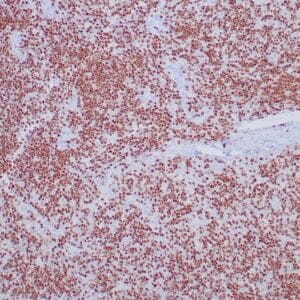
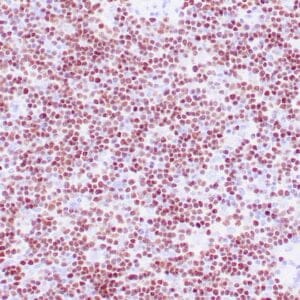
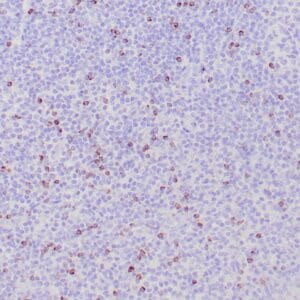
| Human tonsil stained with anti-ZAP-70 antibodies using peroxidase-conjugate and DAB chromogen. Note the positive staining of perifollicular B-cells |
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
| IHC |
Documents
| # | SDS | Certificate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | |||
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.
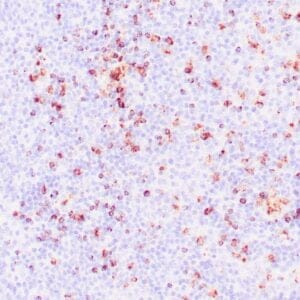
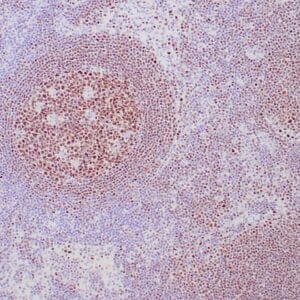
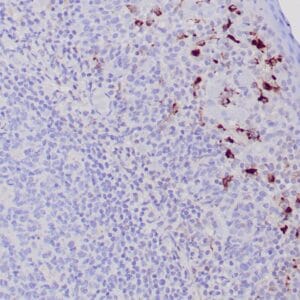
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.