| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| host | mouse |
| isotype | IgG2a |
| clonality | monoclonal |
| concentration | concentrate, predilute |
| applications | IHC |
| reactivity | human |
| available size | 0.1 mL, 0.5 mL, 1 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted |
mouse anti-Fascin monoclonal antibody (ZM192) 6182
Price range: $160.00 through $528.00
Antibody summary
- Mouse monoclonal to Fascin
- Suitable for: Immunohistochemistry (formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues)
- Reacts with: Human
- Isotype:IgG2a
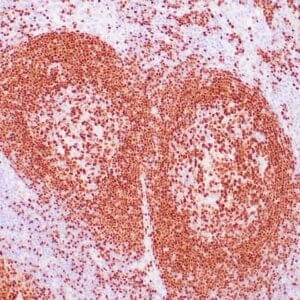
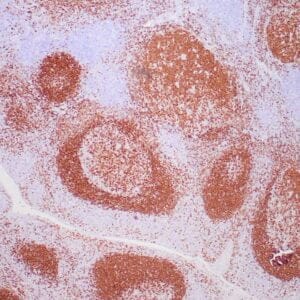
- Control: Hodgkin’s lymphoma or spleen
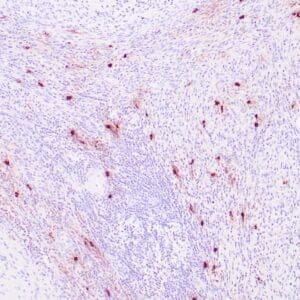
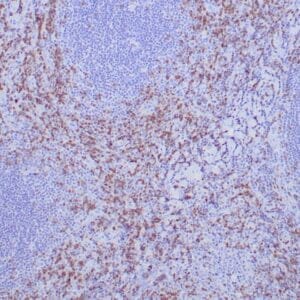
- Visualization: Cytoplasmic
- 0.1, 0.5, 1.0 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted
mouse anti-Fascin monoclonal antibody ZM192 6182
| target relevance |
|---|
| Protein names Fascin (55 kDa actin-bundling protein) (Singed-like protein) (p55) |
| Gene names FSCN1,FSCN1 FAN1 HSN SNL |
| Protein family Fascin family |
| Mass 54530Da |
| Function FUNCTION: Actin-binding protein that contains 2 major actin binding sites (PubMed:21685497, PubMed:23184945). Organizes filamentous actin into parallel bundles (PubMed:20393565, PubMed:21685497, PubMed:23184945). Plays a role in the organization of actin filament bundles and the formation of microspikes, membrane ruffles, and stress fibers (PubMed:22155786). Important for the formation of a diverse set of cell protrusions, such as filopodia, and for cell motility and migration (PubMed:20393565, PubMed:21685497, PubMed:23184945). Mediates reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton and axon growth cone collapse in response to NGF (PubMed:22155786). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20137952, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20393565, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21685497, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22155786, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23184945, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9362073, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9571235}. |
| Subellular location SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: Cytoplasm, cytosol {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21706053, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9571235}. Cytoplasm, cell cortex {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21685497}. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21685497, ECO:0000269|PubMed:3525578, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9571235}. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, stress fiber {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21706053}. Cell projection, filopodium {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20137952, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21685497, ECO:0000269|PubMed:3525578}. Cell projection, invadopodium {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20137952}. Cell projection, microvillus {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9571235}. Cell junction {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9571235}. Note=Colocalized with RUFY3 and F-actin at filipodia of the axonal growth cone. Colocalized with DBN1 and F-actin at the transitional domain of the axonal growth cone (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q61553, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21706053}. |
| Tissues TISSUE SPECIFICITY: Ubiquitous. |
| Structure SUBUNIT: Interacts with RUFY3 (via N-terminus); the interaction induces neuron axon development (By similarity). Interacts with NGFR (By similarity). Associates with CTNNB1 (By similarity). Interacts with PLXNB3 (PubMed:21706053). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P85845, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q61553, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21706053}. |
| Post-translational modification PTM: Phosphorylation at Ser-39 inhibits actin-binding (PubMed:8647875, PubMed:8999969). Phosphorylation is required for the reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton in response to NGF (PubMed:22155786). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22155786, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8647875, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8999969}. |
| Domain DOMAIN: Composed of four fascin beta-trefoil domains. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20393565, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20434460, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21685497, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23184945}. |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: Q16658 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
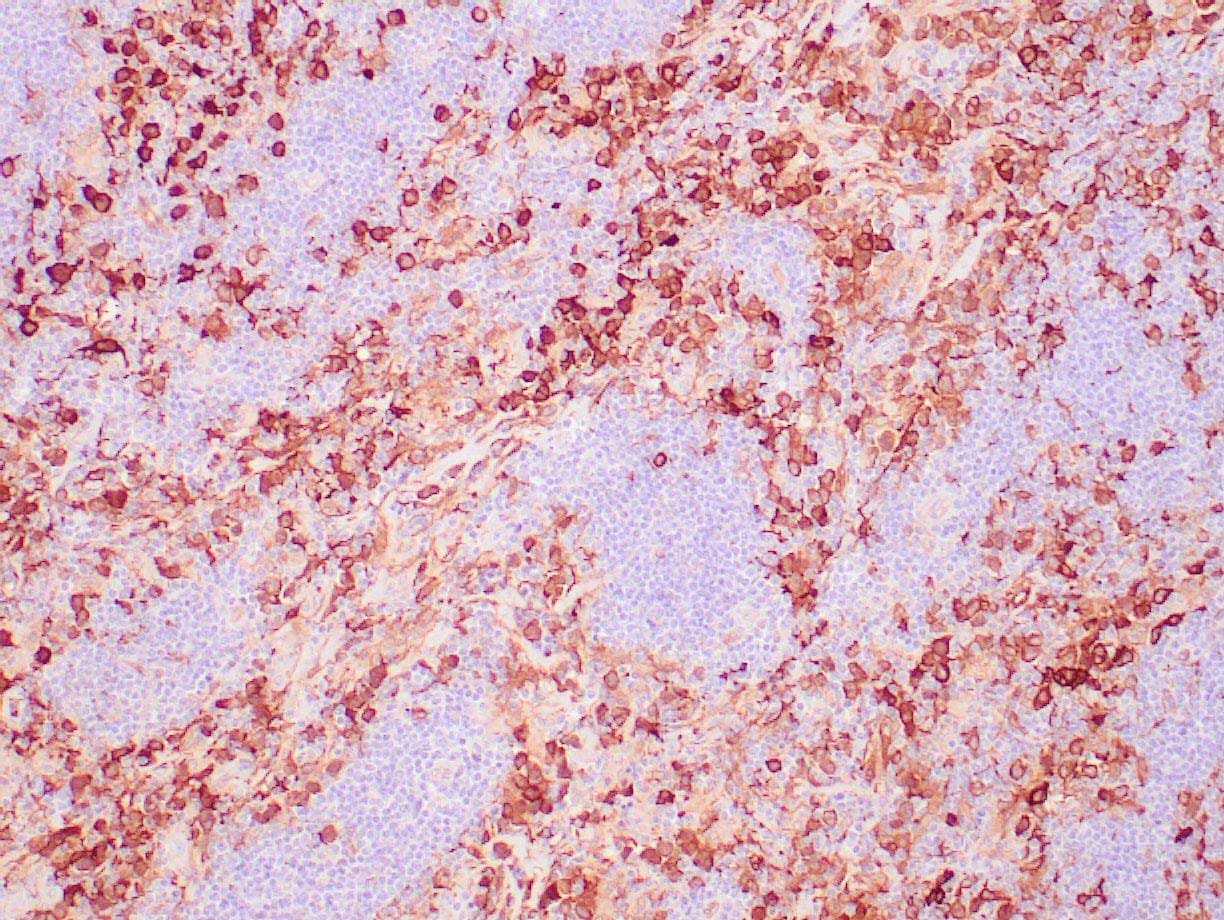 |
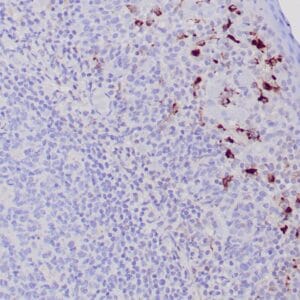
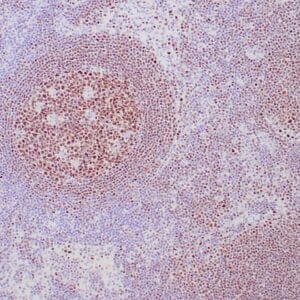
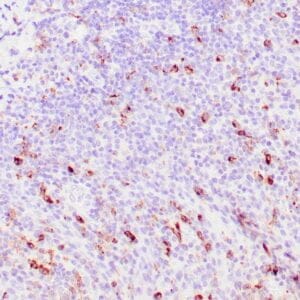
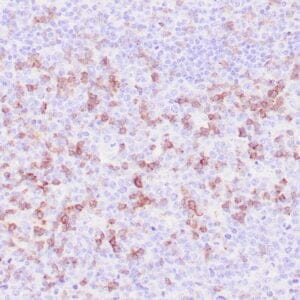
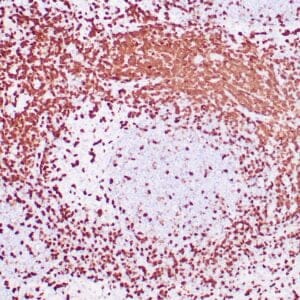
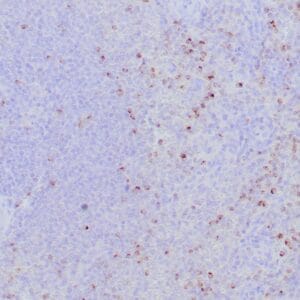
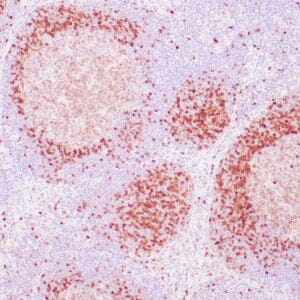
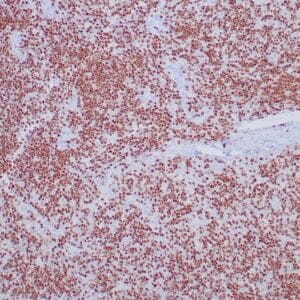
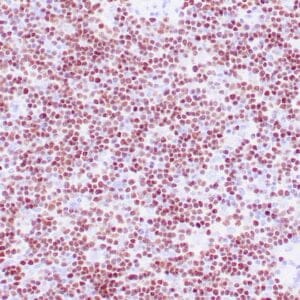
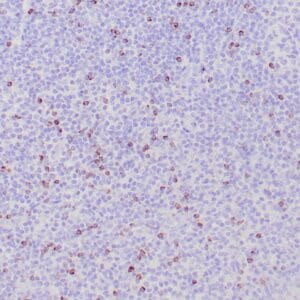
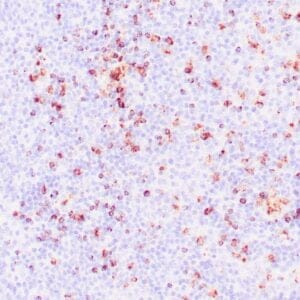
| Human Hodgkin lymphoma stained with anti-Fascin antibody using peroxidase-conjugate and DAB chromogen. Note the cytoplasmic staining of Hodgkin's cells. |
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
| IHC |
Documents
| # | SDS | Certificate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | |||
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.