| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| host | mouse |
| isotype | IgG2a |
| clonality | monoclonal |
| concentration | 1 mg/mL |
| applications | ELISA, ICC/IF, WB |
| reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| available sizes | 1 mg, 100 µg, 25 µg |
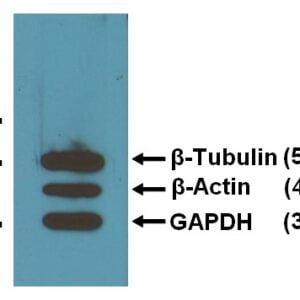
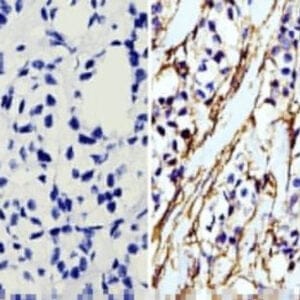
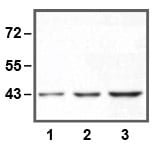
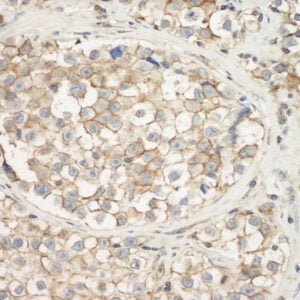
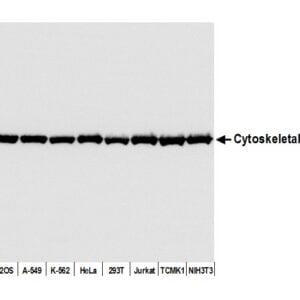
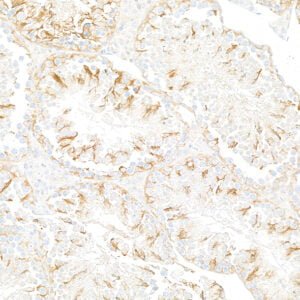
mouse anti-beta Tubulin monoclonal antibody (BT7R) 5007
Price range: $100.00 through $2,600.00
Antibody summary
- Mouse monoclonal to beta Tubulin
- Suitable for: WB,ICC/IF,ELISA
- Reacts with: human, mouse, rat
- Isotype: IgG2a
- 100 µg, 25 µg, 1 mg
mouse anti-beta Tubulin monoclonal antibody (BT7R) 5007
| antibody |
|---|
| Database link: human P07437 mouse P99024 rat P69897 |
| Tested applications WB,ICC/IF,ELISA |
| Recommended dilutions WB: 1:2000-5000 |
| Immunogen β-Tubulin N-terminal peptide-KLH conjugates. |
| Size and concentration 25, 100, 1000µg and 1 mg/mL |
| Form liquid |
| Storage Instructions -20°C for 2 years or more. °Centrifuge after first thaw to maximize product recovery. Aliquot to avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. Store aliquots at 4°C for several days to weeks. |
| Storage buffer PBS, pH 7.2, 0.05% NaN3 |
| Purity affinity purified |
| Clonality monoclonal |
| Isotype IgG2a |
| Compatible secondaries goat anti-mouse IgG, H&L chain specific, peroxidase conjugated polyclonal antibody 5486 goat anti-mouse IgG, H&L chain specific, biotin conjugated, Conjugate polyclonal antibody 2685 goat anti-mouse IgG, H&L chain specific, FITC conjugated polyclonal antibody 7854 goat anti-mouse IgG, H&L chain specific, peroxidase conjugated polyclonal antibody, crossabsorbed 1706 goat anti-mouse IgG, H&L chain specific, biotin conjugated polyclonal antibody, crossabsorbed 1716 goat anti-mouse IgG, H&L chain specific, FITC conjugated polyclonal antibody, crossabsorbed 1721 |
| Isotype control Mouse monocolonal IgG2a - Isotype Control |
| target relevance |
|---|
| Beta tubulin is a structural component of microtubules, beta-tubulin plays a fundamental role in maintaining cell shape, supporting intracellular transport, and facilitating cell division. Due to its stable expression levels and essential cellular functions, beta-tubulin has become widely recognized as a valuable loading control in various experimental techniques, such as Western blotting and immunoblotting. Its consistent presence in most eukaryotic cells ensures that its expression remains relatively constant, making it an ideal reference protein for normalizing and quantifying target protein levels accurately. This antibody can be used as a loading control when run alongside proteins of interest with different and resolvable molecular weights and ideally in combination with antibodies of same host and when using a secondary antibody. Click for more on: loading controls and beta Tubulin |
| Protein names Tubulin beta chain (Tubulin beta-5 chain) |
| Gene names TUBB,TUBB TUBB5 OK/SW-cl.56 |
| Protein family Tubulin family |
| Mass 49671Da |
| Function FUNCTION: Tubulin is the major constituent of microtubules, a cylinder consisting of laterally associated linear protofilaments composed of alpha- and beta-tubulin heterodimers. Microtubules grow by the addition of GTP-tubulin dimers to the microtubule end, where a stabilizing cap forms. Below the cap, tubulin dimers are in GDP-bound state, owing to GTPase activity of alpha-tubulin. |
| Subellular location SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26637975}. |
| Tissues TISSUE SPECIFICITY: Ubiquitously expressed with highest levels in spleen, thymus and immature brain. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20191564}. |
| Structure SUBUNIT: Heterodimer of alpha and beta chains (PubMed:26637975). A typical microtubule is a hollow water-filled tube with an outer diameter of 25 nm and an inner diameter of 15 nM. Alpha-beta heterodimers associate head-to-tail to form protofilaments running lengthwise along the microtubule wall with the beta-tubulin subunit facing the microtubule plus end conferring a structural polarity. Microtubules usually have 13 protofilaments but different protofilament numbers can be found in some organisms and specialized cells. Interacts with CIMAP3 (PubMed:20643351). Interacts with DIAPH1 (PubMed:23325789). Interacts with MX1 (By similarity). May interact with RNABP10 (By similarity). Interacts with CFAP157 (By similarity). Nascent tubulin polypeptide interacts (via beta-tubulin MREI motif) with TTC5/STRAP; this interaction results in tubulin mRNA-targeted degradation (PubMed:31727855). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P69893, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P99024, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20643351, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23325789, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26637975, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31727855}. |
| Post-translational modification PTM: Some glutamate residues at the C-terminus are polyglutamylated, resulting in polyglutamate chains on the gamma-carboxyl group (PubMed:26875866, PubMed:28576883). Polyglutamylation plays a key role in microtubule severing by spastin (SPAST). SPAST preferentially recognizes and acts on microtubules decorated with short polyglutamate tails: severing activity by SPAST increases as the number of glutamates per tubulin rises from one to eight, but decreases beyond this glutamylation threshold (PubMed:26875866). Glutamylation is also involved in cilia motility (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P99024, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26875866, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28576883}.; PTM: Some glutamate residues at the C-terminus are monoglycylated but not polyglycylated due to the absence of functional TTLL10 in human. Monoglycylation is mainly limited to tubulin incorporated into cilia and flagella axonemes, which is required for their stability and maintenance. Flagella glycylation controls sperm motility (Probable) (PubMed:28576883). Both polyglutamylation and monoglycylation can coexist on the same protein on adjacent residues, and lowering glycylation levels increases polyglutamylation, and reciprocally (Probable) (PubMed:28576883). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28576883, ECO:0000305|PubMed:19524510}.; PTM: Phosphorylated on Ser-172 by CDK1 during the cell cycle, from metaphase to telophase, but not in interphase. This phosphorylation inhibits tubulin incorporation into microtubules. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16371510}. |
| Domain DOMAIN: The highly acidic C-terminal region may bind cations such as calcium.; DOMAIN: The MREI motif is common among all beta-tubulin isoforms and may be critical for tubulin autoregulation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:31727855}. |
| Involvement in disease DISEASE: Cortical dysplasia, complex, with other brain malformations 6 (CDCBM6) [MIM:615771]: A disorder of aberrant neuronal migration and disturbed axonal guidance. Affected individuals have microcephaly, ataxia, and severe delayed psychomotor development. Brain imaging shows variable malformations of cortical development, including white matter streaks, dysmorphic basal ganglia, corpus callosum abnormalities, brainstem and cerebellar hypoplasia, cortical dysplasia, polymicrogyria. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23246003}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Skin creases, congenital symmetric circumferential, 1 (CSCSC1) [MIM:156610]: An autosomal dominant disease characterized by multiple, symmetric, circumferential rings of folded skin, affecting primarily the limbs. Affected individuals also exhibit intellectual disability, cleft palate, and dysmorphic features. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26637975}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: P07437 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
| Western blot ICC |
Documents
| # | SDS | Certificate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | |||
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.




Reviews
There are no reviews yet.