| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| host | mouse |
| isotype | IgG |
| clonality | monoclonal |
| concentration | concentrate, predilute |
| applications | IHC |
| reactivity | human |
| available size | 0.1 mL, 0.5 mL, 1 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted |
rabbit anti-PAX-5 monoclonal antibody (ZR268) 6432
Price range: $160.00 through $528.00
Antibody summary
- Rabbit monoclonal to PAX-5
- Suitable for: Immunohistochemistry (formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues)
- Reacts with: Human
- Isotype:IgG
- Control: Tonsil
- Visualization: Nuclear
- 0.1, 0.5, 1.0 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted
rabbit anti-PAX-5 monoclonal antibody ZR268 6432
| target relevance |
|---|
| Protein names Paired box protein Pax-5 (B-cell-specific transcription factor) (BSAP) |
| Gene names PAX5,PAX5 |
| Mass 42149Da |
| Function FUNCTION: Transcription factor that plays an essential role in commitment of lymphoid progenitors to the B-lymphocyte lineage (PubMed:10811620, PubMed:27181361). Fulfills a dual role by repressing B-lineage inappropriate genes and simultaneously activating B-lineage-specific genes (PubMed:10811620, PubMed:27181361). In turn, regulates cell adhesion and migration, induces V(H)-to-D(H)J(H) recombination, facilitates pre-B-cell receptor signaling and promotes development to the mature B-cell stage (PubMed:32612238). Repression of the cohesin-release factor WAPL causes global changes of the chromosomal architecture in pro-B cells to facilitate the generation of a diverse antibody repertoire (PubMed:32612238). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10811620, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27181361, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32612238}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Plays an essential role in the maintenance of Epstein-Barr virus genome copy number within the host cell by promoting EBNA1/oriP-dependent binding and transcription (PubMed:31941781). Also participates in the inhibition of lytic EBV reactivation by modulating viral BZLF1 activity (PubMed:23678172). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23678172, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31941781}. |
| Subellular location SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: Nucleus {ECO:0000269|PubMed:31941781}. |
| Structure SUBUNIT: Interacts with ETS1; this interaction alters PAX5 DNA-binding properties (PubMed:11779502). Binds DNA as a monomer (PubMed:11779502). Interacts with TBP; this interaction allows PAX5 to interact with the basal transcription machinery (PubMed:10197586). Interacts with RB1 (PubMed:10197586). Interacts with TLE4 (PubMed:10811620). Interacts with DAXX (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q02650, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10197586, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10811620, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11779502}.; SUBUNIT: (Microbial infection) Interacts (via N-terminus) with Epstein-Barr virus protein BZLF1 (via C-terminus); this interaction inhibits BZLF1-mediated lytic viral reactivation (PubMed:23678172). Interacts also with EBNA1; this interaction promotes EBNA1-dependent transcription (PubMed:31941781). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23678172, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31941781}. |
| Post-translational modification PTM: O-glycosylated. {ECO:0000305}.; PTM: Phosphorylated by SYK. This phosphorylation plays an important role in the abolition of BLIMP1 repression by PAX5 in order to trigger plasma cell differentiation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27181361}. |
| Involvement in disease DISEASE: Note=A chromosomal aberration involving PAX5 is a cause of acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Translocation t(9;18)(p13;q11.2) with ZNF521. Translocation t(9;3)(p13;p14.1) with FOXP1. Translocation t(9;12)(p13;p13) with ETV6. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17344859}.; DISEASE: Leukemia, acute lymphoblastic, 3 (ALL3) [MIM:613065]: A subtype of acute leukemia, a cancer of the white blood cells. Acute lymphoblastic anemia is a malignant disease of bone marrow and the most common malignancy diagnosed in children. The malignant cells are lymphoid precursor cells (lymphoblasts) that are arrested in an early stage of development. The lymphoblasts replace the normal marrow elements, resulting in a marked decrease in the production of normal blood cells. Consequently, anemia, thrombocytopenia, and neutropenia occur to varying degrees. The lymphoblasts also proliferate in organs other than the marrow, particularly the liver, spleen, and lymphnodes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24013638}. Note=Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: Q02548 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
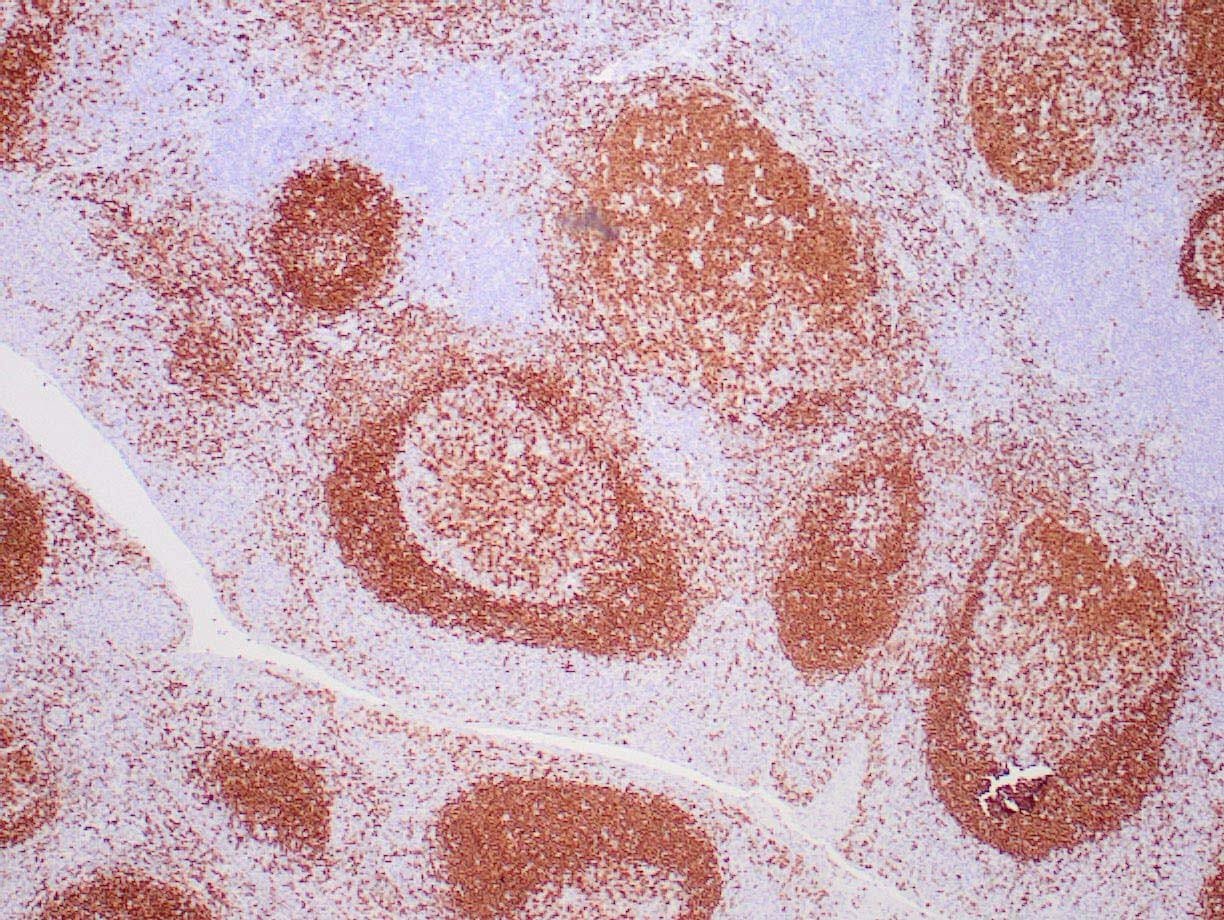 |
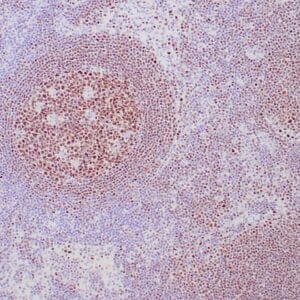
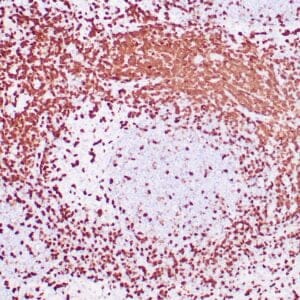
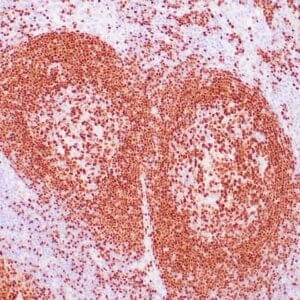
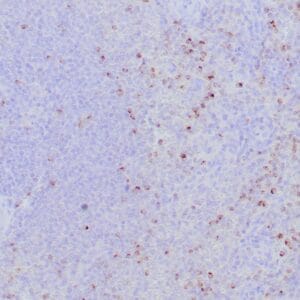
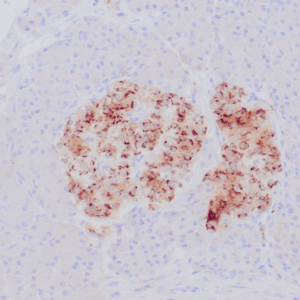
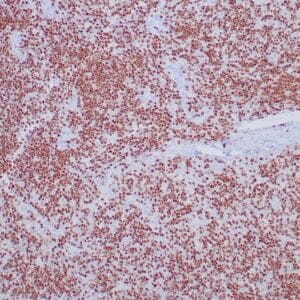
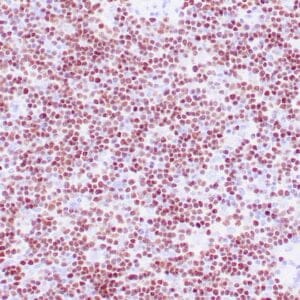
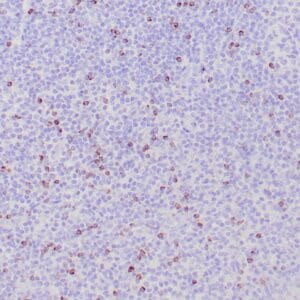
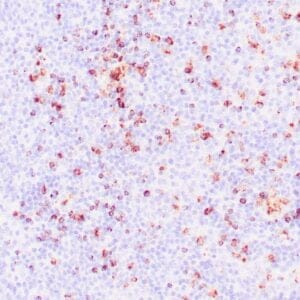
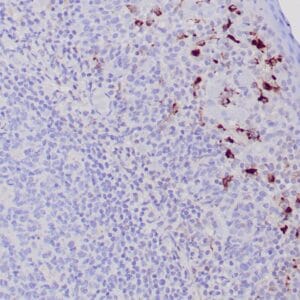
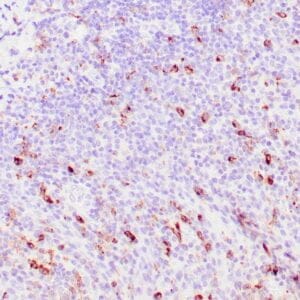
| Human tonsil stained with anti-PAX-5 antibody using peroxidase-conjugate and DAB chromogen. Note the nuclear staining in B cells in follicle. |
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
| IHC |
Documents
| # | SDS | Certificate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | |||
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.