| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| host | mouse |
| isotype | IgG |
| clonality | monoclonal |
| concentration | concentrate, predilute |
| applications | IHC |
| reactivity | human |
| available size | 0.1 mL, 0.5 mL, 1 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted |
rabbit anti-MDM2 monoclonal antibody (ZR258) 6249
Price range: $160.00 through $528.00
Antibody summary
- Rabbit monoclonal to MDM2
- Suitable for: Immunohistochemistry (formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues)
- Reacts with: Human
- Isotype:IgG
- Control: Liposarcoma
- Visualization: Nucleus
- 0.1, 0.5, 1.0 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted
rabbit anti-MDM2 monoclonal antibody ZR258 6249
| target relevance |
|---|
| Protein names E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase Mdm2 (EC 2.3.2.27) (Double minute 2 protein) (Hdm2) (Oncoprotein Mdm2) (RING-type E3 ubiquitin transferase Mdm2) (p53-binding protein Mdm2) |
| Gene names MDM2,MDM2 |
| Protein family MDM2/MDM4 family |
| Mass 55233Da |
| Function FUNCTION: E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase that mediates ubiquitination of p53/TP53, leading to its degradation by the proteasome (PubMed:29681526). Inhibits p53/TP53- and p73/TP73-mediated cell cycle arrest and apoptosis by binding its transcriptional activation domain. Also acts as a ubiquitin ligase E3 toward itself and ARRB1. Permits the nuclear export of p53/TP53. Promotes proteasome-dependent ubiquitin-independent degradation of retinoblastoma RB1 protein. Inhibits DAXX-mediated apoptosis by inducing its ubiquitination and degradation. Component of the TRIM28/KAP1-MDM2-p53/TP53 complex involved in stabilizing p53/TP53. Also a component of the TRIM28/KAP1-ERBB4-MDM2 complex which links growth factor and DNA damage response pathways. Mediates ubiquitination and subsequent proteasome degradation of DYRK2 in nucleus. Ubiquitinates IGF1R and SNAI1 and promotes them to proteasomal degradation (PubMed:12821780, PubMed:15053880, PubMed:15195100, PubMed:15632057, PubMed:16337594, PubMed:17290220, PubMed:19098711, PubMed:19219073, PubMed:19837670, PubMed:19965871, PubMed:20173098, PubMed:20385133, PubMed:20858735, PubMed:22128911). Ubiquitinates DCX, leading to DCX degradation and reduction of the dendritic spine density of olfactory bulb granule cells (By similarity). Ubiquitinates DLG4, leading to proteasomal degradation of DLG4 which is required for AMPA receptor endocytosis (By similarity). Negatively regulates NDUFS1, leading to decreased mitochondrial respiration, marked oxidative stress, and commitment to the mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis (PubMed:30879903). Binds NDUFS1 leading to its cytosolic retention rather than mitochondrial localization resulting in decreased supercomplex assembly (interactions between complex I and complex III), decreased complex I activity, ROS production, and apoptosis (PubMed:30879903). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P23804, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12821780, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15053880, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15195100, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15632057, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16337594, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17290220, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19098711, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19219073, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19837670, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19965871, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20173098, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20385133, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20858735, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22128911, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29681526, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30879903}. |
| Catalytic activity CATALYTIC ACTIVITY: Reaction=S-ubiquitinyl-[E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme]-L-cysteine + [acceptor protein]-L-lysine = [E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme]-L-cysteine + N(6)-ubiquitinyl-[acceptor protein]-L-lysine.; EC=2.3.2.27; Evidence={ECO:0000269|PubMed:12821780}; |
| Subellular location SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: Nucleus, nucleoplasm. Cytoplasm {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30879903}. Nucleus, nucleolus. Nucleus {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30879903}. Note=Expressed predominantly in the nucleoplasm. Interaction with ARF(P14) results in the localization of both proteins to the nucleolus. The nucleolar localization signals in both ARF(P14) and MDM2 may be necessary to allow efficient nucleolar localization of both proteins. Colocalizes with RASSF1 isoform A in the nucleus. |
| Tissues TISSUE SPECIFICITY: Ubiquitous. Isoform Mdm2-A, isoform Mdm2-B, isoform Mdm2-C, isoform Mdm2-D, isoform Mdm2-E, isoform Mdm2-F and isoform Mdm2-G are observed in a range of cancers but absent in normal tissues. |
| Structure SUBUNIT: Interacts with p53/TP53, TP73/p73, RBL5 and RP11. Binds specifically to RNA. Can interact with RB1, E1A-associated protein EP300 and the E2F1 transcription factor. Forms a ternary complex with p53/TP53 and WWOX. Interacts with CDKN2AIP, RFWD3, USP7, PYHIN1, and RBBP6. Interacts with ARRB1 and ARRB2. Interacts with PSMA3. Found in a trimeric complex with MDM2, MDM4 and USP2. Interacts with USP2 (via N-terminus and C-terminus). Interacts with MDM4. Part of a complex with MDM2, DAXX, RASSF1 and USP7. Part of a complex with DAXX, MDM2 and USP7. Interacts directly with DAXX and USP7. Interacts (via C-terminus) with RASSF1 isoform A (via N-terminus); the interaction is independent of TP53. Interacts with APEX1; leading to its ubiquitination and degradation. Interacts with RYBP; this inhibits ubiquitination of TP53. Identified in a complex with RYBP and p53/TP53. Also a component of the TRIM28/KAP1-MDM2-p53/TP53 complex involved in regulating p53/TP53 stabilization and activity. Binds directly both p53/TP53 and TRIM28. Component of the TRIM28/KAP1-ERBB4-MDM2 complex involved in connecting growth factor responses with DNA damage. Interacts directly with both TRIM28 and ERBB4 in the complex. Interacts with DYRK2. Interacts with IGF1R. Interacts with TRIM13; the interaction ubiquitinates MDM2 leading to its proteasomal degradation. Interacts with SNAI1; this interaction promotes SNAI1 ubiquitination. Interacts with NOTCH1 (via intracellular domain). Interacts with FHIT. Interacts with RFFL and RNF34; the interaction stabilizes MDM2. Interacts with CDK5RAP3 and CDKN2A/ARF; form a ternary complex involved in regulation of p53/TP53 (PubMed:16173922). Interacts with MTA1. Interacts with AARB2. Interacts with MTBP. Interacts with PML. Interacts with TBRG1. Interacts (via its RanBP2-type zinc finger domain) with RPL11 in the 5S RNP complex composed of 5S RNA, RPL5 and RPL11; this interaction occurs in the nucleoplasm and negatively regulates MDM2-mediated TP53 ubiquitination and degradation (PubMed:15195100, PubMed:24120868, PubMed:37291423). Interacts with ADGRB1; the interaction results in inhibition of MDM2-mediated ubiquitination and degradation of DLG4/PSD95, promoting DLG4 stability and regulating synaptic plasticity (By similarity). Interacts with RPL23A; this interaction may promote p53/TP53 polyubiquitination (PubMed:26203195). Interacts with NDUFS1 (PubMed:30879903). Interacts with MORN3; the interaction enhances the ubiquitination of p53/TP53 (PubMed:29681526). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P23804, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11351297, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12821780, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15053880, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15195100, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15313915, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15364927, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15632057, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15878855, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16173922, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16219768, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16337594, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16402859, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16474402, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16479015, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16845383, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17110379, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17290220, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17460193, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17470788, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18382127, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18566590, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19098711, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19219073, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19837670, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19838211, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19965871, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20173098, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20385133, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20858735, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21333377, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22128911, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22869143, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24120868, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26203195, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29681526, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30879903, ECO:0000269|PubMed:37291423, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7689721, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8875929}.; SUBUNIT: (Microbial infection) Interacts with herpes virus 8 protein v-IRF4. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19369353}.; SUBUNIT: (Microbial infection) Interacts with and ubiquitinates HIV-1 Tat. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12883554}. |
| Post-translational modification PTM: Phosphorylation on Ser-166 by SGK1 activates ubiquitination of p53/TP53. Phosphorylated at multiple sites near the RING domain by ATM upon DNA damage; this prevents oligomerization and E3 ligase processivity and impedes constitutive p53/TP53 degradation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10611322, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12167711, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18382127, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19756449, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19816404}.; PTM: Autoubiquitination leads to proteasomal degradation; resulting in p53/TP53 activation it may be regulated by SFN. Also ubiquitinated by TRIM13. Deubiquitinated by USP2 leads to its accumulation and increases deubiquitination and degradation of p53/TP53. Deubiquitinated by USP7 leading to its stabilization. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18382127, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30879903}. |
| Domain DOMAIN: Region I is sufficient for binding p53 and inhibiting its G1 arrest and apoptosis functions. It also binds p73 and E2F1. Region II contains most of a central acidic region required for interaction with ribosomal protein L5 and a putative C4-type zinc finger. The RING finger domain which coordinates two molecules of zinc interacts specifically with RNA whether or not zinc is present and mediates the heterooligomerization with MDM4. It is also essential for its ubiquitin ligase E3 activity toward p53 and itself. |
| Involvement in disease DISEASE: Note=Seems to be amplified in certain tumors (including soft tissue sarcomas, osteosarcomas and gliomas). A higher frequency of splice variants lacking p53 binding domain sequences was found in late-stage and high-grade ovarian and bladder carcinomas. Four of the splice variants show loss of p53 binding.; DISEASE: Lessel-Kubisch syndrome (LSKB) [MIM:618681]: An autosomal recessive progeroid syndrome characterized by short stature, pinched facial features, prematurely gray hair, scleroderma-like skin changes, small kidneys and consecutive kidney failure, followed by severe arterial hypertension. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28846075}. Note=The disease may be caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: Q00987 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
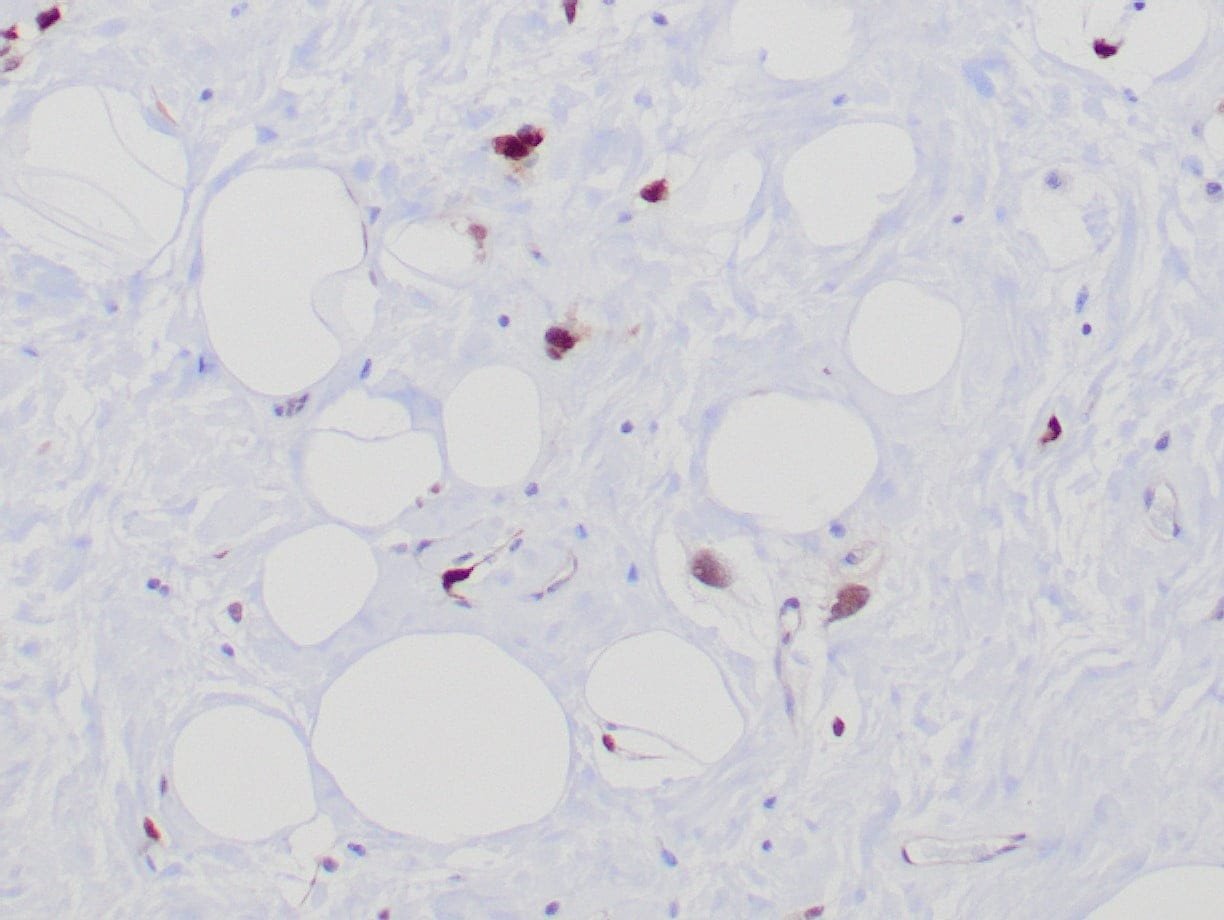 |
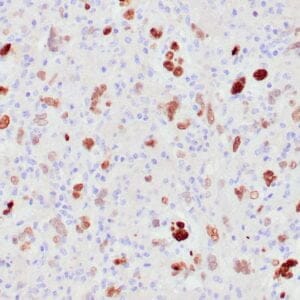
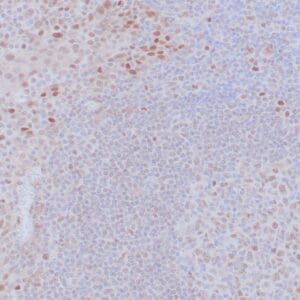
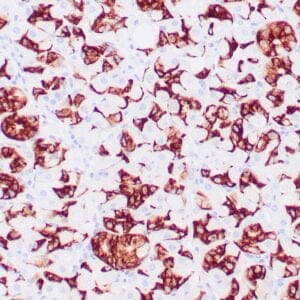
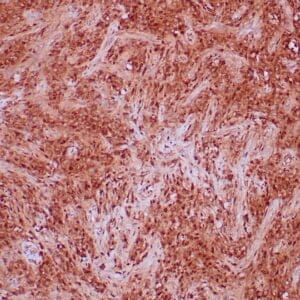
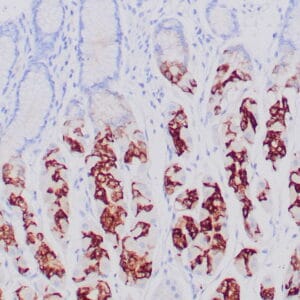
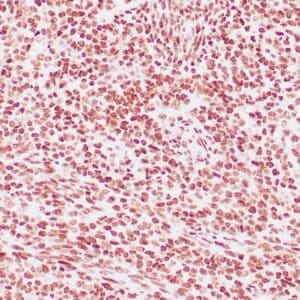
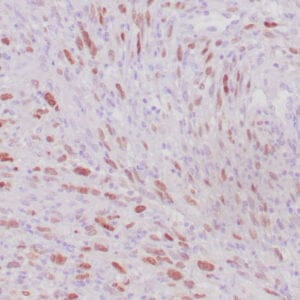
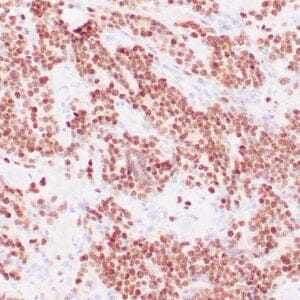
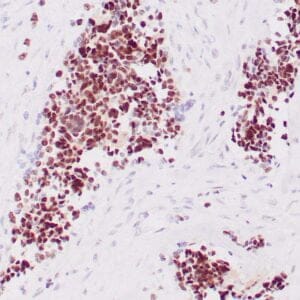
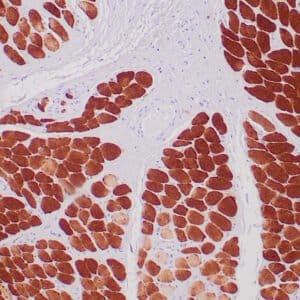
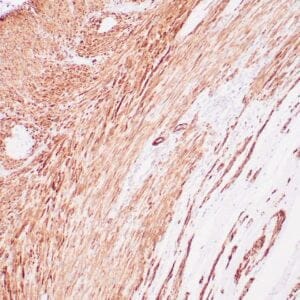
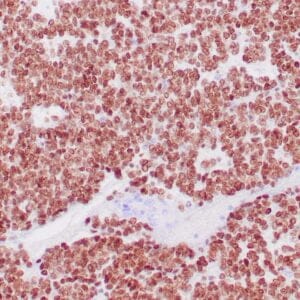
| Formalin-Fixed, paraffin-embedded human atypical lipomatous tumor stained with anti-MDM2 antibody using peroxidase-conjugate and DAB chromogen. Note the nuclear staining of tumor cells |
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
| IHC |
Documents
| # | SDS | Certificate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | |||
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.