| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| host | mouse |
| isotype | IgG |
| clonality | monoclonal |
| concentration | concentrate, predilute |
| applications | IHC |
| reactivity | human |
| available size | 0.1 mL, 0.5 mL, 1 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted |
rabbit anti-Collagen IV monoclonal antibody (ZR108) 6127
Price range: $160.00 through $528.00
Antibody summary
- Rabbit monoclonal to Collagen IV
- Suitable for: Immunohistochemistry (formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues)
- Reacts with: Human
- Isotype:IgG
- Control: Skin
- Visualization: Cytoplasmic and membranous
- 0.1, 0.5, 1.0 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted
rabbit anti-Collagen IV monoclonal antibody ZR108 6127
| target relevance |
|---|
| Protein names Collagen alpha-1(IV) chain [Cleaved into: Arresten] |
| Gene names COL4A1,COL4A1 |
| Protein family Type IV collagen family |
| Mass 160611Da |
| Function FUNCTION: Type IV collagen is the major structural component of glomerular basement membranes (GBM), forming a 'chicken-wire' meshwork together with laminins, proteoglycans and entactin/nidogen. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P02463}.; FUNCTION: Arresten, comprising the C-terminal NC1 domain, inhibits angiogenesis and tumor formation. The C-terminal half is found to possess the anti-angiogenic activity. Specifically inhibits endothelial cell proliferation, migration and tube formation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10811134, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18775695}. |
| Subellular location SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: Secreted, extracellular space, extracellular matrix, basement membrane {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P02463}. |
| Tissues TISSUE SPECIFICITY: Highly expressed in placenta. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10811134, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16481288}. |
| Structure SUBUNIT: There are six type IV collagen isoforms, alpha 1(IV)-alpha 6(IV), each of which can form a triple helix structure with 2 other chains to generate type IV collagen network. Interacts with EFEMP2 (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P02463, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q7SIB2}. |
| Post-translational modification PTM: Lysines at the third position of the tripeptide repeating unit (G-X-Y) are hydroxylated. The modified lysines can be O-glycosylated. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:6434307}.; PTM: Contains 4-hydroxyproline (Probable). Prolines at the third position of the tripeptide repeating unit (G-X-Y) are hydroxylated in some or all of the chains (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P02463, ECO:0000305|PubMed:6434307}.; PTM: Contains 3-hydroxyproline. This modification occurs on the first proline residue in the sequence motif Gly-Pro-Hyp, where Hyp is 4-hydroxyproline. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P02463, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q7SIB2}.; PTM: Type IV collagens contain numerous cysteine residues which are involved in inter- and intramolecular disulfide bonding (PubMed:2844531). 12 of these, located in the NC1 domain, are conserved in all known type IV collagens. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:2844531, ECO:0000305}.; PTM: The trimeric structure of the NC1 domains is stabilized by covalent bonds (sulfilimine cross-links) between Lys and Met residues (PubMed:12011424). These cross-links are important for the mechanical stability of the basement membrane (By similarity). Sulfilimine cross-link is catalyzed by PXDN (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P02463, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12011424}.; PTM: Proteolytic processing produces the C-terminal NC1 peptide, arresten. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10811134}. |
| Domain DOMAIN: Alpha chains of type IV collagen have a non-collagenous domain (NC1) at their C-terminus, frequent interruptions of the G-X-Y repeats in the long central triple-helical domain (which may cause flexibility in the triple helix), and a short N-terminal triple-helical 7S domain. NC1 domain mediates hexamerization of alpha chains of type IV collagen (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P02463, ECO:0000305}. |
| Involvement in disease DISEASE: Hereditary angiopathy with nephropathy aneurysms and muscle cramps (HANAC) [MIM:611773]: The clinical renal manifestations include hematuria and bilateral large cysts. Histologic analysis revealed complex basement membrane defects in kidney and skin. The systemic angiopathy appears to affect both small vessels and large arteries. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18160688, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20818663}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Brain small vessel disease 1 with or without ocular anomalies (BSVD1) [MIM:175780]: An autosomal dominant cerebrovascular disorder with variable manifestations reflecting the location and severity of the vascular defect. BSVD1 features include cerebral hemorrage, unilateral fluid-filled cysts or cavities within the cerebral hemispheres, leukoencephalopathy, hemiplegia, seizures, intellectual disability, and facial paresis. Affected individuals may manifest variable visual defects and ocular anomalies. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15905400, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16107487, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16598045, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17379824, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17696175, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19194877, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19477666, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20385946, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22574627, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23394911, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24628545}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) [MIM:614519]: A pathological condition characterized by bleeding into one or both cerebral hemispheres including the basal ganglia and the cerebral cortex. It is often associated with hypertension and craniocerebral trauma. Intracerebral bleeding is a common cause of stroke. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22522439}. Note=Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Tortuosity of retinal arteries (RATOR) [MIM:180000]: A disease characterized by marked tortuosity of second- and third-order retinal arteries with normal first-order arteries and venous system. Most patients manifest variable degrees of symptomatic transient vision loss due to retinal hemorrhage following minor stress or trauma. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25228067}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Schizencephaly (SCHZC) [MIM:269160]: Extremely rare human congenital disorder characterized by a full-thickness cleft within the cerebral hemispheres. These clefts are lined with gray matter and most commonly involve the parasylvian regions. Large portions of the cerebral hemispheres may be absent and replaced by cerebro-spinal fluid. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23225343}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Microangiopathy and leukoencephalopathy, pontine, autosomal dominant (PADMAL) [MIM:618564]: A form of cerebral small vessel disease characterized by the recurrence of ischemic strokes starting in the thirties or forties, and associated with progressive imbalance and cognitive impairment. MRI examination shows ischemic lacunas in the pons and cerebral hemispheres, and diffuse leukoencephalopathy affecting various brain regions. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27666438, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28369186}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Causative mutations affect a binding site for miR-29 microRNA located within the 3'UTR of COL4A1 and lead to an up-regulation of this gene. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27666438}. |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: P02462 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
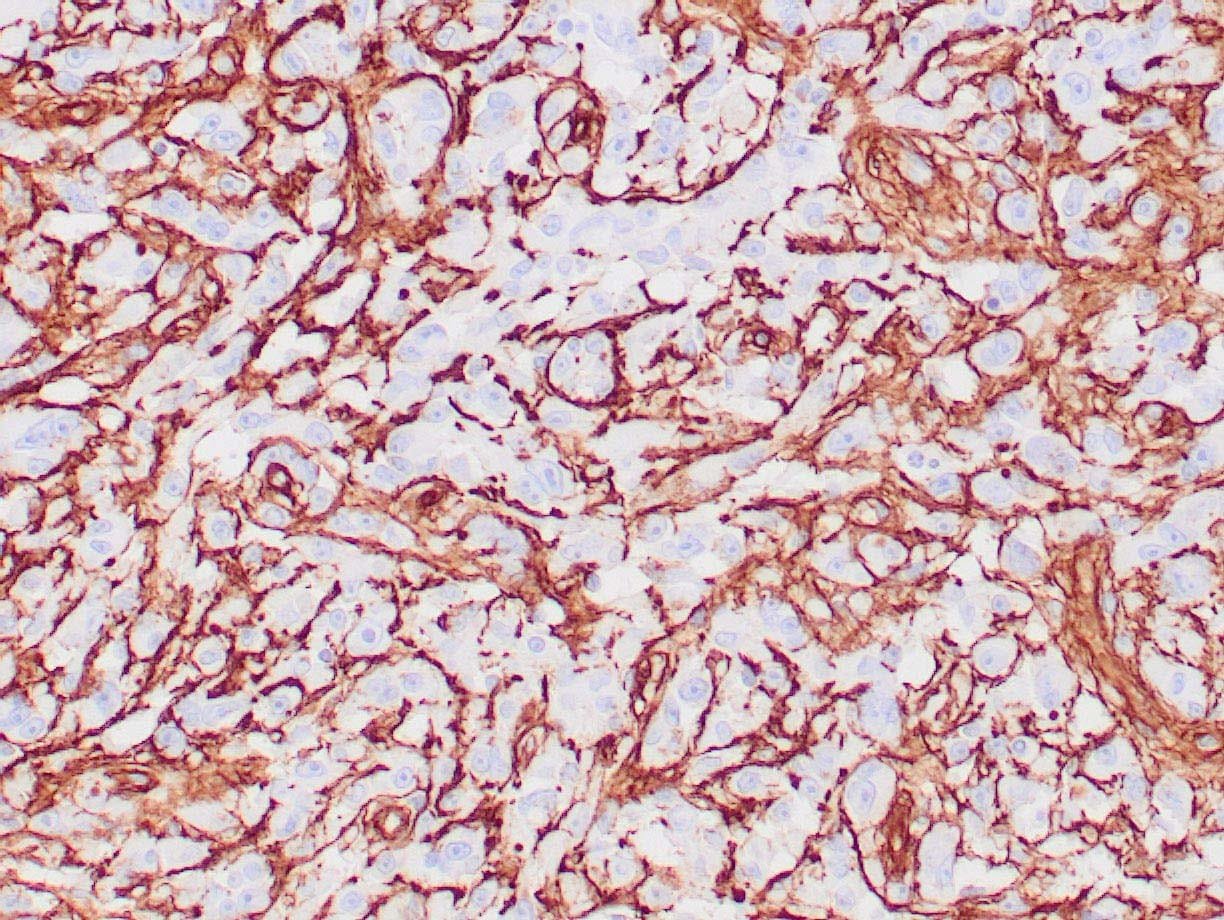 |
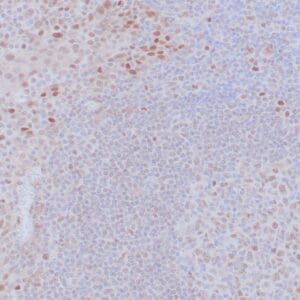
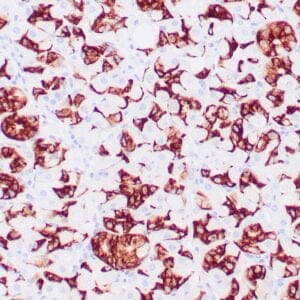
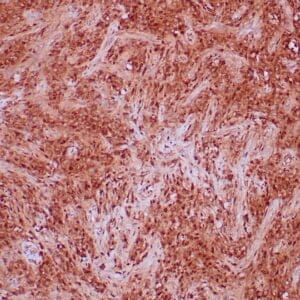
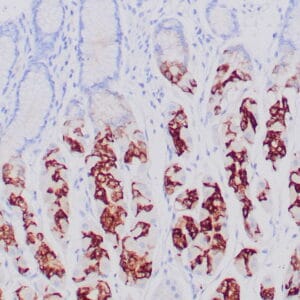
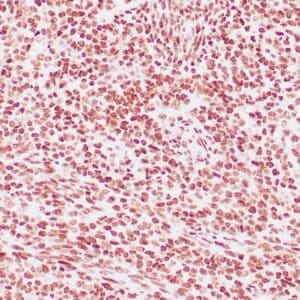
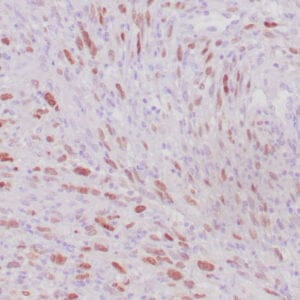
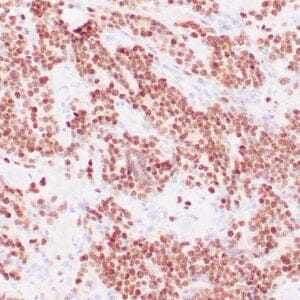
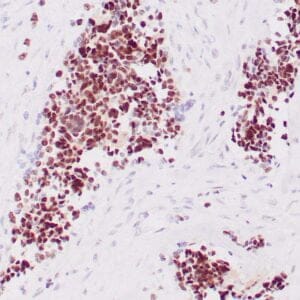
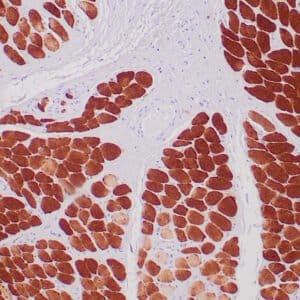
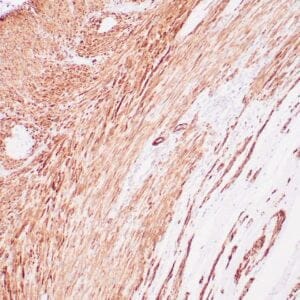
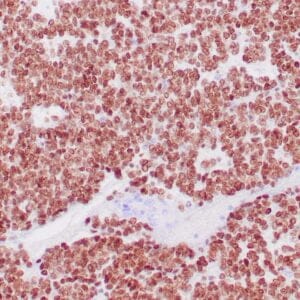
| Human glomus tumor stained with anti-Collagen IV using peroxidase-conjugate and DAB chromogen. Note basement membrane staining of around individual cells. |
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
| IHC |
Documents
| # | SDS | Certificate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | |||
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.