| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| host | mouse |
| isotype | IgG1 |
| clonality | monoclonal |
| concentration | concentrate, predilute |
| applications | IHC |
| reactivity | human |
| available size | 0.1 mL, 0.5 mL, 1 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted |
mouse anti-TIA-1 monoclonal antibody (2G9A10F5) 6386
Price range: $160.00 through $528.00
Antibody summary
- Mouse monoclonal to TIA-1
- Suitable for: Immunohistochemistry (formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues)
- Reacts with: Human
- Isotype:IgG1
- Control: Tonsil
- Visualization: Cytoplasmic
- 0.1, 0.5, 1.0 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted
mouse anti-TIA-1 monoclonal antibody 2G9A10F5 6386
| target relevance |
|---|
| Protein names Cytotoxic granule associated RNA binding protein TIA1 (Nucleolysin TIA-1 isoform p40) (RNA-binding protein TIA-1) (T-cell-restricted intracellular antigen-1) (TIA-1) (p40-TIA-1) |
| Gene names TIA1,TIA1 |
| Mass 42963Da |
| Function FUNCTION: RNA-binding protein involved in the regulation of alternative pre-RNA splicing and mRNA translation by binding to uridine-rich (U-rich) RNA sequences (PubMed:11106748, PubMed:12486009, PubMed:17488725, PubMed:8576255). Binds to U-rich sequences immediately downstream from a 5' splice sites in a uridine-rich small nuclear ribonucleoprotein (U snRNP)-dependent fashion, thereby modulating alternative pre-RNA splicing (PubMed:11106748, PubMed:8576255). Preferably binds to the U-rich IAS1 sequence in a U1 snRNP-dependent manner; this binding is optimal if a 5' splice site is adjacent to IAS1 (By similarity). Activates the use of heterologous 5' splice sites; the activation depends on the intron sequence downstream from the 5' splice site, with a preference for a downstream U-rich sequence (PubMed:11106748). By interacting with SNRPC/U1-C, promotes recruitment and binding of spliceosomal U1 snRNP to 5' splice sites followed by U-rich sequences, thereby facilitating atypical 5' splice site recognition by U1 snRNP (PubMed:11106748, PubMed:12486009, PubMed:17488725). Activates splicing of alternative exons with weak 5' splice sites followed by a U-rich stretch on its own pre-mRNA and on TIAR mRNA (By similarity). Acts as a modulator of alternative splicing for the apoptotic FAS receptor, thereby promoting apoptosis (PubMed:11106748, PubMed:17488725, PubMed:1934064). Binds to the 5' splice site region of FAS intron 5 to promote accumulation of transcripts that include exon 6 at the expense of transcripts in which exon 6 is skipped, thereby leading to the transcription of a membrane-bound apoptotic FAS receptor, which promotes apoptosis (PubMed:11106748, PubMed:17488725, PubMed:1934064). Binds to a conserved AU-rich cis element in COL2A1 intron 2 and modulates alternative splicing of COL2A1 exon 2 (PubMed:17580305). Also binds to the equivalent AT-rich element in COL2A1 genomic DNA, and may thereby be involved in the regulation of transcription (PubMed:17580305). Binds specifically to a polypyrimidine-rich controlling element (PCE) located between the weak 5' splice site and the intronic splicing silencer of CFTR mRNA to promote exon 9 inclusion, thereby antagonizing PTB1 and its role in exon skipping of CFTR exon 9 (PubMed:14966131). Involved in the repression of mRNA translation by binding to AU-rich elements (AREs) located in mRNA 3' untranslated regions (3' UTRs), including target ARE-bearing mRNAs encoding TNF and PTGS2 (By similarity). Also participates in the cellular response to environmental stress, by acting downstream of the stress-induced phosphorylation of EIF2S1/EIF2A to promote the recruitment of untranslated mRNAs to cytoplasmic stress granules (SGs), leading to stress-induced translational arrest (PubMed:10613902). Formation and recruitment to SGs is regulated by Zn(2+) (By similarity). Possesses nucleolytic activity against cytotoxic lymphocyte target cells (PubMed:1934064). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P52912, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10613902, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11106748, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12486009, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14966131, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17488725, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17580305, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1934064, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8576255}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform Short]: Displays enhanced splicing regulatory activity compared with TIA isoform Long. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17488725}. |
| Subellular location SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: Nucleus {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10613902, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15371533, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17984221, ECO:0000305|PubMed:18201561}. Cytoplasm {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17488725}. Cytoplasm, Stress granule {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10613902, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15371533, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17984221}. Note=Accumulates in cytoplasmic stress granules (SG) following cellular damage (PubMed:10613902, PubMed:15371533). Recruitment to SG is induced by Zn(2+) (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P52912, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10613902, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15371533}. |
| Tissues TISSUE SPECIFICITY: Expressed in heart, small intestine, kidney, liver, lung, skeletal muscle, testes, pancreas, and ovary (at protein level). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17488725}. |
| Structure SUBUNIT: Homooligomer; homooligomerization is induced by Zn(2+) (By similarity). Interacts with FASTK; the interactions leads to its phosphorylation (PubMed:17135269, PubMed:7544399). Interacts (via RRM1 and the C-terminal glutamine-rich (Q) sequence) with SNRPC/U1-C (via N-terminus); thereby facilitating spliceosomal U1 snRNP recruitment to 5' splice sites (PubMed:12486009). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P52912, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12486009, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17135269, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7544399}. |
| Post-translational modification PTM: Phosphorylated by FASTK; phosphorylation occurs after FAS ligation in FAS-mediated apoptosis and before DNA fragmentation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:7544399}. |
| Domain DOMAIN: The RNA recognition motif domains RRM 2 and RRM 3 are necessary and sufficient for binding to uridine-rich target pre-mRNA. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12486009, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8576255}.; DOMAIN: The RRM 1 and RRM 2 domains are required for the localization to stress granules (SGs) and for the recruitment of TIAR1 and poly(A) RNA to SGs in response to stress. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10613902}.; DOMAIN: The RRM2 domain and the C-terminal residues 287-340 contribute to nuclear localization. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P52912}.; DOMAIN: The RRM3 domain mediates nuclear export. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P52912}.; DOMAIN: The C-terminal glutamine-rich (Q) sequence in combination with the RRM 1 domain is required for the interaction with SNRPC/U1-C and to facilitate recruitment of spliceosomal U1 snRNP to 5' splice sites. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12486009}. |
| Involvement in disease DISEASE: Welander distal myopathy (WDM) [MIM:604454]: An autosomal dominant disorder characterized by adult onset of distal muscle weakness predominantly affecting the distal long extensors of the hands, with slow progression to involve all small hand muscles and the lower legs. Skeletal muscle biopsy shows myopathic changes and prominent rimmed vacuoles. Rare homozygous patients showed earlier onset, faster progression, and proximal muscle involvement. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23348830, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23401021}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis 26, with or without frontotemporal dementia (ALS26) [MIM:619133]: A form of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, a neurodegenerative disorder affecting upper motor neurons in the brain and lower motor neurons in the brain stem and spinal cord, resulting in fatal paralysis. Sensory abnormalities are absent. The pathologic hallmarks of the disease include pallor of the corticospinal tract due to loss of motor neurons, presence of ubiquitin-positive inclusions within surviving motor neurons, and deposition of pathologic aggregates. The etiology of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is likely to be multifactorial, involving both genetic and environmental factors. The disease is inherited in 5-10% of the cases. ALS26 inheritance is autosomal dominant. Some patients may develop frontotemporal dementia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28817800}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: P31483 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
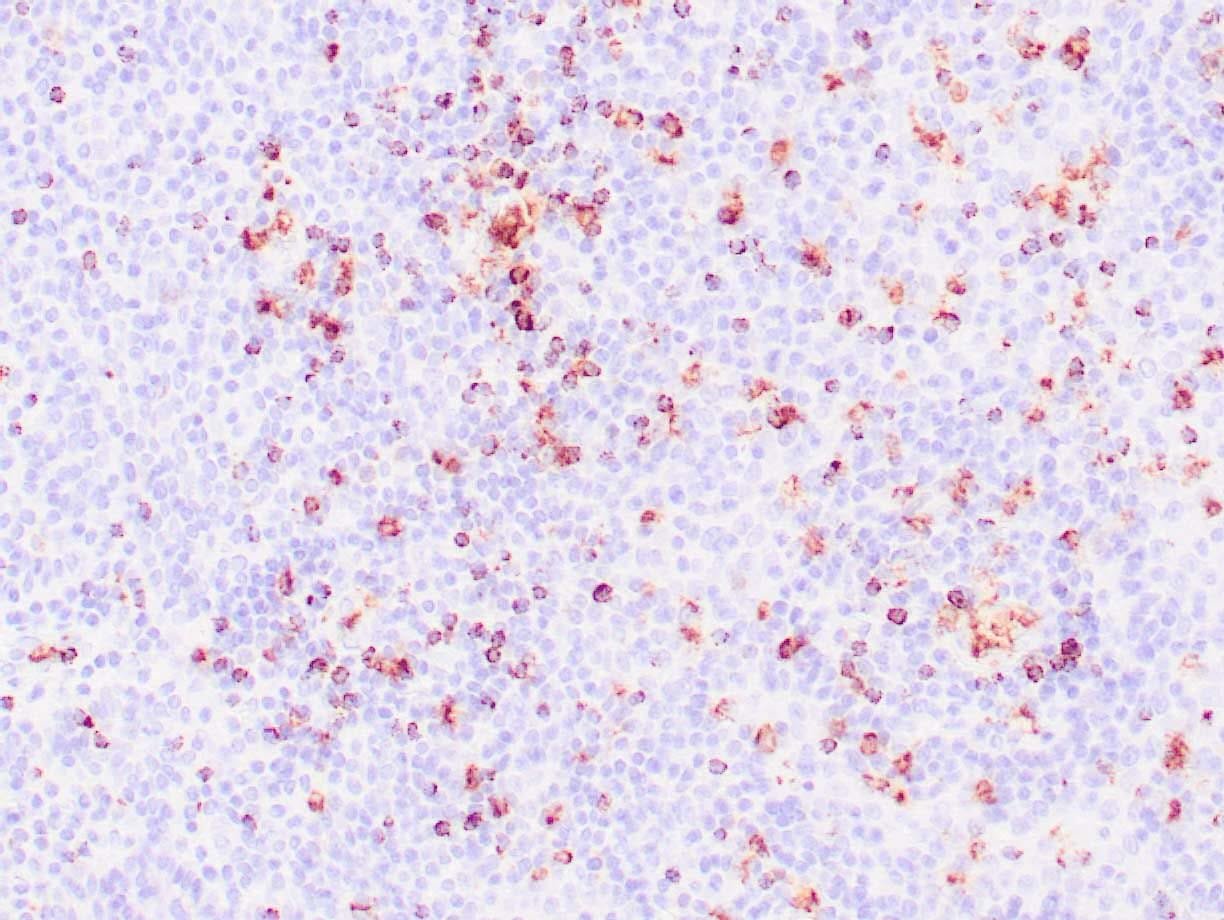 |
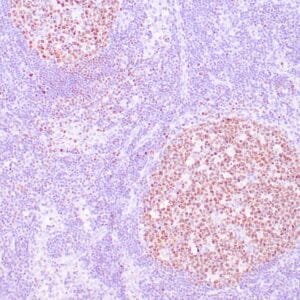
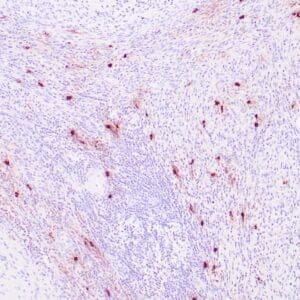
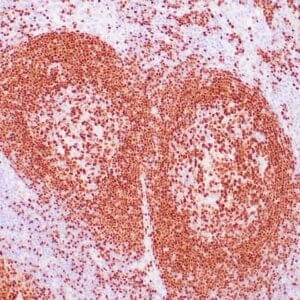
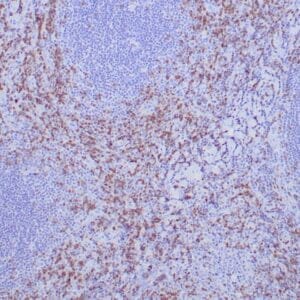
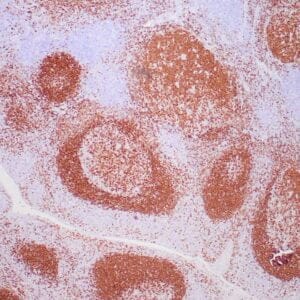
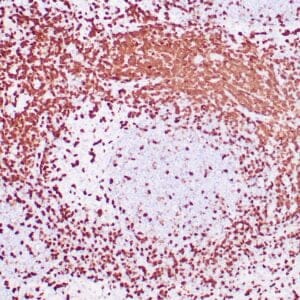
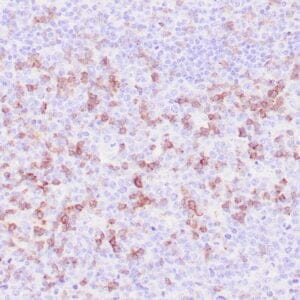
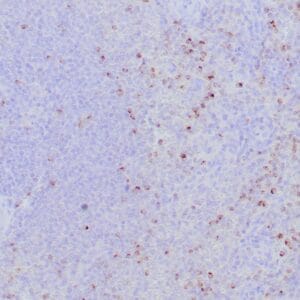
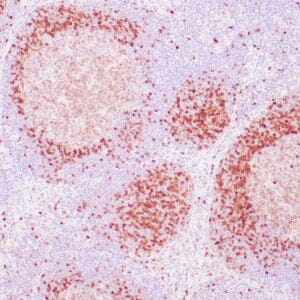
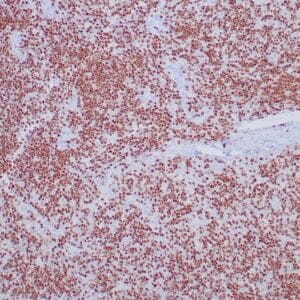
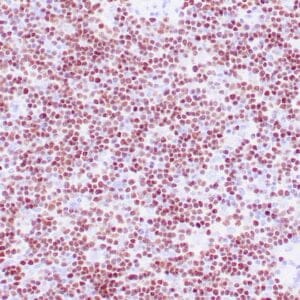
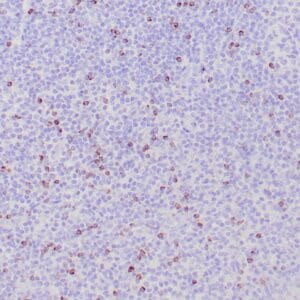
| Human nasal T/NK cell lymphoma stained with anti-TIA-1 antibody using peroxidase-conjugate and DAB chromogen. Note the cytoplasmic granular staining of lymphoma cells. |
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
| IHC |
Documents
| # | SDS | Certificate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | |||
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.
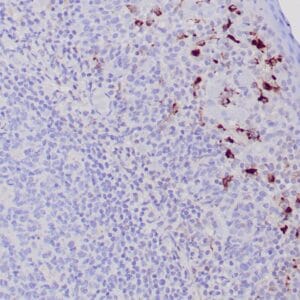
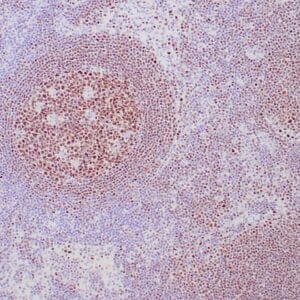
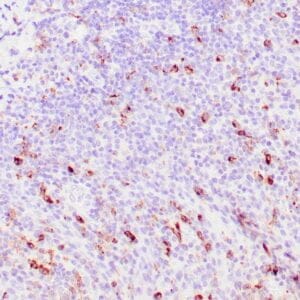
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.