| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| host | mouse |
| isotype | IgG2a/κ |
| clonality | monoclonal |
| concentration | concentrate, predilute |
| applications | IHC |
| reactivity | human |
| available size | 0.1 mL, 0.5 mL, 1 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted |
mouse anti-GLUT-1 monoclonal antibody (ZM137) 6196
Price range: $160.00 through $528.00
Antibody summary
- Mouse monoclonal to GLUT-1
- Suitable for: Immunohistochemistry (formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues)
- Reacts with: Human
- Isotype:IgG2a/κ
- Control: Adenocarcinoma
- Visualization: Cell surface
- 0.1, 0.5, 1.0 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted
mouse anti-GLUT-1 monoclonal antibody ZM137 6196
| target relevance |
|---|
| Protein names Solute carrier family 2, facilitated glucose transporter member 1 (Glucose transporter type 1, erythrocyte/brain) (GLUT-1) (HepG2 glucose transporter) |
| Gene names SLC2A1,SLC2A1 GLUT1 |
| Protein family Major facilitator superfamily, Sugar transporter (TC 2.A.1.1) family, Glucose transporter subfamily |
| Mass 54084Da |
| Function FUNCTION: Facilitative glucose transporter, which is responsible for constitutive or basal glucose uptake (PubMed:10227690, PubMed:10954735, PubMed:18245775, PubMed:19449892, PubMed:25982116, PubMed:27078104, PubMed:32860739). Has a very broad substrate specificity; can transport a wide range of aldoses including both pentoses and hexoses (PubMed:18245775, PubMed:19449892). Most important energy carrier of the brain: present at the blood-brain barrier and assures the energy-independent, facilitative transport of glucose into the brain (PubMed:10227690). In association with BSG and NXNL1, promotes retinal cone survival by increasing glucose uptake into photoreceptors (By similarity). Required for mesendoderm differentiation (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P17809, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P46896, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10227690, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10954735, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18245775, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19449892, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25982116, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27078104, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32860739}. |
| Catalytic activity CATALYTIC ACTIVITY: Reaction=D-glucose(out) = D-glucose(in); Xref=Rhea:RHEA:60376, ChEBI:CHEBI:4167; Evidence={ECO:0000269|PubMed:10227690, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10954735, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25982116, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27078104, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32860739}; |
| Pathway PATHWAY: Carbohydrate degradation. |
| Subellular location SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: Cell membrane {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18245775, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19449892, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23219802, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24847886, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25982116, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30197081}; Multi-pass membrane protein {ECO:0000255}. Melanosome {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17081065}. Photoreceptor inner segment {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P17809}. Note=Localizes primarily at the cell surface (PubMed:18245775, PubMed:19449892, PubMed:23219802, PubMed:24847886, PubMed:25982116). Identified by mass spectrometry in melanosome fractions from stage I to stage IV (PubMed:17081065). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17081065, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18245775, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19449892, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23219802, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24847886, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25982116}. |
| Tissues TISSUE SPECIFICITY: Detected in erythrocytes (at protein level). Expressed at variable levels in many human tissues. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23219802}. |
| Structure SUBUNIT: Interacts with GIPC (via PDZ domain) (By similarity). Found in a complex with ADD2, DMTN and SLC2A1. Interacts (via C-terminus cytoplasmic region) with DMTN isoform 2 (PubMed:18347014). Interacts with SNX27; the interaction is required when endocytosed to prevent degradation in lysosomes and promote recycling to the plasma membrane (PubMed:23563491). Interacts with STOM (PubMed:23219802). Interacts with SGTA (via Gln-rich region) (By similarity). Interacts with isoform 1 of BSG (PubMed:25957687). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P11167, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18347014, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23219802, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23563491, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25957687}. |
| Post-translational modification PTM: Phosphorylation at Ser-226 by PKC promotes glucose uptake by increasing cell membrane localization. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25982116}. |
| Involvement in disease DISEASE: GLUT1 deficiency syndrome 1 (GLUT1DS1) [MIM:606777]: A neurologic disorder showing wide phenotypic variability. The most severe 'classic' phenotype comprises infantile-onset epileptic encephalopathy associated with delayed development, acquired microcephaly, motor incoordination, and spasticity. Onset of seizures, usually characterized by apneic episodes, staring spells, and episodic eye movements, occurs within the first 4 months of life. Other paroxysmal findings include intermittent ataxia, confusion, lethargy, sleep disturbance, and headache. Varying degrees of cognitive impairment can occur, ranging from learning disabilities to severe intellectual disability. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10227690, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10980529, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11136715, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11603379, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12325075, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15622525, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19901175, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20129935, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20221955, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20574033, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24847886, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25982116, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30197081}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: GLUT1 deficiency syndrome 2 (GLUT1DS2) [MIM:612126]: A clinically variable disorder characterized primarily by onset in childhood of paroxysmal exercise-induced dyskinesia. The dyskinesia involves transient abnormal involuntary movements, such as dystonia and choreoathetosis, induced by exercise or exertion, and affecting the exercised limbs. Some patients may also have epilepsy, most commonly childhood absence epilepsy. Mild intellectual disability may also occur. In some patients involuntary exertion-induced dystonic, choreoathetotic, and ballistic movements may be associated with macrocytic hemolytic anemia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:14605501, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18451999, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19630075, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19798636, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20129935, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20574033, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20621801, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20830593, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21204808}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Epilepsy, idiopathic generalized 12 (EIG12) [MIM:614847]: A disorder characterized by recurring generalized seizures in the absence of detectable brain lesions and/or metabolic abnormalities. Generalized seizures arise diffusely and simultaneously from both hemispheres of the brain. Seizure types include juvenile myoclonic seizures, absence seizures, and generalized tonic-clonic seizures. In some EIG12 patients seizures may remit with age. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19798636, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22282645, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23280796, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25982116}. Note=Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Dystonia 9 (DYT9) [MIM:601042]: An autosomal dominant neurologic disorder characterized by childhood onset of paroxysmal choreoathetosis and progressive spastic paraplegia. Most patients show some degree of cognitive impairment. Other variable features may include seizures, migraine headaches, and ataxia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21832227}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Stomatin-deficient cryohydrocytosis with neurologic defects (SDCHCN) [MIM:608885]: A rare form of stomatocytosis characterized by episodic hemolytic anemia, cold-induced red cells cation leak, erratic hyperkalemia, neonatal hyperbilirubinemia, hepatosplenomegaly, cataracts, seizures, intellectual disability, and movement disorder. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21791420, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22492876}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: P11166 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
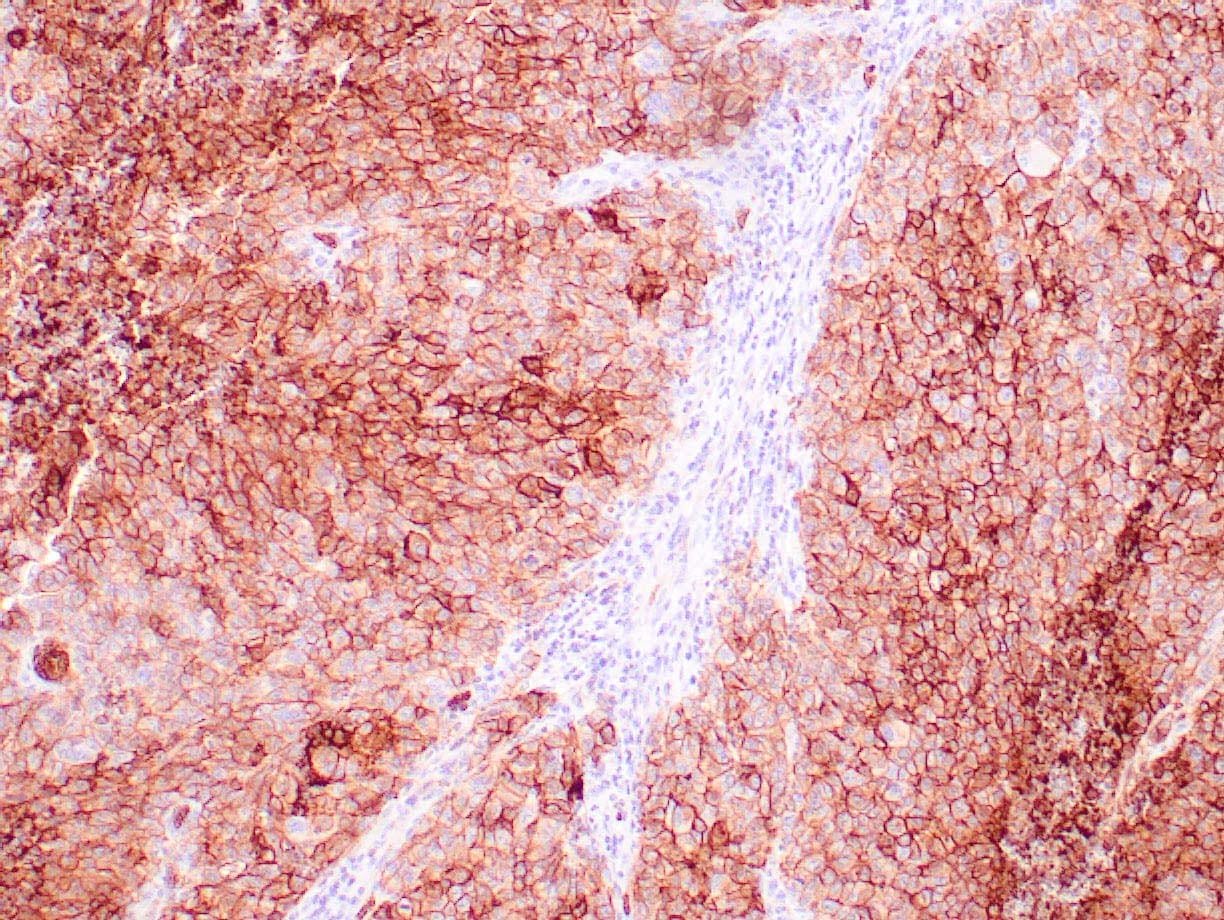 |
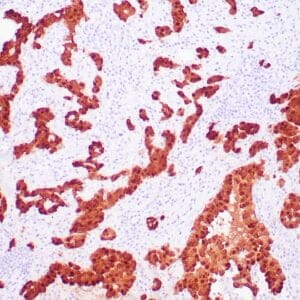
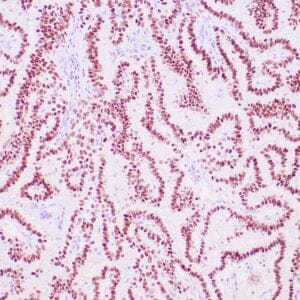
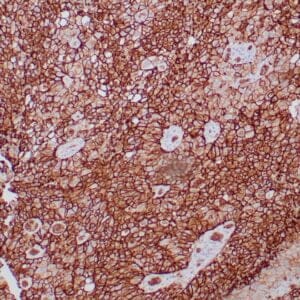
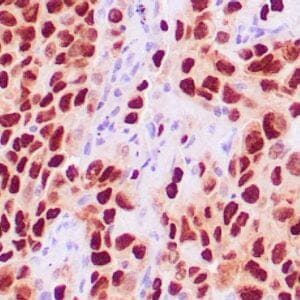
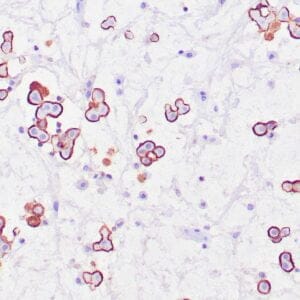
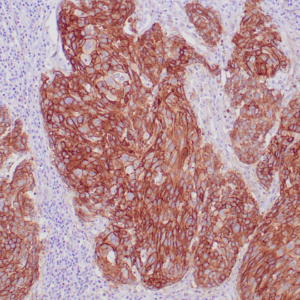
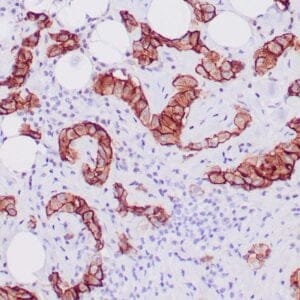
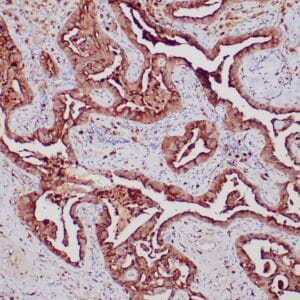
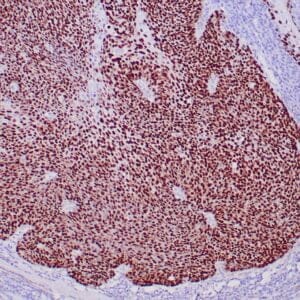
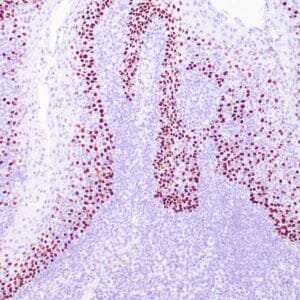
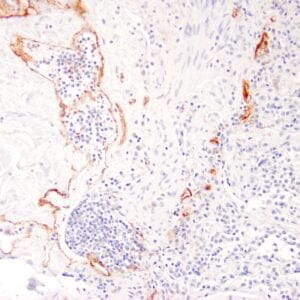
| Human breast carcinoma stained with anti-Glut-1 using peroxidase-conjugate and DAB chromogen. Note membranous staining of tumor cells. |
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
| IHC |
Documents
| # | SDS | Certificate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | |||
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.