| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| host | mouse |
| isotype | IgG2a |
| clonality | monoclonal |
| concentration | concentrate, predilute |
| applications | IHC |
| reactivity | human |
| available size | 0.1 mL, 0.5 mL, 1 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted |
mouse anti-Cyclin D1 monoclonal antibody (ZM178) 6132
Price range: $160.00 through $528.00
Antibody summary
- Mouse monoclonal to Cyclin D1
- Suitable for: Immunohistochemistry (formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues)
- Reacts with: Human
- Isotype:IgG2a
- Control: Mantle cell lymphoma
- Visualization: Nuclear
- 0.1, 0.5, 1.0 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted
mouse anti-Cyclin D1 monoclonal antibody ZM178 6132
| target relevance |
|---|
| Protein names G1/S-specific cyclin-D1 (B-cell lymphoma 1 protein) (BCL-1) (BCL-1 oncogene) (PRAD1 oncogene) |
| Gene names CCND1,CCND1 BCL1 PRAD1 |
| Protein family Cyclin family, Cyclin D subfamily |
| Mass 33729Da |
| Function FUNCTION: Regulatory component of the cyclin D1-CDK4 (DC) complex that phosphorylates and inhibits members of the retinoblastoma (RB) protein family including RB1 and regulates the cell-cycle during G(1)/S transition (PubMed:1827756, PubMed:1833066, PubMed:19412162, PubMed:33854235, PubMed:8114739, PubMed:8302605). Phosphorylation of RB1 allows dissociation of the transcription factor E2F from the RB/E2F complex and the subsequent transcription of E2F target genes which are responsible for the progression through the G(1) phase (PubMed:1827756, PubMed:1833066, PubMed:19412162, PubMed:8114739, PubMed:8302605). Hypophosphorylates RB1 in early G(1) phase (PubMed:1827756, PubMed:1833066, PubMed:19412162, PubMed:8114739, PubMed:8302605). Cyclin D-CDK4 complexes are major integrators of various mitogenenic and antimitogenic signals (PubMed:1827756, PubMed:1833066, PubMed:19412162, PubMed:8302605). Also a substrate for SMAD3, phosphorylating SMAD3 in a cell-cycle-dependent manner and repressing its transcriptional activity (PubMed:15241418). Component of the ternary complex, cyclin D1/CDK4/CDKN1B, required for nuclear translocation and activity of the cyclin D-CDK4 complex (PubMed:9106657). Exhibits transcriptional corepressor activity with INSM1 on the NEUROD1 and INS promoters in a cell cycle-independent manner (PubMed:16569215, PubMed:18417529). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15241418, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16569215, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1827756, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1833066, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18417529, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19412162, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33854235, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8114739, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8302605, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9106657}. |
| Subellular location SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: Nucleus {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20399237, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9106657}. Cytoplasm {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9106657}. Nucleus membrane {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9106657}. Note=Cyclin D-CDK4 complexes accumulate at the nuclear membrane and are then translocated to the nucleus through interaction with KIP/CIP family members. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9106657}. |
| Structure SUBUNIT: Interacts with either CDK4 or CDK6 protein kinase to form a serine/threonine kinase holoenzyme complex (PubMed:19237565, PubMed:8114739). The cyclin subunit imparts substrate specificity to the complex (PubMed:19237565, PubMed:20399237, PubMed:8302605, PubMed:9106657). Component of the ternary complex CCND1/CDK4/CDKN1B required for nuclear translocation and modulation of CDK4-mediated kinase activity (PubMed:9106657). Interacts directly with CDKN1B (By similarity). Can form similar complexes with either CDKN1A or CDKN2A (By similarity). Interacts with FBXO4 (By similarity). Interacts with UHRF2; the interaction ubiquitinates CCND1 and appears to occur independently of phosphorylation (PubMed:21952639). Interacts with USP2 (PubMed:19917254). Interacts (via cyclin N-terminal domain) with INSM1 (via N-terminal region); the interaction competes with the binding of CCND1 to CDK4 during cell cycle progression and inhibits CDK4 activity (PubMed:16569215, PubMed:18417529, PubMed:19124461). Interacts with CDK4; the interaction is prevented with the binding of CCND1 to INSM1 during cell cycle progression (PubMed:19124461). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P25322, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16569215, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18417529, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19124461, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19237565, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19917254, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20399237, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21952639, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8114739, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8302605, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9106657}. |
| Post-translational modification PTM: Phosphorylation at Thr-286 by MAP kinases is required for ubiquitination and degradation by the DCX(AMBRA1) complex (PubMed:10766840, PubMed:33854232, PubMed:33854235, PubMed:33854239). It also plays an essential role for recognition by the FBXO31 component of SCF (SKP1-cullin-F-box) protein ligase complex following DNA damage (PubMed:19412162). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10766840, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19412162, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33854232, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33854235, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33854239}.; PTM: Ubiquitinated at Lys-269 by the DCX(AMBRA1) complex during the transition from G1 to S cell phase, leading to its degradation: ubiquitination is dependent on Thr-286 phosphorylation (PubMed:33854232, PubMed:33854235, PubMed:33854239). The DCX(AMBRA1) complex represents the major regulator of CCND1 stability during the G1/S transition (PubMed:33854232, PubMed:33854235, PubMed:33854239). Also ubiquitinated by a SCF (SKP1-CUL1-F-box protein) ubiquitin-protein ligase complex containing FBXO4 and CRYAB (By similarity). Following DNA damage it is ubiquitinated by some SCF (SKP1-cullin-F-box) protein ligase complex containing FBXO31 (PubMed:19412162). SCF-type ubiquitination is dependent on Thr-286 phosphorylation (PubMed:10766840, PubMed:19412162). Ubiquitinated also by UHRF2 apparently in a phosphorylation-independent manner (PubMed:21952639). Ubiquitination leads to its degradation and G1 arrest. Deubiquitinated by USP2; leading to its stabilization (PubMed:19917254). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P25322, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10766840, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19412162, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19917254, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21952639, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33854232, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33854235, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33854239}. |
| Involvement in disease DISEASE: Note=A chromosomal aberration involving CCND1 may be a cause of B-lymphocytic malignancy, particularly mantle-cell lymphoma (MCL). Translocation t(11;14)(q13;q32) with immunoglobulin gene regions. Activation of CCND1 may be oncogenic by directly altering progression through the cell cycle. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:1826542, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8204893, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8695815}.; DISEASE: Note=A chromosomal aberration involving CCND1 may be a cause of parathyroid adenomas. Translocation t(11;11)(q13;p15) with the parathyroid hormone (PTH) enhancer. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:1826542}.; DISEASE: Multiple myeloma (MM) [MIM:254500]: A malignant tumor of plasma cells usually arising in the bone marrow and characterized by diffuse involvement of the skeletal system, hyperglobulinemia, Bence-Jones proteinuria and anemia. Complications of multiple myeloma are bone pain, hypercalcemia, renal failure and spinal cord compression. The aberrant antibodies that are produced lead to impaired humoral immunity and patients have a high prevalence of infection. Amyloidosis may develop in some patients. Multiple myeloma is part of a spectrum of diseases ranging from monoclonal gammopathy of unknown significance (MGUS) to plasma cell leukemia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:8695815}. Note=The gene represented in this entry is involved in disease pathogenesis. A chromosomal aberration involving CCND1 is found in multiple myeloma. Translocation t(11;14)(q13;q32) with the IgH locus. |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: P24385 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
 |
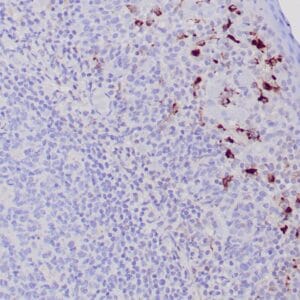
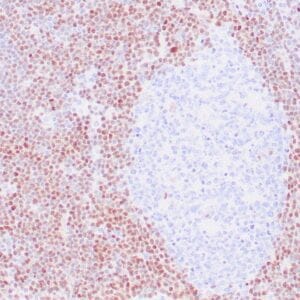
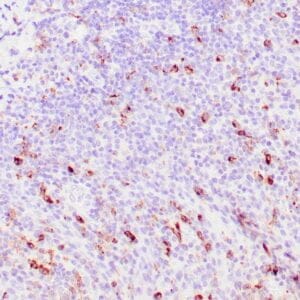
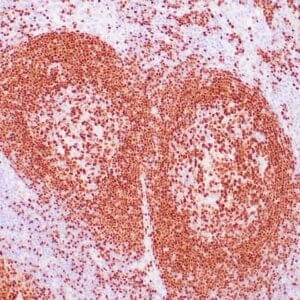
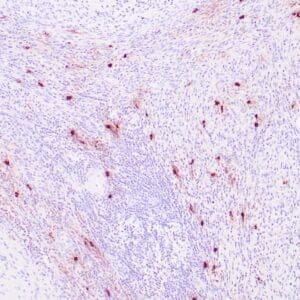
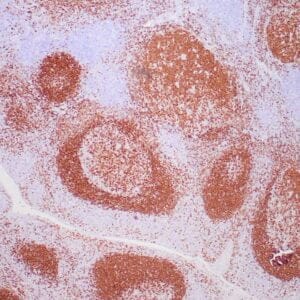
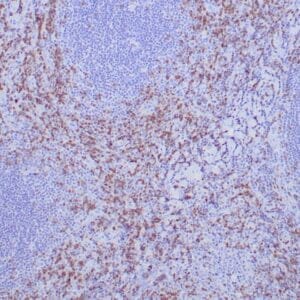
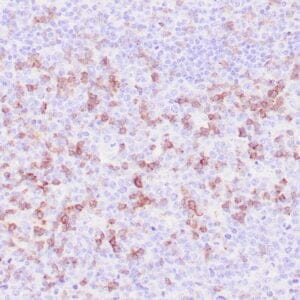
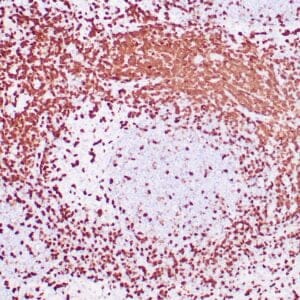
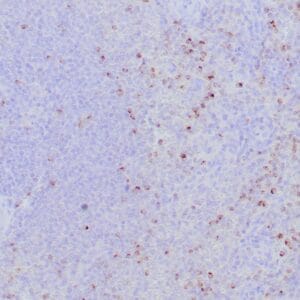
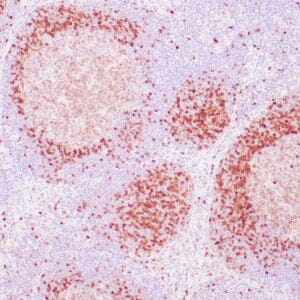
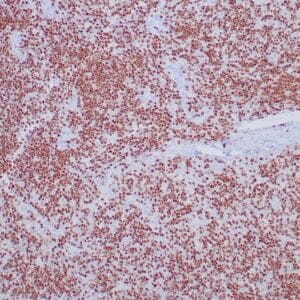
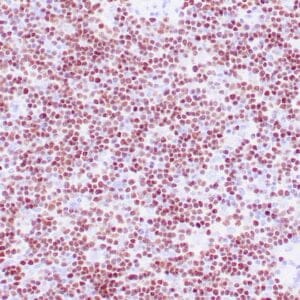
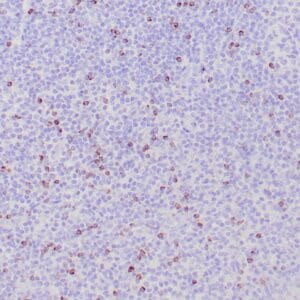
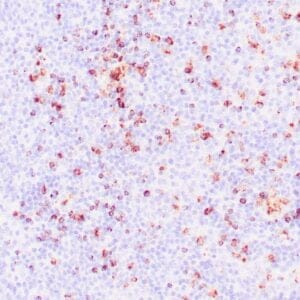
| Human mantle cell lymphoma stained with anti-Cyclin D1 antibody using peroxidase-conjugate and DAB chromogen. Note the nuclear staining of lymphoma cells. |
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
| IHC |
Documents
| # | SDS | Certificate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | |||
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.