| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| host | mouse |
| isotype | IgG1 |
| clonality | monoclonal |
| concentration | concentrate, predilute |
| applications | IHC |
| reactivity | human |
| available size | 0.1 mL, 0.5 mL, 1 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted |
mouse anti-BCL-6 monoclonal antibody (ZM22) 6443
Price range: $160.00 through $528.00
Antibody summary
- Mouse monoclonal to BCL-6
- Suitable for: Immunohistochemistry (formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues)
- Reacts with: Human
- Isotype:IgG1
- Control: Tonsi lor diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- Visualization: Nuclear
- 0.1, 0.5, 1.0 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted
mouse anti-BCL-6 monoclonal antibody ZM22 6443
| target relevance |
|---|
| Protein names B-cell lymphoma 6 protein (BCL-6) (B-cell lymphoma 5 protein) (BCL-5) (Protein LAZ-3) (Zinc finger and BTB domain-containing protein 27) (Zinc finger protein 51) |
| Gene names BCL6,BCL6 BCL5 LAZ3 ZBTB27 ZNF51 |
| Mass 78846Da |
| Function FUNCTION: Transcriptional repressor mainly required for germinal center (GC) formation and antibody affinity maturation which has different mechanisms of action specific to the lineage and biological functions. Forms complexes with different corepressors and histone deacetylases to repress the transcriptional expression of different subsets of target genes. Represses its target genes by binding directly to the DNA sequence 5'-TTCCTAGAA-3' (BCL6-binding site) or indirectly by repressing the transcriptional activity of transcription factors. In GC B-cells, represses genes that function in differentiation, inflammation, apoptosis and cell cycle control, also autoregulates its transcriptional expression and up-regulates, indirectly, the expression of some genes important for GC reactions, such as AICDA, through the repression of microRNAs expression, like miR155. An important function is to allow GC B-cells to proliferate very rapidly in response to T-cell dependent antigens and tolerate the physiological DNA breaks required for immunglobulin class switch recombination and somatic hypermutation without inducing a p53/TP53-dependent apoptotic response. In follicular helper CD4(+) T-cells (T(FH) cells), promotes the expression of T(FH)-related genes but inhibits the differentiation of T(H)1, T(H)2 and T(H)17 cells. Also required for the establishment and maintenance of immunological memory for both T- and B-cells. Suppresses macrophage proliferation through competition with STAT5 for STAT-binding motifs binding on certain target genes, such as CCL2 and CCND2. In response to genotoxic stress, controls cell cycle arrest in GC B-cells in both p53/TP53-dependedent and -independent manners. Besides, also controls neurogenesis through the alteration of the composition of NOTCH-dependent transcriptional complexes at selective NOTCH targets, such as HES5, including the recruitment of the deacetylase SIRT1 and resulting in an epigenetic silencing leading to neuronal differentiation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10981963, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12402037, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12414651, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12504096, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15454082, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15577913, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16142238, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17828269, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18212045, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18280243, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22113614, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23166356, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23911289, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9649500}. |
| Subellular location SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: Nucleus {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12504096, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17828269, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22113614, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23166356}. |
| Tissues TISSUE SPECIFICITY: Expressed in germinal center T- and B-cells and in primary immature dendritic cells. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10981963, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12402037, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15454082, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16142238, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16455075, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17828269, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18212045, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9649500}. |
| Structure SUBUNIT: Homodimer. Interacts (via BTB domain) with the corepressors BCOR, NCOR1 and SMRT/NCOR2; the interactions are direct. Forms preferably ternary complexes with BCOR and SMRT/NCOR2 on target gene promoters but, on enhancer elements, interacts with SMRT/NCOR2 and HDAC3 to repress proximal gene expression. Interacts with histone deacetylases HDAC2, HDAC5 and HDAC9 (via the catalytic domain). Interacts with ZBTB7 and BCL6B. Interacts with SCF(FBXO11) complex; the interaction is independent of phosphorylation and promotes ubiquitination. Interacts (when phosphorylated) with PIN1; the interaction is required for BCL6 degradation upon genotoxic stress. Interacts with ZBTB17; inhibits ZBTB17 transcriptional activity. Interacts with CTBP1, autoinhibits its transcriptional expression. Interacts with NOTCH1 NCID and SIRT1; leads to a epigenetic repression of selective NOTCH1-target genes. Interacts (nor via BTB domain neither acetylated) with the NuRD complex components CHD4, HDAC1, MBD3 and MTA3; the interaction with MTA3 inhibits BCL6 acetylation and is required for BCL6 transpriptional repression. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12402037, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12504096, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12590135, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14690607, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15454082, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16142238, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17828269, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18212045, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18280243, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20385364, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22113614, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23911289}. |
| Post-translational modification PTM: Phosphorylated by MAPK1 in response to antigen receptor activation at Ser-333 and Ser-343. Phosphorylated by ATM in response to genotoxic stress. Phosphorylation induces its degradation by ubiquitin/proteasome pathway. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17828269, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22113614, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9649500}.; PTM: Polyubiquitinated (PubMed:22113614, PubMed:30190310, PubMed:9649500). Polyubiquitinated by SCF(FBXO11), leading to its degradation by the proteasome (PubMed:22113614). Ubiquitinated by the SCF(FBXL17) complex, leading to its degradation by the proteasome: ubiquitination by the SCF(FBXL17) complex takes place when aberrant BTB domain dimers are formed (PubMed:30190310). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22113614, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30190310, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9649500}.; PTM: Acetylated at Lys-379 by EP300 which inhibits the interaction with NuRD complex and the transcriptional repressor function. Deacetylated by HDAC- and SIR2-dependent pathways. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12402037, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15454082}. |
| Domain DOMAIN: The BTB domain mediates homodimerization. Its dimer interface mediates peptide binding such as to corepressors BCOR and NCOR2 (PubMed:18212045). Interaction with corepressors through the BTB domain is needed to facilitate the rapid proliferation and survival of GC B-cells but is not involved in the T(FH) formation and BCL6-mediated suppression of T(H)2 and T(H)17 differentiationrequired for GC formation (By similarity). {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18212045}. |
| Involvement in disease DISEASE: Note=Chromosomal aberrations involving BCL6 are a cause of B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas (B-cell NHL), including diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and follicular lymphoma. Approximately 40% of diffuse large B-cell lymphomas and 5 to 10% of follicular lymphomas are associated with chromosomal translocations that deregulate expression of BCL6 by juxtaposing heterologous promoters to the BCL6 coding domain (PubMed:10469447, PubMed:10753856, PubMed:11821949, PubMed:12414651). Translocation t(3;14)(q27;q32). Translocation t(3;22)(q27;q11) with immunoglobulin gene regions (PubMed:11821949). Translocation t(3;7)(q27;p12) with IKZF1 gene 5'non-coding region (PubMed:10753856). Translocation t(3;6)(q27;p21) with Histone H4 (PubMed:12414651). Translocation t(3;16)(q27;p11) with IL21R. Translocation t(3;13)(q27;q14) with LCP1 (PubMed:10469447). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10469447, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10753856, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11821949, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12414651}.; DISEASE: Note=A chromosomal aberration involving BCL6 may be a cause of a form of B-cell leukemia. Translocation t(3;11)(q27;q23) with POU2AF1/OBF1.; DISEASE: Note=A chromosomal aberration involving BCL6 may be a cause of lymphoma. Translocation t(3;4)(q27;p11) with ARHH/TTF. |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: P41182 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
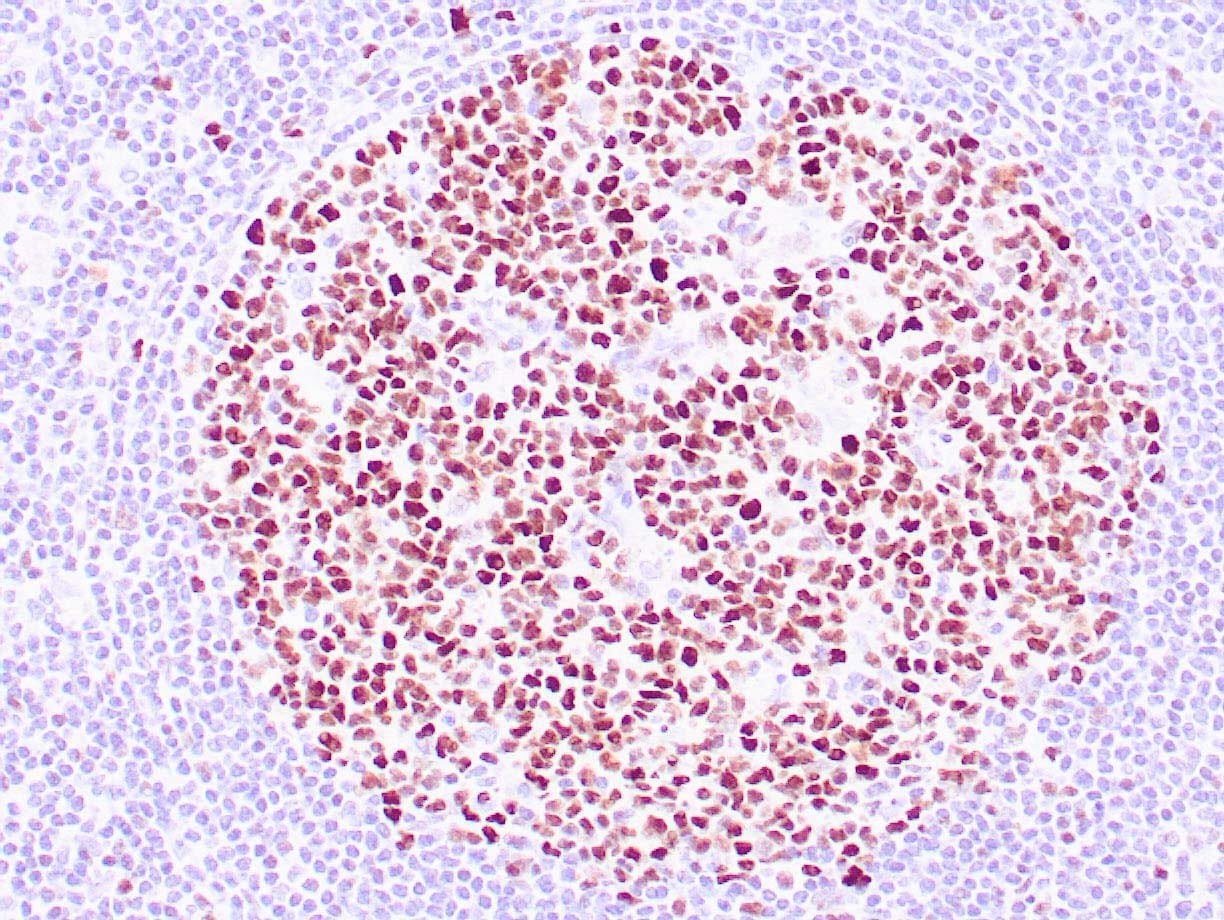 |
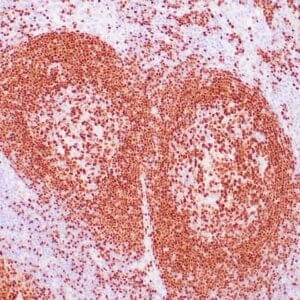
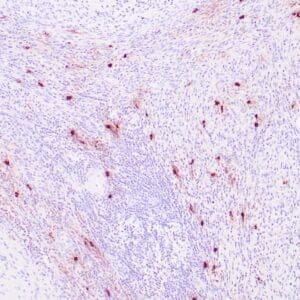
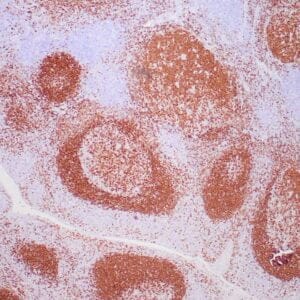
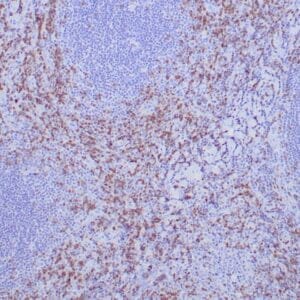
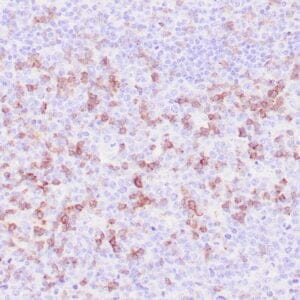
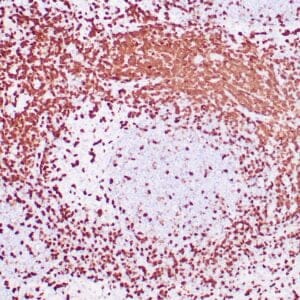
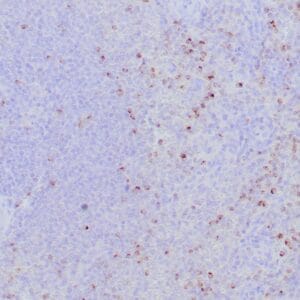
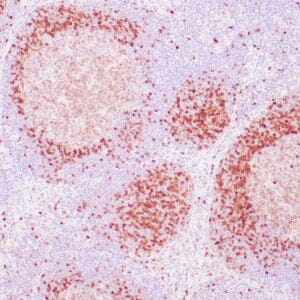
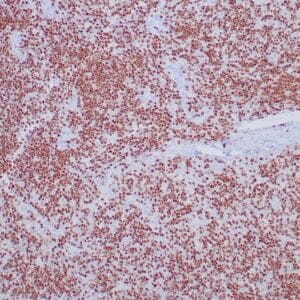
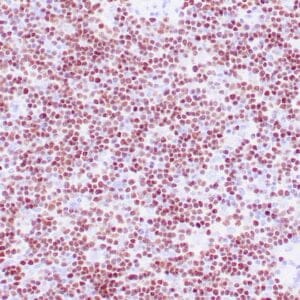
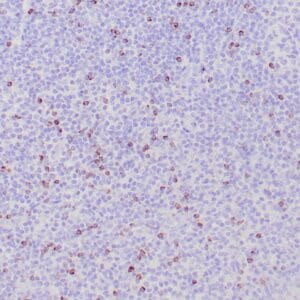
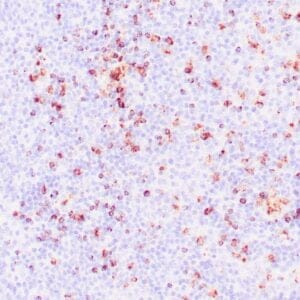
| Human reactive lymph node stained with anti-BCL-6 antibody using peroxidase-conjugate and DAB chromogen. Note nuclear staining of follicular center B-cells. |
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
| IHC |
Documents
| # | SDS | Certificate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | |||
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.
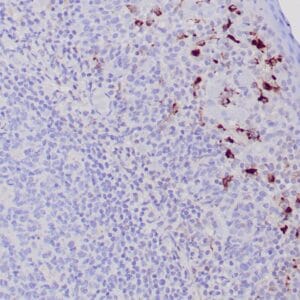
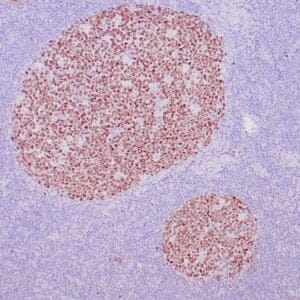
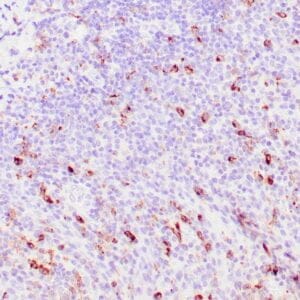
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.