| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| host | rabbit |
| isotype | IgG |
| clonality | monoclonal |
| concentration | 1 mg/mL |
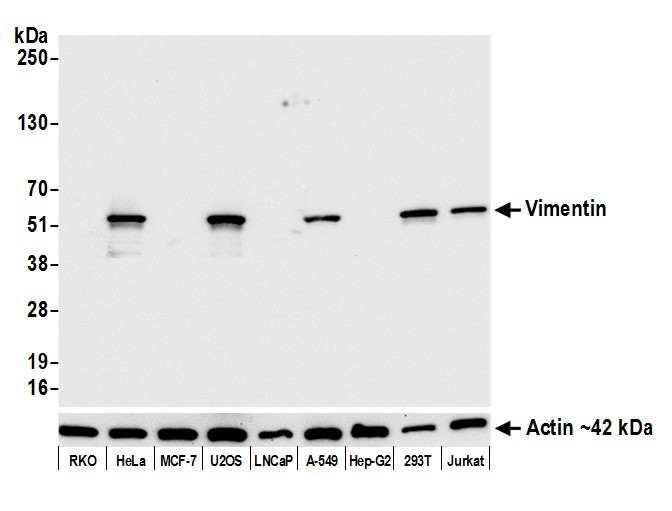
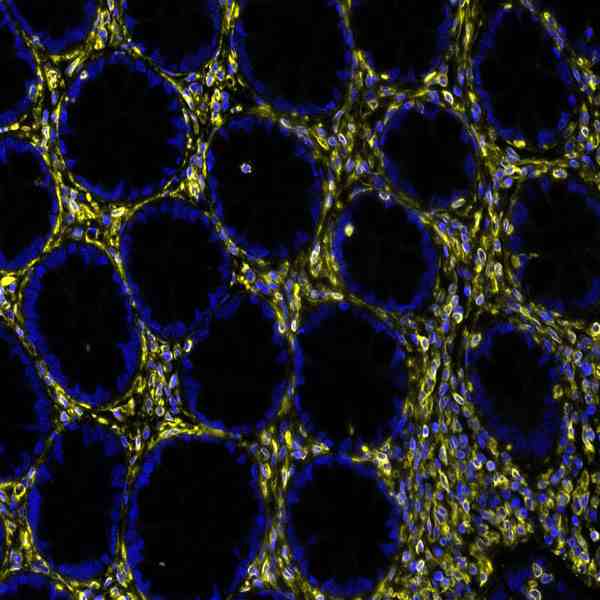
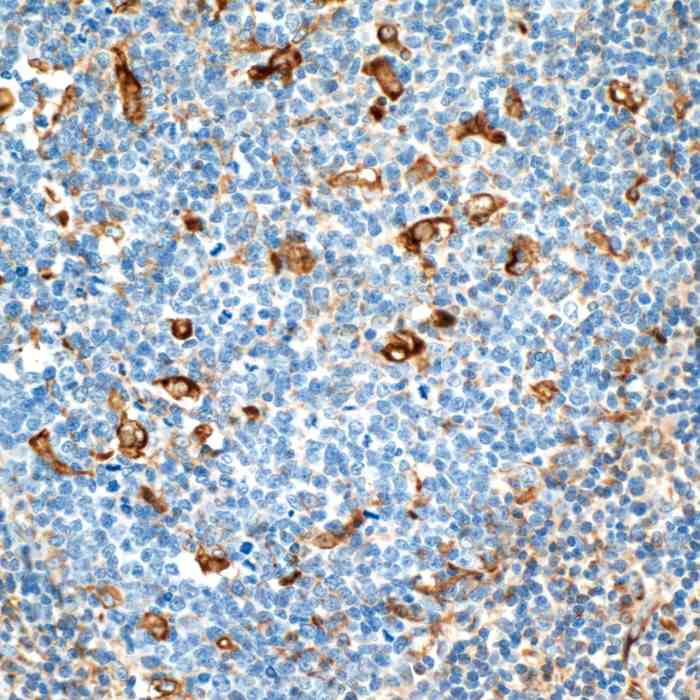
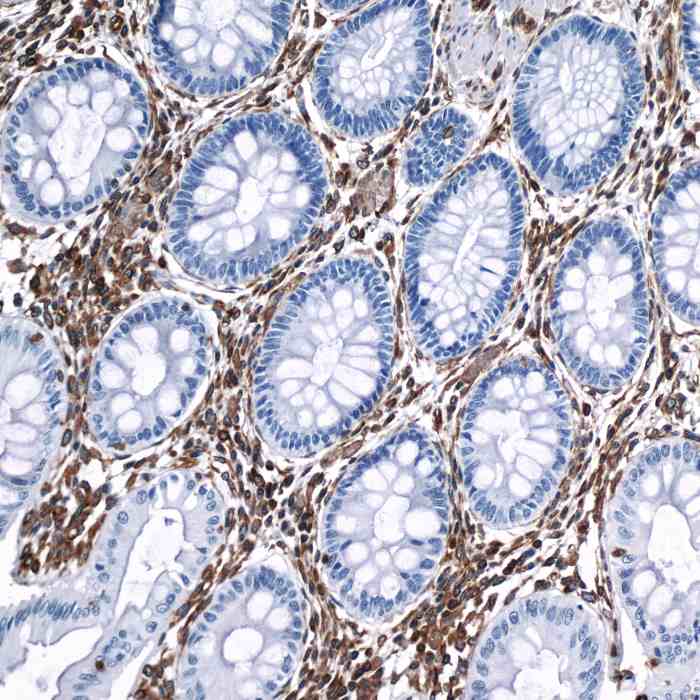
| applications | ICC/IF, IHC, WB |
| available sizes | 100 µg |
rabbit anti-Vimentin monoclonal antibody (BLR100G) 9046
$409.00
Antibody summary
- Rabbit monoclonal to Vimentin
- Suitable for: WB, ICC/IF, IHC
- Reacts with: human, mouse, rat
- Isotype: IgG
- 100 µg
rabbit anti-Vimentin monoclonal antibody (BLR100G) 9046
| target relevance |
|---|
| Vimentin, a key protein constituent of the intermediate filament cytoskeleton, plays a pivotal role in maintaining cellular integrity and structure. In research, vimentin has become a valuable biomarker due to its tissue-specific expression and involvement in various cellular processes. Immunohistochemical analysis of vimentin has been extensively utilized to identify and characterize mesenchymal cells, such as fibroblasts, endothelial cells, and immune cells, aiding in the study of tissue development, wound healing, and cancer progression. Additionally, vimentin has been linked to epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), a critical process implicated in embryonic development and metastasis. Furthermore, efforts to develop vimentin-targeting therapies for cancer treatment have shown promise, as vimentin's involvement in EMT and tumor progression make it a potential therapeutic target for limiting cancer metastasis. Click for more on: cell markers and Vimentin |
| Protein names Vimentin |
| Gene names VIM,VIM |
| Protein family Intermediate filament family |
| Mass 53652Da |
| Function FUNCTION: Vimentins are class-III intermediate filaments found in various non-epithelial cells, especially mesenchymal cells. Vimentin is attached to the nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, and mitochondria, either laterally or terminally. Plays a role in cell directional movement, orientation, cell sheet organization and Golgi complex polarization at the cell migration front (By similarity). Protects SCRIB from proteasomal degradation and facilitates its localization to intermediate filaments in a cell contact-mediated manner (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:A0A8C0N8E3, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P31000}.; FUNCTION: Involved with LARP6 in the stabilization of type I collagen mRNAs for CO1A1 and CO1A2. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21746880}. |
| Subellular location SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: Cytoplasm {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19386766, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21465480, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29496907}. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18408015, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29496907}. Nucleus matrix {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P31000}. Cell membrane {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P20152}. |
| Tissues TISSUE SPECIFICITY: Highly expressed in fibroblasts, some expression in T- and B-lymphocytes, and little or no expression in Burkitt's lymphoma cell lines. Expressed in many hormone-independent mammary carcinoma cell lines. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:2472876, ECO:0000269|PubMed:3371665}. |
| Structure SUBUNIT: Homomer assembled from elementary dimers (PubMed:20176112). Identified in complexes that contain VIM, EZR, AHNAK, BFSP1, BFSP2, ANK2, PLEC, PRX and spectrin (By similarity). Interacts with BCAS3 (PubMed:17505058). Interacts with LGSN (By similarity). Interacts with SYNM (By similarity). Interacts (via rod region) with PLEC (via CH 1 domain) (By similarity). Interacts with PLEC isoform 1C (PubMed:24940650). Interacts with STK33 (PubMed:18811945). Interacts with LARP6 (PubMed:21746880). Interacts with RAB8B (By similarity). Interacts with TOR1A; the interaction associates TOR1A with the cytoskeleton (PubMed:16361107, PubMed:18827015). Interacts with TOR1AIP1 (PubMed:16361107). Interacts with DIAPH1 (PubMed:23325789). Interacts with EPPK1; interaction is dependent of higher-order structure of intermediate filament (PubMed:16923132). Interacts with the non-receptor tyrosine kinase SRMS; the interaction leads to phosphorylation of VIM (PubMed:29496907). Interacts with NOD2 (PubMed:27812135). Interacts (via head region) with CORO1C (By similarity). Interacts with HDGF (isoform 2) (PubMed:26845719). Interacts with PRKCE (via phorbol-ester/DAG-type 2 domain) (PubMed:18408015). Interacts with BFSP2 (By similarity). Interacts with PPL (By similarity). Interacts (via rod domain) with PKP1 (PubMed:10852826). Interacts with PKP2 (PubMed:10852826). Interacts with SCRIB (via PDZ domains); the interaction protects SCRIB from proteasomal degradation and facilitates SCRIB localization to intermediate filaments, the interaction is reduced by cell contact inhibition (PubMed:19386766). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P20152, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P31000, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10852826, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16361107, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16923132, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17505058, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18408015, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18811945, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18827015, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19386766, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20176112, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21746880, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23325789, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24940650, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26845719, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27812135, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29496907}.; SUBUNIT: (Microbial infection) Interacts with HCV core protein. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15846844}.; SUBUNIT: (Microbial infection) Interacts with Chandipura virus glycoprotein; this interaction might facilitate the binding of the virus to the cells. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:32418904}. |
| Post-translational modification PTM: Filament disassembly during mitosis is promoted by phosphorylation at Ser-55 as well as by nestin (By similarity). One of the most prominent phosphoproteins in various cells of mesenchymal origin. Phosphorylation is enhanced during cell division, at which time vimentin filaments are significantly reorganized. Phosphorylation by PKN1 inhibits the formation of filaments. Phosphorylated at Ser-56 by CDK5 during neutrophil secretion in the cytoplasm (PubMed:21465480). Phosphorylated by STK33 (PubMed:18811945). Phosphorylated on tyrosine residues by SRMS (PubMed:29496907). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P31000, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18811945, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21465480, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29496907, ECO:0000269|Ref.14}.; PTM: O-glycosylated during cytokinesis at sites identical or close to phosphorylation sites, this interferes with the phosphorylation status. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20068230}.; PTM: S-nitrosylation is induced by interferon-gamma and oxidatively-modified low-densitity lipoprotein (LDL(ox)) possibly implicating the iNOS-S100A8/9 transnitrosylase complex. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:25417112}. |
| Domain DOMAIN: The central alpha-helical coiled-coil IF rod domain mediates elementary homodimerization. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20176112}.; DOMAIN: The [IL]-x-C-x-x-[DE] motif is a proposed target motif for cysteine S-nitrosylation mediated by the iNOS-S100A8/A9 transnitrosylase complex. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:25417112}. |
| Involvement in disease DISEASE: Cataract 30, multiple types (CTRCT30) [MIM:116300]: An opacification of the crystalline lens of the eye that frequently results in visual impairment or blindness. Opacities vary in morphology, are often confined to a portion of the lens, and may be static or progressive. In general, the more posteriorly located and dense an opacity, the greater the impact on visual function. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19126778, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26694549, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28450710}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: P08670 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
| Western blot IHC ICC |
Documents
| # | SDS | Certificate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | |||
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.
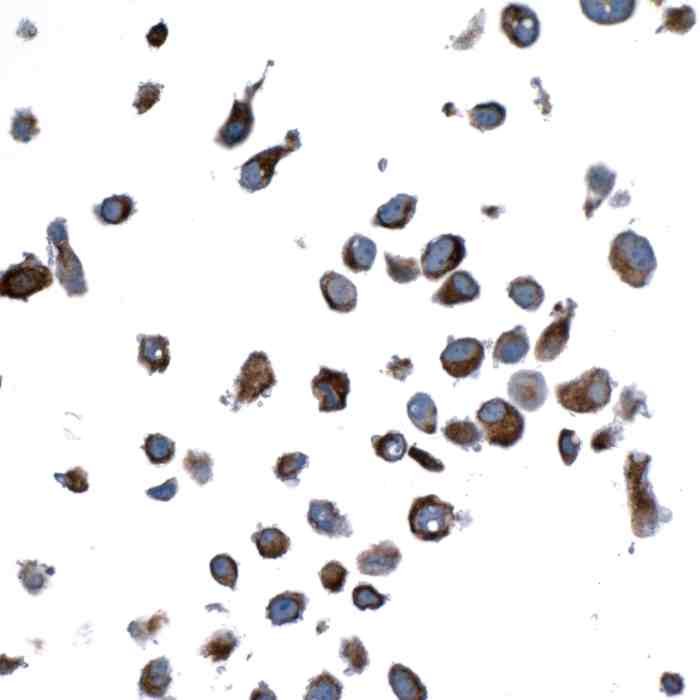



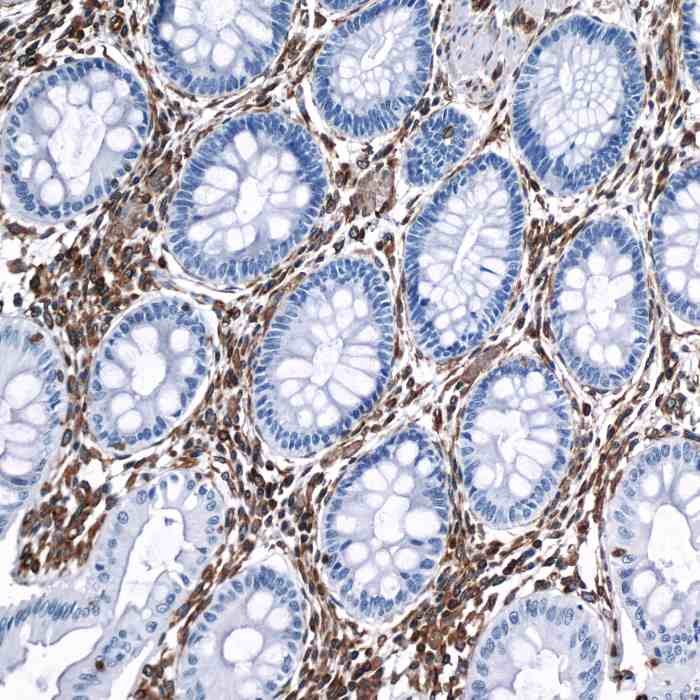

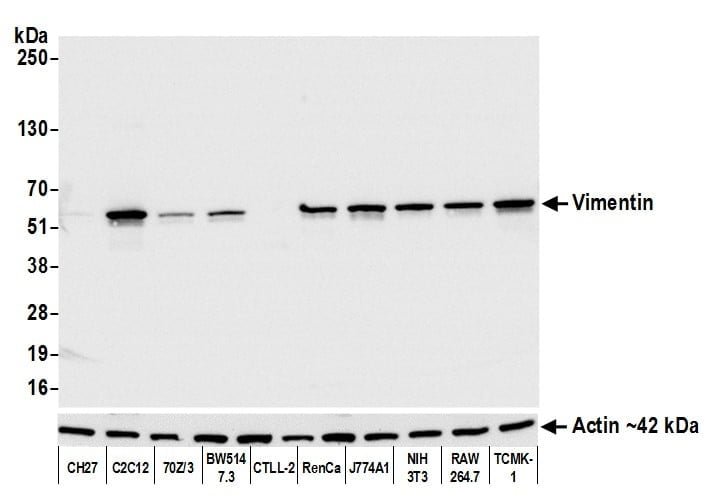
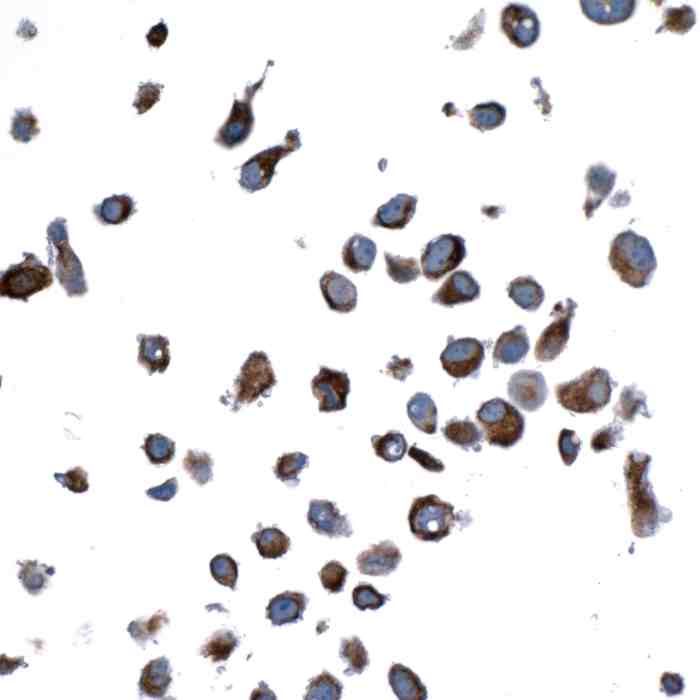
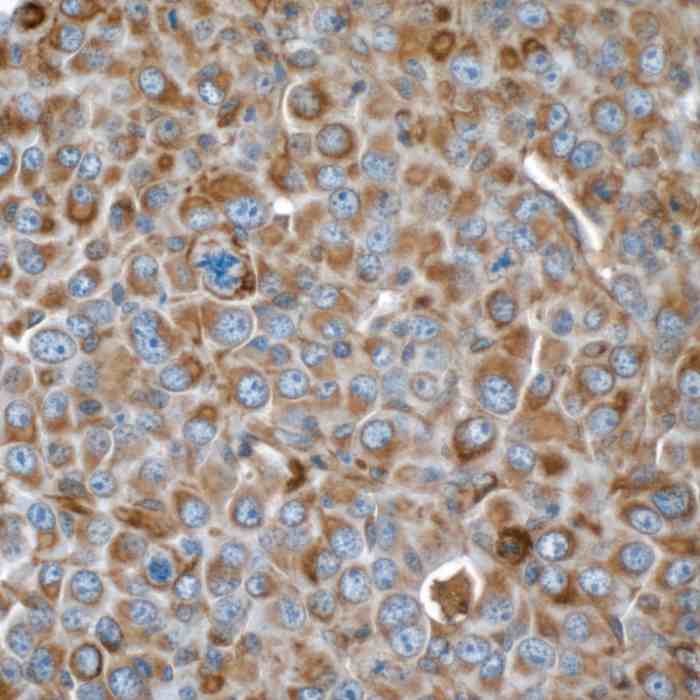
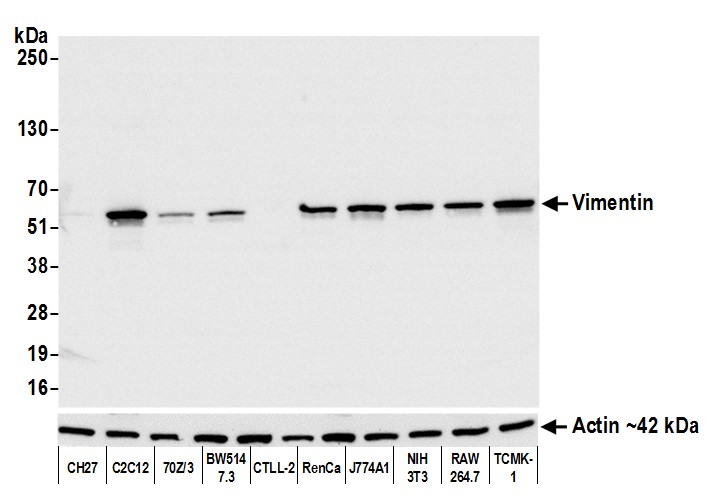
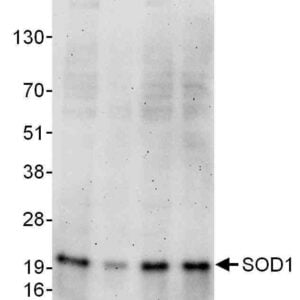
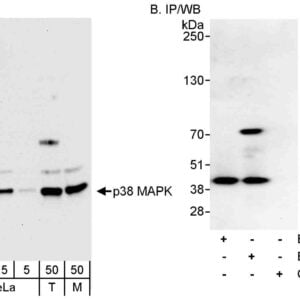
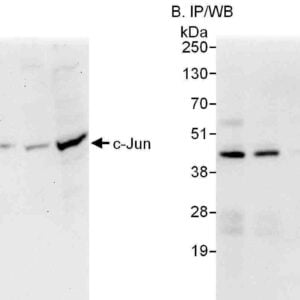
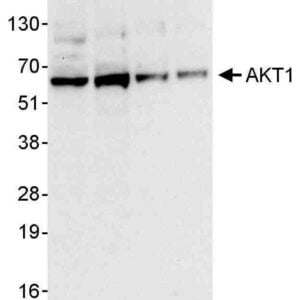
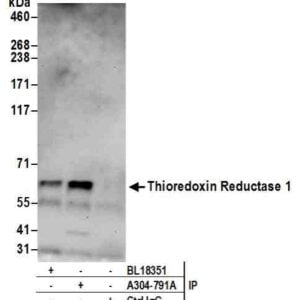
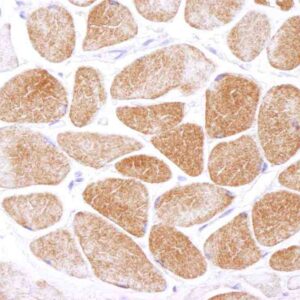
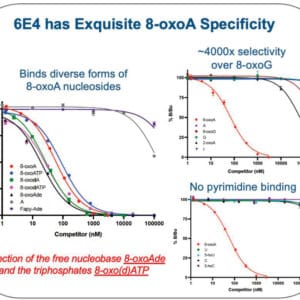


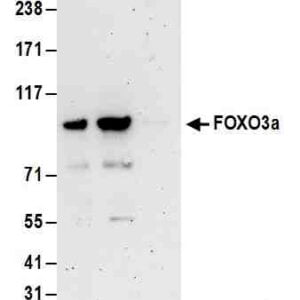
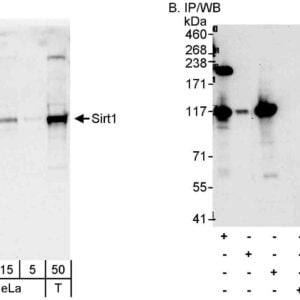
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.