| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| host | mouse |
| isotype | IgG |
| clonality | monoclonal |
| concentration | concentrate, predilute |
| applications | IHC |
| reactivity | human |
| available size | 0.1 mL, 0.5 mL, 1 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted |
rabbit anti-VEGF monoclonal antibody (ZR389) 6401
Price range: $160.00 through $528.00
Antibody summary
- Rabbit monoclonal to VEGF
- Suitable for: Immunohistochemistry (formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues)
- Reacts with: Human
- Isotype:IgG
- Control: Tumor cells in astrocytomas, breast or ovarian carcinomas
- Visualization: Cytoplasm, cell surface
- 0.1, 0.5, 1.0 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted
rabbit anti-VEGF monoclonal antibody ZR389 6401
| antibody |
|---|
| Database link: human P15692 |
| Tested applications IHC |
| Recommended dilutions Concentrated 1:100-200 |
| Application Notes Positive control: Tumor cells in astrocytomas, breast or ovarian carcinomas |
| Immunogen Recombinant fragment (around aa1-200) of human VEGFA protein (exact sequence is proprietary) |
| Size and concentration 7 mL prediluted or 0.1, 0.5, 1.0 mL and concentrated |
| Form liquid |
| Storage Instructions 2-8°C for short term, for longer term at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. |
| Purity affinity purified |
| Clonality monoclonal |
| Isotype IgG |
| Compatible secondaries goat anti-rabbit IgG, H&L chain specific, peroxidase conjugated, conjugated polyclonal antibody 9512 goat anti-rabbit IgG, H&L chain specific, biotin conjugated polyclonal antibody 2079 goat anti-rabbit IgG, H&L chain specific, FITC conjugated polyclonal antibody 7863 goat anti-rabbit IgG, H&L chain specific, Cross Absorbed polyclonal antibody 2371 goat anti-rabbit IgG, H&L chain specific, biotin conjugated polyclonal antibody, crossabsorbed 1715 goat anti-rabbit IgG, H&L chain specific, FITC conjugated polyclonal antibody, crossabsorbed 1720 |
| Isotype control Rabbit polyclonal - Isotype Control |
| target relevance |
|---|
| Protein names Vascular endothelial growth factor A, long form (L-VEGF) (Vascular permeability factor) (VPF) [Cleaved into: N-VEGF; VEGFA] |
| Gene names VEGFA,VEGFA VEGF |
| Protein family PDGF/VEGF growth factor family |
| Mass 43597Da |
| Function FUNCTION: [N-VEGF]: Participates in the induction of key genes involved in the response to hypoxia and in the induction of angiogenesis such as HIF1A (PubMed:35455969). Involved in protecting cells from hypoxia-mediated cell death (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q00731, ECO:0000269|PubMed:35455969}.; FUNCTION: [VEGFA]: Growth factor active in angiogenesis, vasculogenesis and endothelial cell growth (PubMed:34530889). Induces endothelial cell proliferation, promotes cell migration, inhibits apoptosis and induces permeabilization of blood vessels. Binds to the FLT1/VEGFR1 and KDR/VEGFR2 receptors, heparan sulfate and heparin. Binds to the NRP1/neuropilin-1 receptor. Binding to NRP1 initiates a signaling pathway needed for motor neuron axon guidance and cell body migration, including for the caudal migration of facial motor neurons from rhombomere 4 to rhombomere 6 during embryonic development (By similarity). Also binds the DEAR/FBXW7-AS1 receptor (PubMed:17446437). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q00731, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11427521, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16489009, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17446437, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25825981, ECO:0000269|PubMed:34530889}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform VEGF165B]: Binds to the KDR receptor but does not activate downstream signaling pathways, does not activate angiogenesis and inhibits tumor growth. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15520188}. |
| Subellular location SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: [N-VEGF]: Cytoplasm {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15896327}. Nucleus {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15896327, ECO:0000269|PubMed:35455969}. Note=Cytoplasmic in normoxic conditions and localizes to the nucleus under hypoxic conditions. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15896327, ECO:0000269|PubMed:35455969}.; SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: [VEGFA]: Secreted {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11563986, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11731620, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15896327}.; SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: [Isoform L-VEGF189]: Endoplasmic reticulum {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11731620}. Golgi apparatus {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11731620}. Secreted, extracellular space, extracellular matrix {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11563986}.; SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: [Isoform VEGF121]: Secreted {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15896327}.; SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: [Isoform VEGF165]: Secreted {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15896327}.; SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: [Isoform VEGF189]: Secreted. Note=Cell-associated after secretion and is bound avidly by heparin and the extracellular matrix, although it may be released as a soluble form by heparin, heparinase or plasmin. |
| Tissues TISSUE SPECIFICITY: Higher expression in pituitary tumors than the pituitary gland. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22009797}.; TISSUE SPECIFICITY: [Isoform VEGF189]: Widely expressed.; TISSUE SPECIFICITY: [Isoform VEGF165]: Widely expressed.; TISSUE SPECIFICITY: [Isoform VEGF121]: Widely expressed.; TISSUE SPECIFICITY: [Isoform VEGF206]: Not widely expressed.; TISSUE SPECIFICITY: [Isoform VEGF145]: Not widely expressed. |
| Structure SUBUNIT: [VEGFA]: Homodimer; disulfide-linked (By similarity). Also found as heterodimer with PGF (By similarity). Interacts with NRP1 (PubMed:26503042). Interacts with isoform 2 of BSG (PubMed:25825981). Interacts with CD82; this interaction inhibits VEGFA-mediated signaling pathway (PubMed:34530889). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P16612, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25825981, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26503042, ECO:0000269|PubMed:34530889}. |
| Post-translational modification PTM: [Vascular endothelial growth factor A, long form]: Produced by use of an alternative upstream CUG codon and post-translationally processed into the N-terminal N-VEGF form and the C-terminal secreted VEGFA form. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11731620}. |
| Involvement in disease DISEASE: Microvascular complications of diabetes 1 (MVCD1) [MIM:603933]: Pathological conditions that develop in numerous tissues and organs as a consequence of diabetes mellitus. They include diabetic retinopathy, diabetic nephropathy leading to end-stage renal disease, and diabetic neuropathy. Diabetic retinopathy remains the major cause of new-onset blindness among diabetic adults. It is characterized by vascular permeability and increased tissue ischemia and angiogenesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11978667}. Note=Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: P15692 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
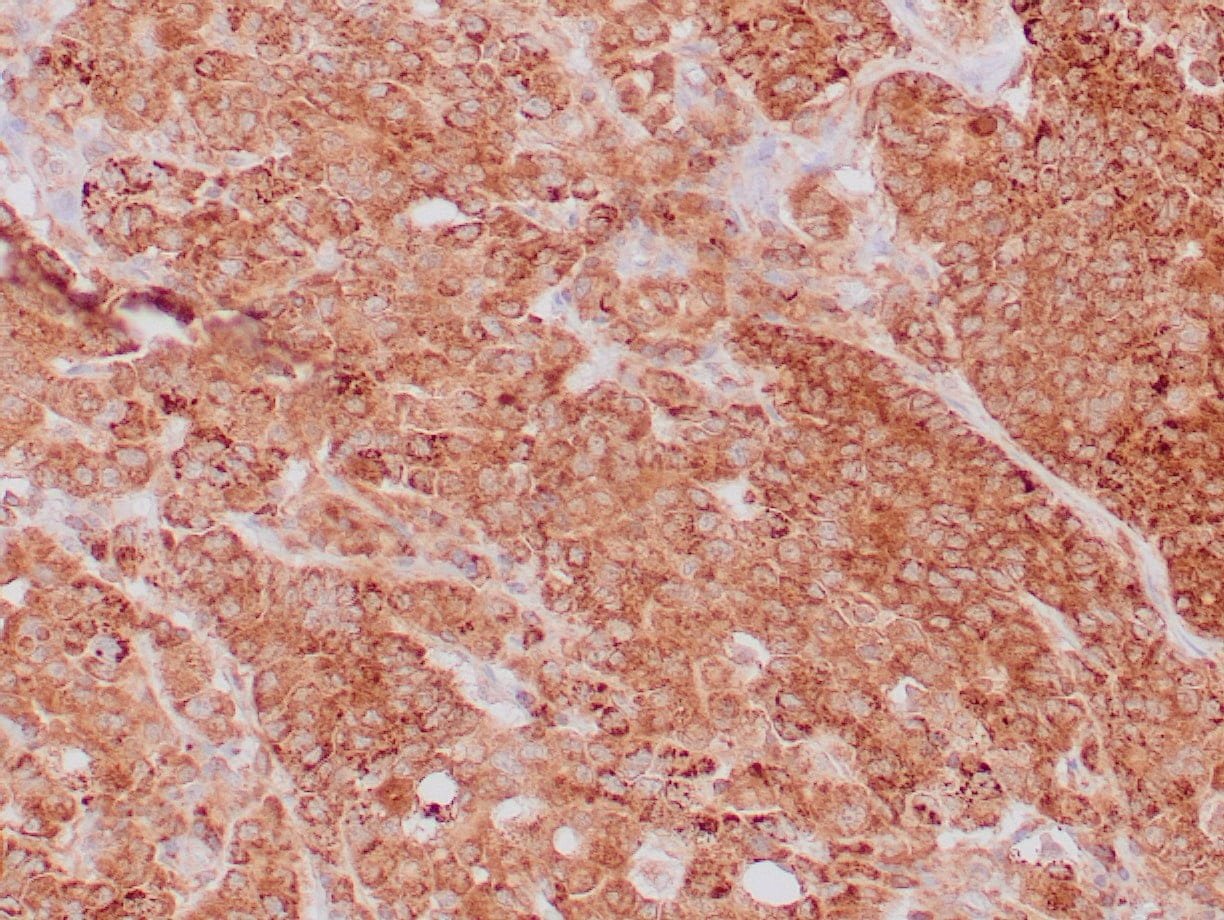 |
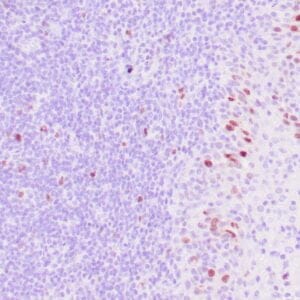
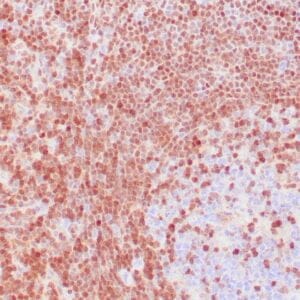
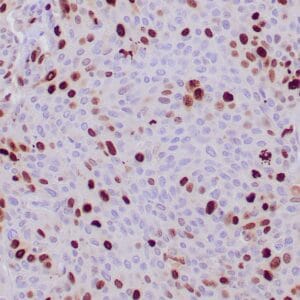
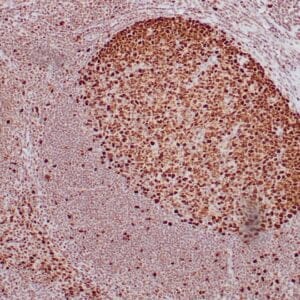
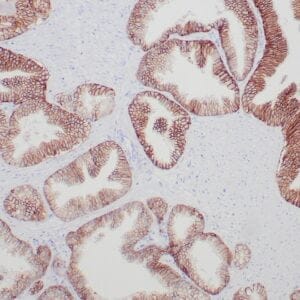
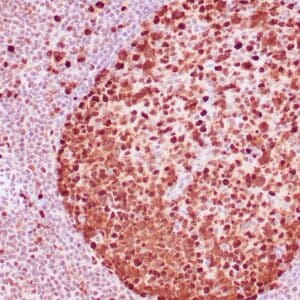
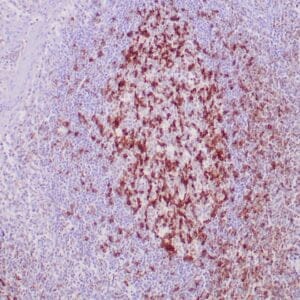
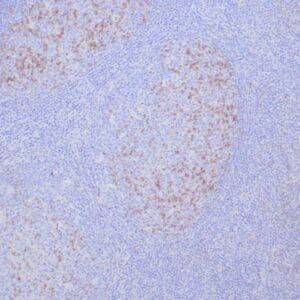
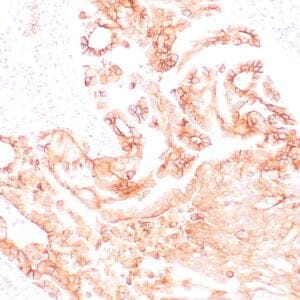
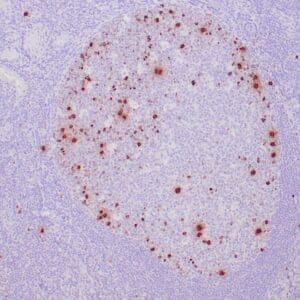
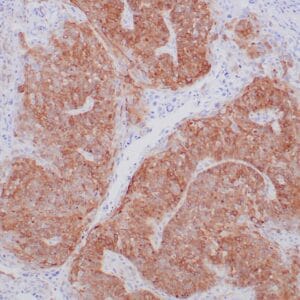
| Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human breast carcinoma stained with anti-VEGF antibody using peroxidase-conjugate and DAB chromogen. Note the cell surface and cytoplasmic staining of tumor cells |
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
| IHC |
Documents
| # | SDS | Certificate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | |||
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.