| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| host | mouse |
| isotype | IgG |
| clonality | monoclonal |
| concentration | concentrate, predilute |
| applications | IHC |
| reactivity | human |
| available size | 0.1 mL, 0.5 mL, 1 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted |
rabbit anti-PGP9.5 monoclonal antibody (ZR401) 6331
Price range: $160.00 through $528.00
Antibody summary
- Rabbit monoclonal to PGP9.5
- Suitable for: Immunohistochemistry (formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues)
- Reacts with: Human
- Isotype:IgG
- Control: Nerve tissue, small intestine wall (Cajal cells)
- Visualization: Cytoplasmic
- 0.1, 0.5, 1.0 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted
rabbit anti-PGP9.5 monoclonal antibody ZR401 6331
| target relevance |
|---|
| Protein names Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase isozyme L1 (UCH-L1) (EC 3.4.19.12) (Neuron cytoplasmic protein 9.5) (PGP 9.5) (PGP9.5) (Ubiquitin thioesterase L1) |
| Gene names UCHL1,UCHL1 |
| Protein family Peptidase C12 family |
| Mass 24824Da |
| Function FUNCTION: Deubiquitinase that plays a role in the regulation of several processes such as maintenance of synaptic function, cardiac function, inflammatory response or osteoclastogenesis (PubMed:22212137, PubMed:23359680). Abrogates the ubiquitination of multiple proteins including WWTR1/TAZ, EGFR, HIF1A and beta-site amyloid precursor protein cleaving enzyme 1/BACE1 (PubMed:22212137, PubMed:25615526). In addition, recognizes and hydrolyzes a peptide bond at the C-terminal glycine of ubiquitin to maintain a stable pool of monoubiquitin that is a key requirement for the ubiquitin-proteasome and the autophagy-lysosome pathways (PubMed:12408865, PubMed:8639624, PubMed:9774100). Regulates amyloid precursor protein/APP processing by promoting BACE1 degradation resulting in decreased amyloid beta production (PubMed:22212137). Plays a role in the immune response by regulating the ability of MHC I molecules to reach cross-presentation compartments competent for generating Ag-MHC I complexes (By similarity). Mediates the 'Lys-48'-linked deubiquitination of the transcriptional coactivator WWTR1/TAZ leading to its stabilization and inhibition of osteoclastogenesis (By similarity). Deubiquitinates and stabilizes epidermal growth factor receptor EGFR to prevent its degradation and to activate its downstream mediators (By similarity). Modulates oxidative activity in skeletal muscle by regulating key mitochondrial oxidative proteins (By similarity). Enhances the activity of hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha/HIF1A by abrogateing its VHL E3 ligase-mediated ubiquitination and consequently inhibiting its degradation (PubMed:25615526). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9R0P9, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12408865, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22212137, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23359680, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25615526, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8639624, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9774100}. |
| Catalytic activity CATALYTIC ACTIVITY: Reaction=Thiol-dependent hydrolysis of ester, thioester, amide, peptide and isopeptide bonds formed by the C-terminal Gly of ubiquitin (a 76-residue protein attached to proteins as an intracellular targeting signal).; EC=3.4.19.12; Evidence={ECO:0000269|PubMed:12408865, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12705903, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16475834, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20439756, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23359680, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25615526, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8639624, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9774100}; |
| Subellular location SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: Cytoplasm {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19261853}. Endoplasmic reticulum membrane {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19261853}; Lipid-anchor {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19261853}. Note=About 30% of total UCHL1 is associated with membranes in brain. Localizes near and/or within mitochondria to potentially interact with mitochondrial proteins. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9R0P9}. |
| Tissues TISSUE SPECIFICITY: Found in neuronal cell bodies and processes throughout the neocortex (at protein level). Expressed in neurons and cells of the diffuse neuroendocrine system and their tumors. Weakly expressed in ovary. Down-regulated in brains from Parkinson disease and Alzheimer disease patients. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:14722078, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9790970}. |
| Structure SUBUNIT: Monomer. Homodimer. Interacts with SNCA (By similarity). Interacts with COPS5. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12082530, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16537382, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20439756}. |
| Post-translational modification PTM: O-glycosylated. {ECO:0000250}. |
| Involvement in disease DISEASE: Parkinson disease 5 (PARK5) [MIM:613643]: A complex neurodegenerative disorder with manifestations ranging from typical Parkinson disease to dementia with Lewy bodies. Clinical features include parkinsonian symptoms (resting tremor, rigidity, postural instability and bradykinesia), dementia, diffuse Lewy body pathology, autonomic dysfunction, hallucinations and paranoia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12408865, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12705903, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9774100}. Note=Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Spastic paraplegia 79A, autosomal dominant, with ataxia (SPG79A) [MIM:620221]: A form of spastic paraplegia, a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by a slow, gradual, progressive weakness and spasticity of the lower limbs. Rate of progression and the severity of symptoms are quite variable. Initial symptoms may include difficulty with balance, weakness and stiffness in the legs, muscle spasms, and dragging the toes when walking. In some forms of the disorder, bladder symptoms (such as incontinence) may appear, or the weakness and stiffness may spread to other parts of the body. SPG79A is a slowly progressive form characterized by late-onset spastic ataxia, neuropathy, and often optic atrophy. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:35986737}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Spastic paraplegia 79B, autosomal recessive (SPG79B) [MIM:615491]: A form of spastic paraplegia, a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by a slow, gradual, progressive weakness and spasticity of the lower limbs. Rate of progression and the severity of symptoms are quite variable. Initial symptoms may include difficulty with balance, weakness and stiffness in the legs, muscle spasms, and dragging the toes when walking. In some forms of the disorder, bladder symptoms (such as incontinence) may appear, or the weakness and stiffness may spread to other parts of the body. SPG79B is characterized by childhood onset blindness, cerebellar ataxia, nystagmus, dorsal column dysfunction, and spasticity with upper motor neuron dysfunction. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23359680, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28007905}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: P09936 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
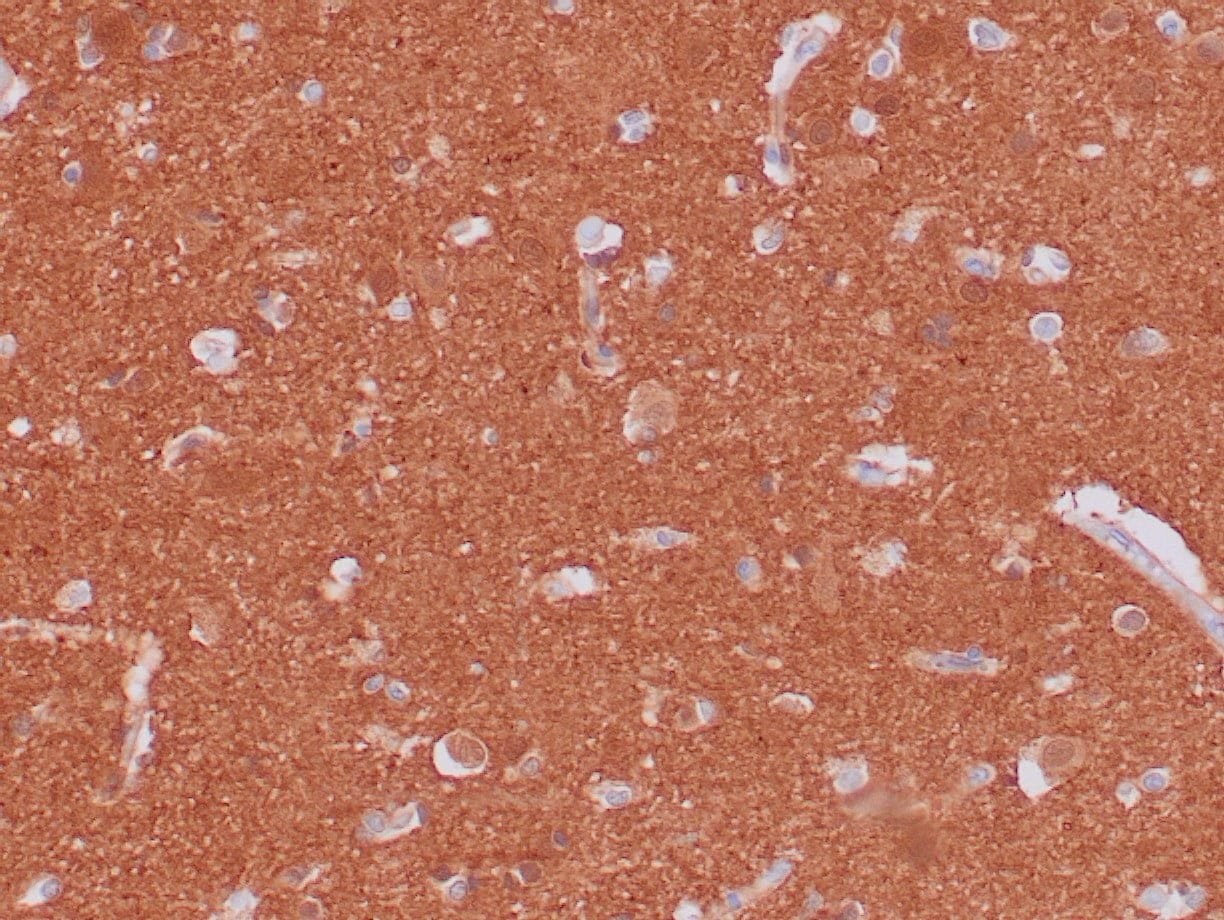 |
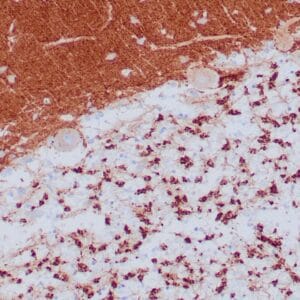
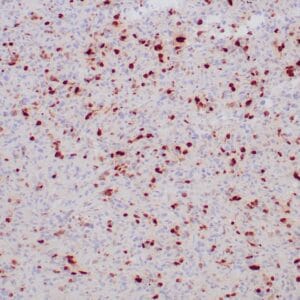
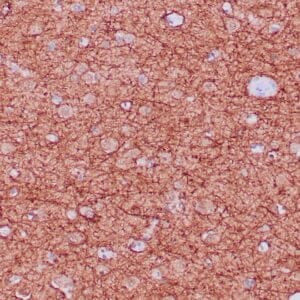
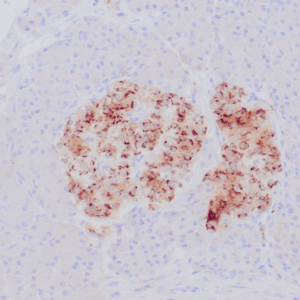
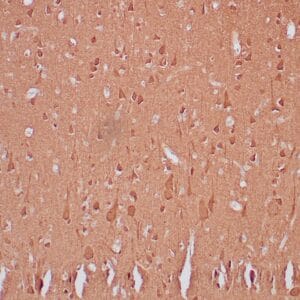
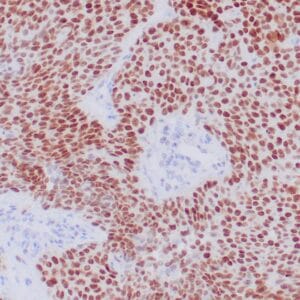
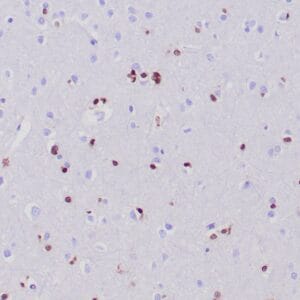
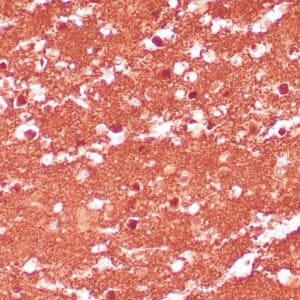
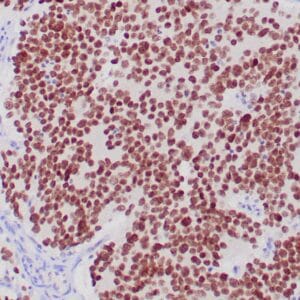
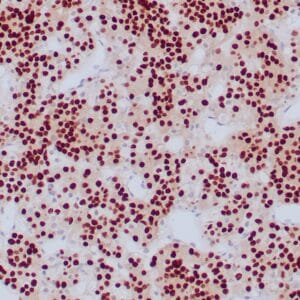
| Formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded human brain stained with anti-PGP 9.5 antibody using peroxidase-conjugate and DAB chromogen. Note the cytoplasmic staining of glial cells |
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
| IHC |
Documents
| # | SDS | Certificate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | |||
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.