| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| host | mouse |
| isotype | IgG |
| clonality | monoclonal |
| concentration | concentrate, predilute |
| applications | IHC |
| reactivity | human |
| available size | 0.1 mL, 0.5 mL, 1 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted |
rabbit anti-PD-L1 monoclonal antibody (ZR3) 6328
Price range: $160.00 through $528.00
Antibody summary
- Rabbit monoclonal to PD-L1
- Suitable for: Immunohistochemistry (formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues)
- Reacts with: Human
- Isotype:IgG
- Control: Placenta or lung adenocarcinoma
- Visualization: Membrane
- 0.1, 0.5, 1.0 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted
rabbit anti-PD-L1 monoclonal antibody ZR3 6328
| target relevance |
|---|
| Protein names Programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 (PD-L1) (PDCD1 ligand 1) (Programmed death ligand 1) (hPD-L1) (B7 homolog 1) (B7-H1) (CD antigen CD274) |
| Gene names CD274,CD274 B7H1 PDCD1L1 PDCD1LG1 PDL1 |
| Protein family Immunoglobulin superfamily, BTN/MOG family |
| Mass 33275Da |
| Function FUNCTION: Plays a critical role in induction and maintenance of immune tolerance to self (PubMed:11015443, PubMed:28813410, PubMed:28813417, PubMed:31399419). As a ligand for the inhibitory receptor PDCD1/PD-1, modulates the activation threshold of T-cells and limits T-cell effector response (PubMed:11015443, PubMed:28813410, PubMed:28813417, PubMed:36727298). Through a yet unknown activating receptor, may costimulate T-cell subsets that predominantly produce interleukin-10 (IL10) (PubMed:10581077). Can also act as a transcription coactivator: in response to hypoxia, translocates into the nucleus via its interaction with phosphorylated STAT3 and promotes transcription of GSDMC, leading to pyroptosis (PubMed:32929201). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10581077, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11015443, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28813410, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28813417, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31399419, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32929201, ECO:0000269|PubMed:36727298}.; FUNCTION: The PDCD1-mediated inhibitory pathway is exploited by tumors to attenuate anti-tumor immunity and escape destruction by the immune system, thereby facilitating tumor survival (PubMed:28813410, PubMed:28813417). The interaction with PDCD1/PD-1 inhibits cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) effector function (By similarity). The blockage of the PDCD1-mediated pathway results in the reversal of the exhausted T-cell phenotype and the normalization of the anti-tumor response, providing a rationale for cancer immunotherapy (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9EP73, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28813410, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28813417}. |
| Subellular location SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: Cell membrane {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28813410, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28813417, ECO:0000269|PubMed:36232715}; Single-pass type I membrane protein {ECO:0000255}. Early endosome membrane {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28813417}; Single-pass type I membrane protein {ECO:0000255}. Recycling endosome membrane {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28813417}; Single-pass type I membrane protein {ECO:0000255}. Nucleus {ECO:0000269|PubMed:32929201}. Note=Associates with CMTM6 at recycling endosomes, where it is protected from being targeted for lysosomal degradation (PubMed:28813417). Translocates to the nucleus in response to hypoxia via its interaction with phosphorylated STAT3 (PubMed:32929201). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28813417, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32929201}.; SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: [Isoform 1]: Cell membrane {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15780196}; Single-pass type I membrane protein {ECO:0000255}.; SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: [Isoform 2]: Endomembrane system {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15780196}; Single-pass type I membrane protein {ECO:0000255}.; SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: [Isoform 4]: Secreted {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30564891}. |
| Tissues TISSUE SPECIFICITY: Highly expressed in the heart, skeletal muscle, placenta and lung. Weakly expressed in the thymus, spleen, kidney and liver. Expressed on activated T- and B-cells, dendritic cells, keratinocytes and monocytes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10581077, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11015443}.; TISSUE SPECIFICITY: [Isoform 4]: Widely expressed, highest in lung, liver and pituitary and in various peripheral blood cells, including neutrophils and some subtypes of lymphoid and myeloid cells. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30564891}. |
| Structure SUBUNIT: Interacts with PDCD1 (PubMed:11015443, PubMed:18287011, PubMed:26602187). Interacts (via transmembrane domain) with CMTM4 and CMTM6 (PubMed:28813410, PubMed:28813417). Interacts with (phosphorylated) STAT3; promoting nuclear translocation (PubMed:32929201). Interacts with CD80 (PubMed:36727298). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11015443, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18287011, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26602187, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28813410, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28813417, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32929201, ECO:0000269|PubMed:36727298}.; SUBUNIT: [Isoform 4]: May form homomultimers. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30564891}. |
| Post-translational modification PTM: Ubiquitinated; STUB1 likely mediates polyubiquitination of PD-L1/CD274 triggering its degradation (PubMed:28813410). Ubiquitinated by MARCHF8; leading to degradation (PubMed:34183449). Deubiquitinated by USP22; leading to stabilization (PubMed:31399419). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28813410, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31399419, ECO:0000269|PubMed:34183449}. |
| Involvement in disease DISEASE: Note=Truncation of the 3'-untranslated (3'-UTR) region of CD274 transcripts leads to elevated expression of CD274 in multiple cancers including T-cell leukemia, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and stomach adenocarcinoma (PubMed:27281199). Disruption of 3'-UTR region is caused by structural variants that stabilize CD274 transcripts, leading to overexpression (PubMed:27281199). Increased expression in tumors promotes immune evasion and tumor cell growth by allowing malignant cells to escape destruction by the immune system (PubMed:27281199). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27281199}. |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: Q9NZQ7 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
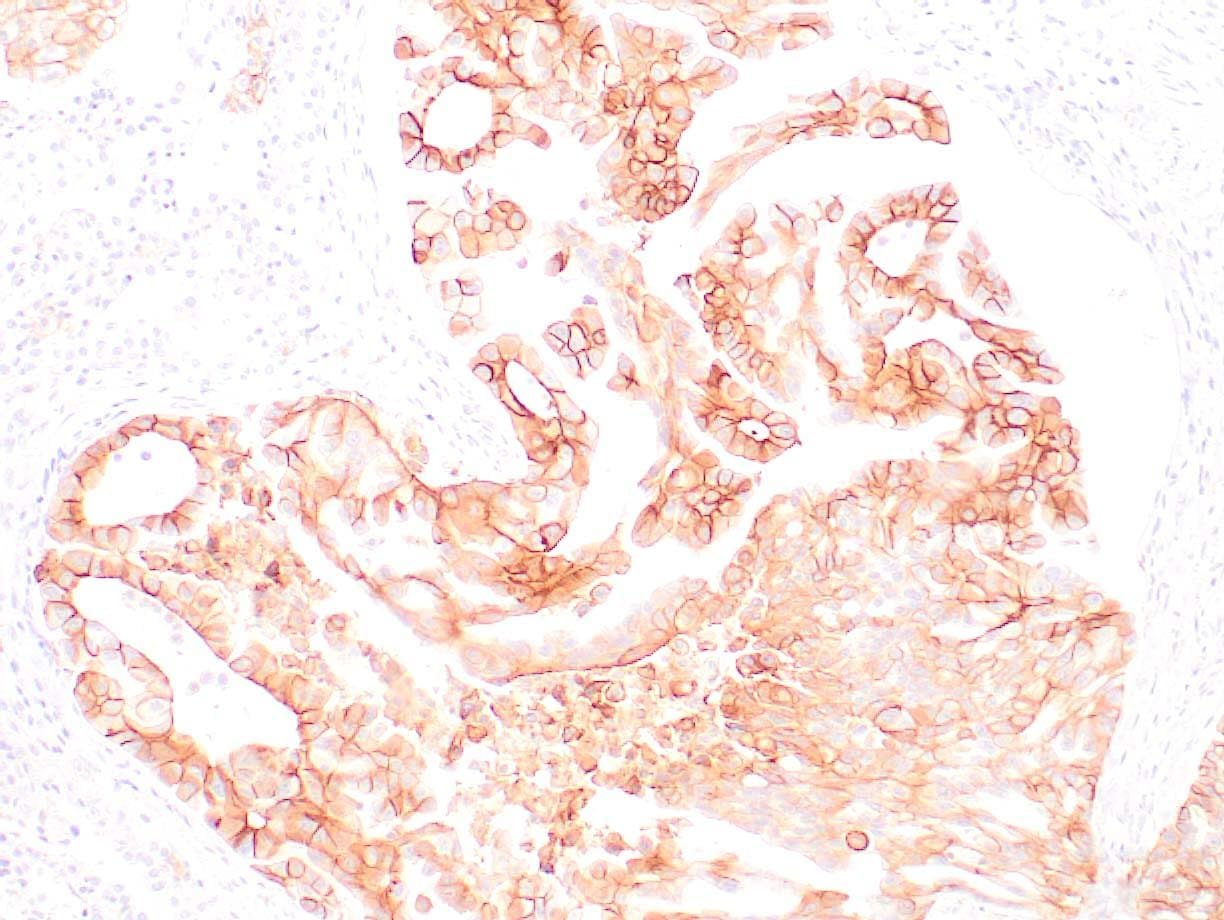 |
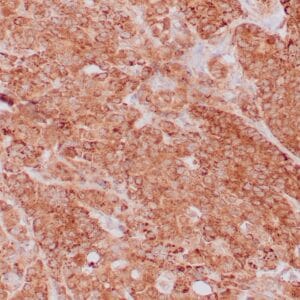
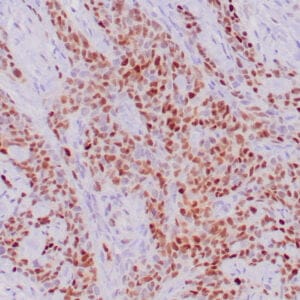
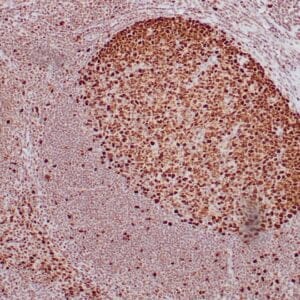
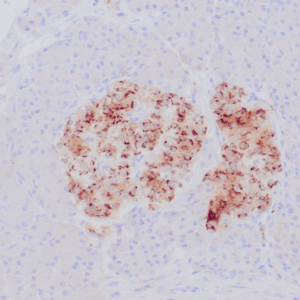
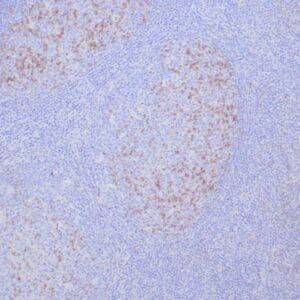
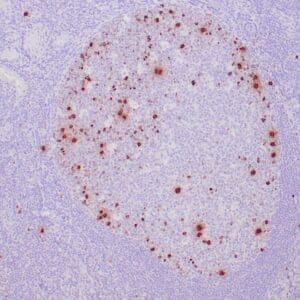
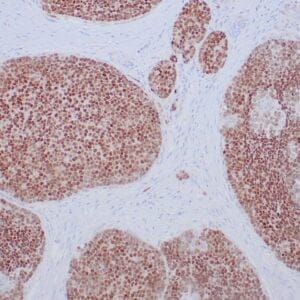
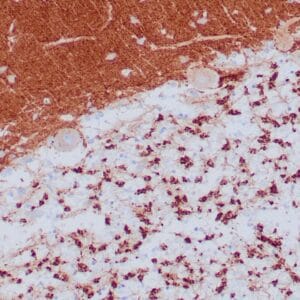
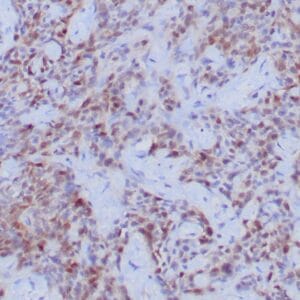
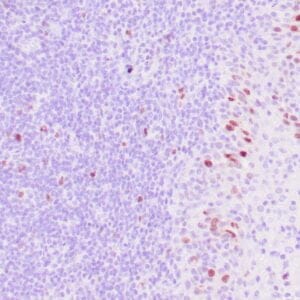
| Human lung adenocarcinoma stained with anti-PD-L1 (Clone ZR3) using peroxidase-conjugate and DAB chromogen. Note membranous staining of tumor cells. |
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
| IHC |
Documents
| # | SDS | Certificate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | |||
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.