| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| host | mouse |
| isotype | IgG |
| clonality | monoclonal |
| concentration | concentrate, predilute |
| applications | IHC |
| reactivity | human |
| available size | 0.1 mL, 0.5 mL, 1 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted |
rabbit anti-Neurofilament monoclonal antibody (ZR216) 6287
Price range: $160.00 through $528.00
Antibody summary
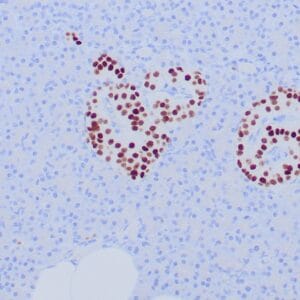
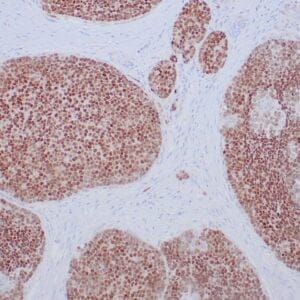
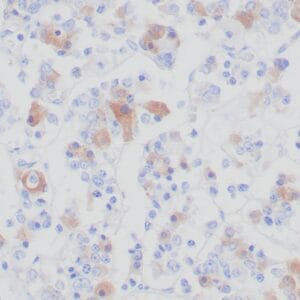
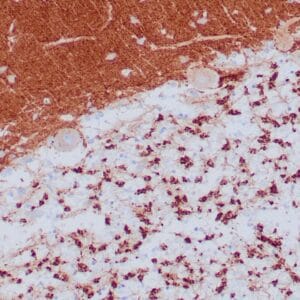
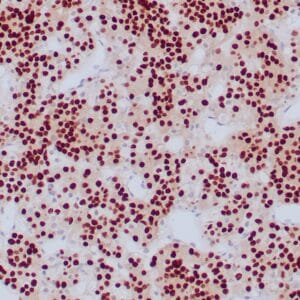
- Rabbit monoclonal to Neurofilament
- Suitable for: Immunohistochemistry (formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues)
- Reacts with: Human
- Isotype:IgG
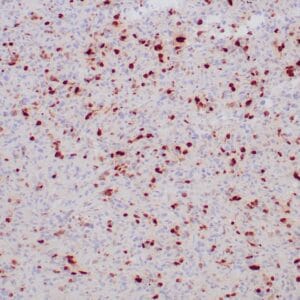
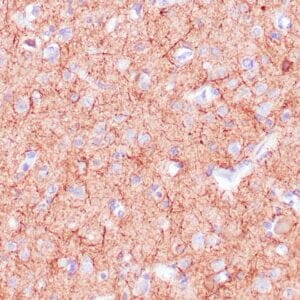
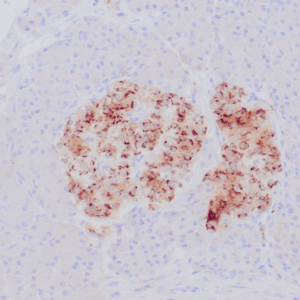
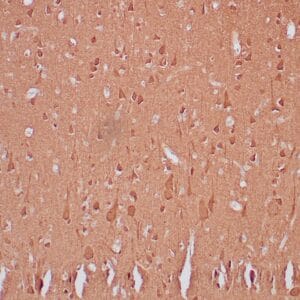
- Control: Brain
- Visualization: Cytoplasmic
- 0.1, 0.5, 1.0 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted
rabbit anti-Neurofilament monoclonal antibody ZR216 6287
| target relevance |
|---|
| Protein names Neurofilament light polypeptide (NF-L) (68 kDa neurofilament protein) (Neurofilament triplet L protein) |
| Gene names NEFL,NEFL NF68 NFL |
| Protein family Intermediate filament family |
| Mass 61517Da |
| Function FUNCTION: Neurofilaments usually contain three intermediate filament proteins: NEFL, NEFM, and NEFH which are involved in the maintenance of neuronal caliber. May additionally cooperate with the neuronal intermediate filament proteins PRPH and INA to form neuronal filamentous networks (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P08551}. |
| Subellular location SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: Cell projection, axon {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P08551}. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P08551}. |
| Structure SUBUNIT: Forms homodimers (in vitro) (By similarity). Forms heterodimers with NEFH or NEFM; which can further hetero-oligomerize (in vitro) (By similarity). Forms heterodimers with INA (in vitro) (By similarity). Interacts with ARHGEF28. Interacts with TRIM2. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P19527}. |
| Post-translational modification PTM: O-glycosylated. {ECO:0000250}.; PTM: Phosphorylated in the head and rod regions by the PKC kinase PKN1, leading to the inhibition of polymerization. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:8621664}.; PTM: Ubiquitinated in the presence of TRIM2 and UBE2D1. {ECO:0000250}. |
| Domain DOMAIN: The extra mass and high charge density that distinguish the neurofilament proteins from all other intermediate filament proteins are due to the tailpiece extensions. This region may form a charged scaffolding structure suitable for interaction with other neuronal components or ions. |
| Involvement in disease DISEASE: Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, demyelinating, 1F (CMT1F) [MIM:607734]: A dominant demyelinating form of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, a disorder of the peripheral nervous system, characterized by progressive weakness and atrophy, initially of the peroneal muscles and later of the distal muscles of the arms. Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease is classified in two main groups on the basis of electrophysiologic properties and histopathology: primary peripheral demyelinating neuropathies (designated CMT1 when they are dominantly inherited) and primary peripheral axonal neuropathies (CMT2). Demyelinating neuropathies are characterized by severely reduced nerve conduction velocities (less than 38 m/sec), segmental demyelination and remyelination with onion bulb formations on nerve biopsy, slowly progressive distal muscle atrophy and weakness, absent deep tendon reflexes, and hollow feet. CMT1F is characterized by onset in infancy or childhood (range 1 to 13 years). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12566280, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15241803}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, axonal, 2E (CMT2E) [MIM:607684]: A dominant axonal form of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, a disorder of the peripheral nervous system, characterized by progressive weakness and atrophy, initially of the peroneal muscles and later of the distal muscles of the arms. Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease is classified in two main groups on the basis of electrophysiologic properties and histopathology: primary peripheral demyelinating neuropathies (designated CMT1 when they are dominantly inherited) and primary peripheral axonal neuropathies (CMT2). Neuropathies of the CMT2 group are characterized by signs of axonal degeneration in the absence of obvious myelin alterations, normal or slightly reduced nerve conduction velocities, and progressive distal muscle weakness and atrophy. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10841809, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11220745, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12481988, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15241803, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17052987, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22206013, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25802885}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, dominant intermediate G (CMTDIG) [MIM:617882]: An autosomal dominant, intermediate form of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, a disorder of the peripheral nervous system, characterized by progressive weakness and atrophy, initially of the peroneal muscles and later of the distal muscles of the arms. Dominant intermediate forms are characterized by clinical and pathologic features intermediate between demyelinating and axonal peripheral neuropathies, and motor median nerve conduction velocities ranging from 25 to 45 m/sec. CMTDIG is phenotypically variable. Most affected individuals have onset in the first or second decades of slowly progressive distal motor weakness and atrophy, resulting in gait instability and distal upper limb impairment, as well as distal sensory impairment. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:14733962, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17052987, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25877835, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26645395}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: P07196 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
| IHC |
Documents
| # | SDS | Certificate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | |||
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.



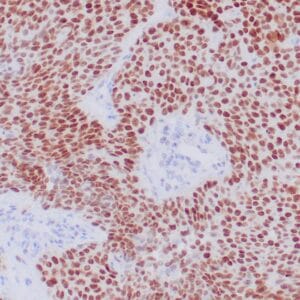
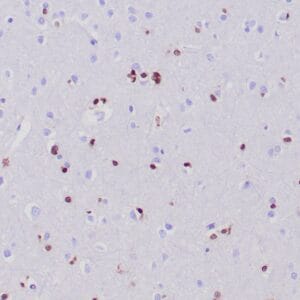
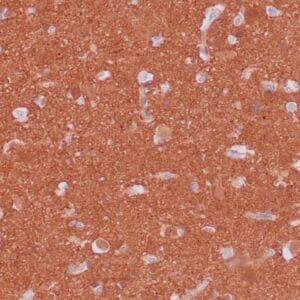
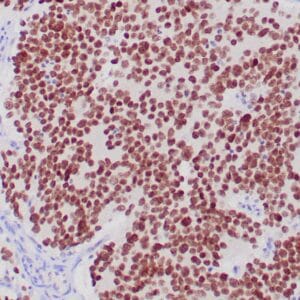
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.