| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| host | mouse |
| isotype | IgG |
| clonality | monoclonal |
| concentration | concentrate, predilute |
| applications | IHC |
| reactivity | human |
| available size | 0.1 mL, 0.5 mL, 1 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted |
rabbit anti-IgM monoclonal antibody (ZR249) 6226
Price range: $160.00 through $528.00
Antibody summary
- Rabbit monoclonal to IgM
- Suitable for: Immunohistochemistry (formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues)
- Reacts with: Human
- Isotype:IgG
- Control: Lymph node
- Visualization: Cytoplasmic
- 0.1, 0.5, 1.0 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted
rabbit anti-IgM monoclonal antibody ZR249 6226
| target relevance |
|---|
| Protein names Immunoglobulin heavy constant mu (Ig mu chain C region) (Ig mu chain C region BOT) (Ig mu chain C region GAL) (Ig mu chain C region OU) |
| Gene names IGHM,IGHM |
| Mass 51924Da |
| Function FUNCTION: Constant region of immunoglobulin heavy chains. Immunoglobulins, also known as antibodies, are membrane-bound or secreted glycoproteins produced by B lymphocytes. In the recognition phase of humoral immunity, the membrane-bound immunoglobulins serve as receptors which, upon binding of a specific antigen, trigger the clonal expansion and differentiation of B lymphocytes into immunoglobulins-secreting plasma cells. Secreted immunoglobulins mediate the effector phase of humoral immunity, which results in the elimination of bound antigens (PubMed:20176268, PubMed:22158414). The antigen binding site is formed by the variable domain of one heavy chain, together with that of its associated light chain. Thus, each immunoglobulin has two antigen binding sites with remarkable affinity for a particular antigen. The variable domains are assembled by a process called V-(D)-J rearrangement and can then be subjected to somatic hypermutations which, after exposure to antigen and selection, allow affinity maturation for a particular antigen (PubMed:17576170, PubMed:20176268). {ECO:0000303|PubMed:17576170, ECO:0000303|PubMed:20176268, ECO:0000303|PubMed:22158414}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 1]: Constant region of secreted IgM (sIgM), also known as the Fc region of IgM antibody. Able to multimerize, forms high order polymers, mainly pentamers and occasionally hexamers, providing for multivalency and high avidity recognition of antigens (PubMed:32029689, PubMed:37095205). Natural sIgM are polyreactive and recognize conserved self- and pathogen-derived structures, whereas immune sIgM are secreted only upon exposure to pathogens and are antigen-specific. Both natural and immune sIgM are required for an efficient humoral immune response to infection (By similarity). Mediates sIgM effector functions mostly via Fc receptors and the complement system. On lymphoid cells binds high-affinity Fc receptor FCMR and promotes induction of an efficient neutralizing IgG response while maintaining tolerance to self-antigens. Recruits C1q complement component to initiate the classical complement pathway, facilitating the recognition and neutralization of pathogens by the host. Together with C1q and mannose-binding lectin promotes the phagocytosis of apoptotic cells by macrophages, ensuring the clearance of potential autoimmune epitopes from tissues (By similarity) (PubMed:12847249, PubMed:19006321, PubMed:28230186, PubMed:32029689). Involved in mucosal immunity. It is transported by transcytosis across mucosal epithelium by PIGR and secreted on the apical side in complex with PIGR secretory component to scan mucosal lining for pathogens. IgM-antigen complexes undergo FCMR-mediated retrotranscytosis across mucosal M cells toward antigen-presenting cells in mucosal lymphoid tissues (By similarity) (PubMed:32029689). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P01872, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12847249, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19006321, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28230186, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32029689, ECO:0000269|PubMed:37095205}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 2]: Constant region of membrane-bound IgM, part of the B cell receptor complex (BCR). IgM BCR provides constitutive tonic signaling for B cell survival. Mediates pre-BCR signaling that regulates B cell selection and rearrangement of Ig genes via allelic exclusion. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P01872, ECO:0000269|PubMed:35981043}. |
| Subellular location SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: [Isoform 1]: Secreted. Note=During differentiation, B-lymphocytes switch from expression of membrane-bound IgM to secretion of IgM. {ECO:0000305}.; SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: [Isoform 2]: Cell membrane; Single-pass membrane protein {ECO:0000255}. |
| Structure SUBUNIT: The basic structural unit of both sIgM and mIgM molecules consists of two identical heavy chains and two identical light chains; disulfide-linked. N-terminal variable regions of the heavy and light chains form the antigen binding sites, whereas the C-terminal constant regions of the heavy chains interact with immune receptors to mediate effector functions. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:32029689, ECO:0000269|PubMed:35981043}.; SUBUNIT: [Isoform 1]: Part of IgM antibody. Forms high order oligomers, homopentamers stabilized by the JCHAIN and homohexamers that lack JCHAIN. The oligomerization amplifies an inherently low affinity of IgM antibodies for the antigen by multi-point attachment (avidity). Adjacent IgM protomers associate via interchain disulfide links to form an asymmetric pentameric structure with a 50 degree gap. A single copy of JCHAIN is covalently linked to the first and the fifth IgM monomers via interchain disulfide bonds thus closing the pentamer ring. Only JCHAIN-containing IgM binds PIGR secretory component (via D1-CDR1 region); this interaction is a prerequisite for IgM transcytosis across mucosal epithelium (PubMed:1472500, PubMed:30324136, PubMed:32029689, PubMed:36949194). Pentameric sIgM interacts (via CH4 domain) with FCRM (via Ig-like domain); the interaction is glycan-independent and multivalent theoretically involving up to eight binding sites for the IgM pentamer (PubMed:28230186, PubMed:36949194, PubMed:37095205). Interacts with FCAMR; this interaction facilitates the endocytosis of IgM-coated microbes or IgM-antigen immune complexes (By similarity). Antigen-bound IgM (via the Fc region) binds to globular domains of C1q component of the complement system, all three modules C1QA, C1QB and C1QC being involved in IgM binding; this interaction is multivalent (PubMed:12847249, PubMed:19006321). Pentameric sIgM (via Fc region) interacts with CD5L (via SRCR2) through interchain disulfide-linkages; this interaction protects CD5L from renal excretion and provides for high levels of CD5L in circulation (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P01872, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12847249, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1472500, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19006321, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28230186, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30324136, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32029689, ECO:0000269|PubMed:36949194, ECO:0000269|PubMed:37095205}.; SUBUNIT: [Isoform 2]: Part of IgM B cell receptor complex on pre-B cells, immature and mature B cells. The BCR complex consists of one membrane-bound IgM molecule responsible for antigen binding, non-covalently associated with CD79A and CD79B signaling chains. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:35981043}. |
| Post-translational modification PTM: N-glycosylated; important for IgM secretion and its localization at the plasma membrane. The interaction with FCMR is glycan-independent. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28230186, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32029689, ECO:0000269|PubMed:35981043}. |
| Domain DOMAIN: [Isoform 1]: The C-terminal beta-strands mediate sIgM oligomerization. The region encompassing residues Tyr-437 to Met-453 in each protomer forms a beta-strand, and the ten strands arrange in two five-stranded parallel beta-sheets packed in an antiparallel way, reminiscent of beta-sheet amyloid structures. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:32029689}.; DOMAIN: [Isoform 1]: The CH4 domains of pentameric IgM mediate multivalent interactions with the Ig-like domain of FCMR, thereby facilitating receptor clustering and signaling. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:37095205}.; DOMAIN: [Isoform 2]: The transmembrane helices of two heavy chains and CD79A and CD79B chains assembly in a four-helix bundle structure that appears to be conserved among different BCR isotypes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:35981043}. |
| Involvement in disease DISEASE: Agammaglobulinemia 1, autosomal recessive (AGM1) [MIM:601495]: A primary immunodeficiency characterized by profoundly low or absent serum antibodies and low or absent circulating B cells due to an early block of B-cell development. Affected individuals develop severe infections in the first years of life. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:8890099}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: P01871 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
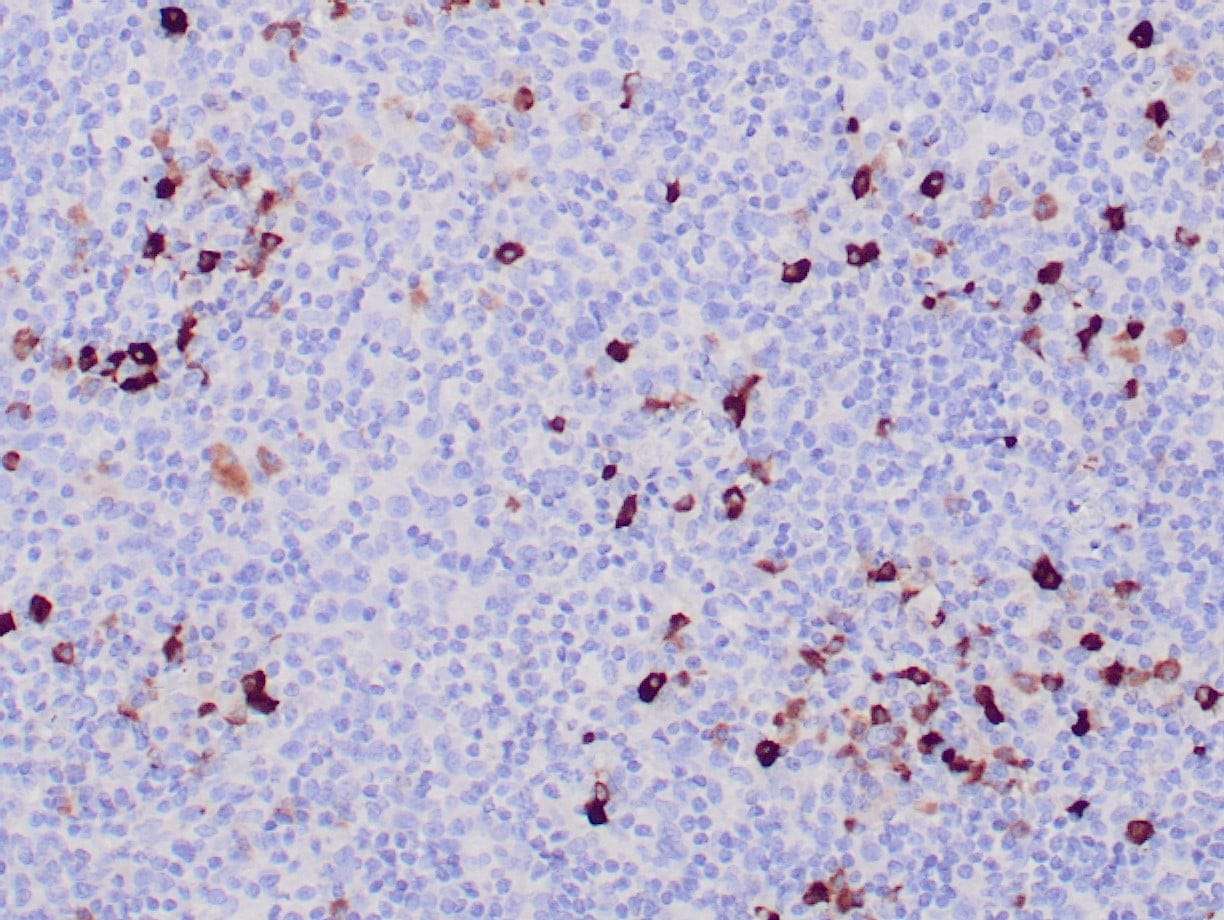 |
| Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human tonsil stained with anti-IgM antibody using peroxidase-conjugate and DAB chromogen. Note cytoplasmic staining of plasma cells |
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
| IHC |
Documents
| # | SDS | Certificate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | |||
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.








Reviews
There are no reviews yet.