| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| host | rabbit |
| isotype | IgG |
| clonality | monoclonal |
| concentration | 0.4 mg/mL |
| applications | ChIP, ICC, IHC, IP, WB |
| reactivity | human |
| available sizes | 100 µL, 20 µL |
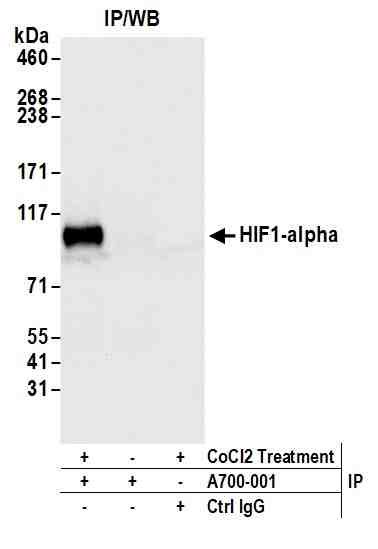
rabbit anti-HIF1a monoclonal antibody BL1243F7 1009
Price range: $127.00 through $300.00
Antibody summary
- Rabbit polyclonal to HIF-1α (Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha)
- Suitable for: ChIP, ICC, IHC, IP, WB
- Reacts with: Hu
- Isotype: IgG
- 100 µL (10 blots), 20 µL
rabbit anti- hif1a monoclonal antibody BL1243F7 1009
| antibody |
|---|
| Database link: human Q16665 |
| Tested applications ChIP, ICC, IHC, IP, WB |
| Recommended dilutions ChIP-Seq 10 µl per 30 µg of chromatin, Immunocytochemistry (ICC) 1:100 - 1:1000. Epitope retrieval with citrate buffer pH 6.0 for 20 minutes using a pressure cooker is recommended for FFPE cell sections, Immunohistochemistry (IHC)1:100 - 1:1000. Epitope retrieval with citrate buffer pH 6 |
| Immunogen Between 433 and 826 |
| Size and concentration 100µL and 0.4 mg/mL |
| Form liquid |
| Storage Instructions 2-8°C for short term, for longer term at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. |
| Storage buffer Borate Buffered Saline (BBS) pH 8.2 with 0.1% BSA and 0.09% Sodium Azide |
| Purity affinity purified |
| Clonality monoclonal |
| Isotype IgG |
| Compatible secondaries goat anti-rabbit IgG, H&L chain specific, peroxidase conjugated, conjugated polyclonal antibody 9512 goat anti-rabbit IgG, H&L chain specific, biotin conjugated polyclonal antibody 2079 goat anti-rabbit IgG, H&L chain specific, FITC conjugated polyclonal antibody 7863 goat anti-rabbit IgG, H&L chain specific, Cross Absorbed polyclonal antibody 2371 goat anti-rabbit IgG, H&L chain specific, biotin conjugated polyclonal antibody, crossabsorbed 1715 goat anti-rabbit IgG, H&L chain specific, FITC conjugated polyclonal antibody, crossabsorbed 1720 |
| Isotype control Rabbit monoclonal - Isotype Control |
| target relevance |
|---|
| Protein names Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha (HIF-1-alpha) (HIF1-alpha) (ARNT-interacting protein) (Basic-helix-loop-helix-PAS protein MOP1) (Class E basic helix-loop-helix protein 78) (bHLHe78) (Member of PAS protein 1) (PAS domain-containing protein 8) |
| Gene names HIF1A,HIF1A BHLHE78 MOP1 PASD8 |
| Mass 92670Da |
| Function FUNCTION: Functions as a master transcriptional regulator of the adaptive response to hypoxia (PubMed:11292861, PubMed:11566883, PubMed:15465032, PubMed:16973622, PubMed:17610843, PubMed:18658046, PubMed:20624928, PubMed:22009797, PubMed:30125331, PubMed:9887100). Under hypoxic conditions, activates the transcription of over 40 genes, including erythropoietin, glucose transporters, glycolytic enzymes, vascular endothelial growth factor, HILPDA, and other genes whose protein products increase oxygen delivery or facilitate metabolic adaptation to hypoxia (PubMed:11292861, PubMed:11566883, PubMed:15465032, PubMed:16973622, PubMed:17610843, PubMed:20624928, PubMed:22009797, PubMed:30125331, PubMed:9887100). Plays an essential role in embryonic vascularization, tumor angiogenesis and pathophysiology of ischemic disease (PubMed:22009797). Heterodimerizes with ARNT; heterodimer binds to core DNA sequence 5'-TACGTG-3' within the hypoxia response element (HRE) of target gene promoters (By similarity). Activation requires recruitment of transcriptional coactivators such as CREBBP and EP300 (PubMed:16543236, PubMed:9887100). Activity is enhanced by interaction with NCOA1 and/or NCOA2 (PubMed:10594042). Interaction with redox regulatory protein APEX1 seems to activate CTAD and potentiates activation by NCOA1 and CREBBP (PubMed:10202154, PubMed:10594042). Involved in the axonal distribution and transport of mitochondria in neurons during hypoxia (PubMed:19528298). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q61221, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10202154, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10594042, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11292861, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11566883, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15465032, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16543236, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16973622, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17610843, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18658046, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19528298, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20624928, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22009797, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30125331, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9887100}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Upon infection by human coronavirus SARS-CoV-2, is required for induction of glycolysis in monocytes and the consequent pro-inflammatory state (PubMed:32697943). In monocytes, induces expression of ACE2 and cytokines such as IL1B, TNF, IL6, and interferons (PubMed:32697943). Promotes human coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 replication and monocyte inflammatory response (PubMed:32697943). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:32697943}. |
| Subellular location SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: Cytoplasm {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9822602}. Nucleus {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22009797, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9822602}. Nucleus speckle {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q61221}. Note=Colocalizes with HIF3A in the nucleus and speckles (By similarity). Cytoplasmic in normoxia, nuclear translocation in response to hypoxia (PubMed:9822602). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q61221, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9822602}. |
| Tissues TISSUE SPECIFICITY: Expressed in most tissues with highest levels in kidney and heart. Overexpressed in the majority of common human cancers and their metastases, due to the presence of intratumoral hypoxia and as a result of mutations in genes encoding oncoproteins and tumor suppressors. A higher level expression seen in pituitary tumors as compared to the pituitary gland. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22009797}. |
| Structure SUBUNIT: Interacts with the ARNT; forms a heterodimer that binds core DNA sequence 5'-TACGTG-3' within the hypoxia response element (HRE) of target gene promoters (PubMed:10944113, PubMed:20699359). Interacts with COPS5; the interaction increases the transcriptional activity of HIF1A through increased stability (By similarity). Interacts with EP300 (via TAZ-type 1 domains); the interaction is stimulated in response to hypoxia and inhibited by CITED2 (PubMed:11959990, PubMed:12778114, PubMed:16543236, PubMed:16973622, PubMed:8917528, PubMed:9887100). Interacts with CREBBP (via TAZ-type 1 domains) (PubMed:11959977, PubMed:8917528). Interacts with NCOA1, NCOA2, APEX1 and HSP90 (PubMed:10202154, PubMed:10594042). Interacts (hydroxylated within the ODD domain) with VHLL (via beta domain); the interaction, leads to polyubiquitination and subsequent HIF1A proteasomal degradation (PubMed:14757845). During hypoxia, sumoylated HIF1A also binds VHL; the interaction promotes the ubiquitination of HIF1A (PubMed:10944113, PubMed:11006129, PubMed:12004076, PubMed:12050673, PubMed:16862177). Interacts with SENP1; the interaction desumoylates HIF1A resulting in stabilization and activation of transcription (By similarity). Interacts (via the ODD domain) with NAA10; the interaction appears not to acetylate HIF1A nor have any affect on protein stability, during hypoxia (PubMed:12464182, PubMed:16288748). Interacts with RWDD3; the interaction enhances HIF1A sumoylation (PubMed:17956732, PubMed:23469069). Interacts with TSGA10 (By similarity). Interacts with HIF3A (By similarity). Interacts with RORA (via the DNA binding domain); the interaction enhances HIF1A transcription under hypoxia through increasing protein stability (PubMed:18658046). Interaction with PSMA7 inhibits the transactivation activity of HIF1A under both normoxic and hypoxia-mimicking conditions (PubMed:11389899). Interacts with USP20 (PubMed:15776016). Interacts with RACK1; promotes HIF1A ubiquitination and proteasome-mediated degradation (PubMed:17244529). Interacts (via N-terminus) with USP19 (PubMed:22128162). Interacts with SIRT2 (PubMed:24681946). Interacts (deacetylated form) with EGLN1 (PubMed:24681946). Interacts with CBFA2T3 (PubMed:25974097). Interacts with HSP90AA1 and HSP90AB1 (PubMed:26517842). Interacts with DCUN1D1; this interaction increases the interaction between VHL and DCUN1D1 (PubMed:23401859). Interacts with HIF1AN (PubMed:12446723). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q61221, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10202154, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10594042, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10944113, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11006129, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11389899, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11959977, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11959990, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12004076, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12050673, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12446723, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12464182, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12778114, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14757845, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15776016, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16288748, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16543236, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16862177, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16973622, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17244529, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17956732, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18658046, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20699359, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22128162, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23401859, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23469069, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24681946, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25974097, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26517842, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8917528, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9887100}. |
| Post-translational modification PTM: S-nitrosylation of Cys-800 may be responsible for increased recruitment of p300 coactivator necessary for transcriptional activity of HIF-1 complex. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12560087, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12914934}.; PTM: Requires phosphorylation for DNA-binding. Phosphorylation at Ser-247 by CSNK1D/CK1 represses kinase activity and impairs ARNT binding (PubMed:20699359, PubMed:20889502). Phosphorylation by GSK3-beta and PLK3 promote degradation by the proteasome (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q61221, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20699359, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20889502}.; PTM: Sumoylated; with SUMO1 under hypoxia (PubMed:15465032, PubMed:15776016, PubMed:17610843). Sumoylation is enhanced through interaction with RWDD3 (PubMed:17956732). Both sumoylation and desumoylation seem to be involved in the regulation of its stability during hypoxia (PubMed:15465032, PubMed:15776016, PubMed:17610843). Sumoylation can promote either its stabilization or its VHL-dependent degradation by promoting hydroxyproline-independent HIF1A-VHL complex binding, thus leading to HIF1A ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation (PubMed:15465032, PubMed:15776016, PubMed:17610843). Desumoylation by SENP1 increases its stability amd transcriptional activity (By similarity). There is a disaccord between various publications on the effect of sumoylation and desumoylation on its stability and transcriptional activity (Probable). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q61221, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15465032, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15776016, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17610843, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17956732, ECO:0000305}.; PTM: Acetylation of Lys-532 by ARD1 increases interaction with VHL and stimulates subsequent proteasomal degradation (PubMed:12464182). Deacetylation of Lys-709 by SIRT2 increases its interaction with and hydroxylation by EGLN1 thereby inactivating HIF1A activity by inducing its proteasomal degradation (PubMed:24681946). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12464182, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24681946}.; PTM: Polyubiquitinated; in normoxia, following hydroxylation and interaction with VHL. Lys-532 appears to be the principal site of ubiquitination. Clioquinol, the Cu/Zn-chelator, inhibits ubiquitination through preventing hydroxylation at Asn-803. Ubiquitinated by E3 ligase VHL (PubMed:25615526). Deubiquitinated by UCHL1 (PubMed:25615526). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12080085, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15776016, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16862177, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22537386, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25615526, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25974097}.; PTM: In normoxia, is hydroxylated on Pro-402 and Pro-564 in the oxygen-dependent degradation domain (ODD) by EGLN1/PHD2 and EGLN2/PHD1 (PubMed:11292861, PubMed:11566883, PubMed:12351678, PubMed:15776016, PubMed:25974097). EGLN3/PHD3 has also been shown to hydroxylate Pro-564 (PubMed:11292861, PubMed:11566883, PubMed:12351678, PubMed:15776016, PubMed:25974097). The hydroxylated prolines promote interaction with VHL, initiating rapid ubiquitination and subsequent proteasomal degradation (PubMed:11292861, PubMed:11566883, PubMed:12351678, PubMed:15776016, PubMed:25974097). Deubiquitinated by USP20 (PubMed:11292861, PubMed:11566883, PubMed:12351678, PubMed:15776016, PubMed:25974097). Under hypoxia, proline hydroxylation is impaired and ubiquitination is attenuated, resulting in stabilization (PubMed:11292861, PubMed:11566883, PubMed:12351678, PubMed:15776016, PubMed:25974097). In normoxia, is hydroxylated on Asn-803 by HIF1AN, thus abrogating interaction with CREBBP and EP300 and preventing transcriptional activation (PubMed:12080085). This hydroxylation is inhibited by the Cu/Zn-chelator, Clioquinol (PubMed:12080085). Repressed by iron ion, via Fe(2+) prolyl hydroxylase (PHD) enzymes-mediated hydroxylation and subsequent proteasomal degradation (PubMed:28296633). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11292861, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11566883, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12080085, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12351678, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15776016, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25974097, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28296633}.; PTM: The iron and 2-oxoglutarate dependent 3-hydroxylation of asparagine is (S) stereospecific within HIF CTAD domains. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12080085}.; PTM: (Microbial infection) Glycosylated at Arg-18 by enteropathogenic E.coli protein NleB1: arginine GlcNAcylation enhances transcription factor activity and impairs glucose metabolism. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30125331}. |
| Domain DOMAIN: Contains two independent C-terminal transactivation domains, NTAD and CTAD, which function synergistically. Their transcriptional activity is repressed by an intervening inhibitory domain (ID). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10202154, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9235919}. |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: Q16665 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
| Western blot |
Documents
| # | SDS | Certificate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | |||
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.




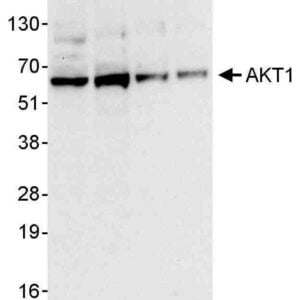


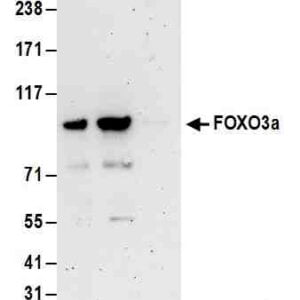
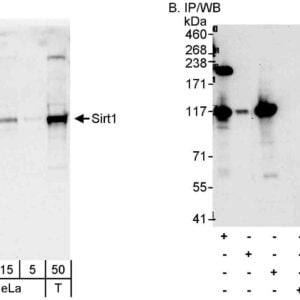
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.