| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| host | rabbit |
| isotype | IgG |
| clonality | monoclonal |
| concentration | 1 mg/mL |
| applications | ICC/IF, IHC, WB |
| available sizes | 100 µg |
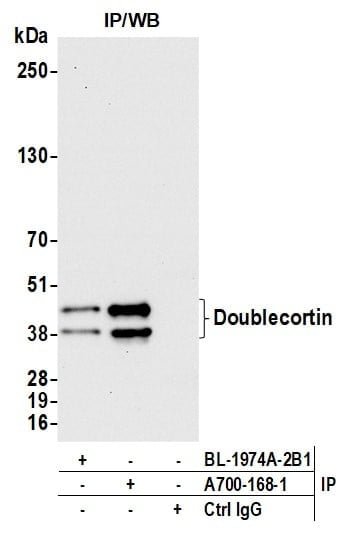
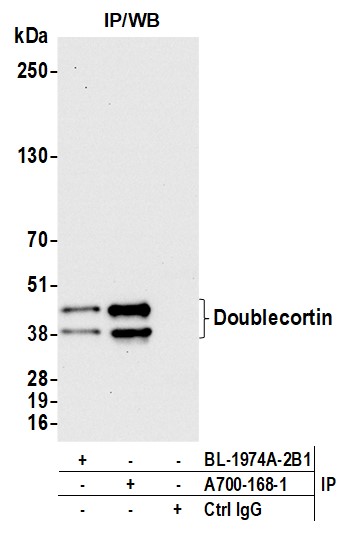
rabbit anti-Doublecortin monoclonal antibody 9059
$409.00
Antibody summary
- Rabbit monoclonal to Doublecortin
- Suitable for: WB, ICC/IF, IHC
- Reacts with: human, mouse, rat
- Isotype: IgG
- 100 µg
rabbit anti-Doublecortin monoclonal antibody 9059
| target relevance |
|---|
| Doublecortin (DCX) is a widely used cell marker in neuroscience and developmental biology research. It is a microtubule-associated protein that plays a critical role in neuronal migration and maturation, particularly in the developing brain. DCX is selectively expressed in migrating neuroblasts and immature neurons, making it a valuable marker for identifying and studying neurogenesis and neuronal migration processes. Immunohistochemistry and immunofluorescence techniques utilizing antibodies targeting DCX enable researchers to visualize and quantify these migrating neuroblasts and young neurons in the brain and other tissues. Moreover, DCX has been employed in studies related to neuroplasticity and adult neurogenesis in the hippocampus, providing valuable insights into learning and memory processes in the adult brain. Click for more on: cell markers and Doubelcortin |
| Protein names Neuronal migration protein doublecortin (Doublin) (Lissencephalin-X) (Lis-X) |
| Gene names DCX,DCX DBCN LISX |
| Mass 40574Da |
| Function FUNCTION: Microtubule-associated protein required for initial steps of neuronal dispersion and cortex lamination during cerebral cortex development. May act by competing with the putative neuronal protein kinase DCLK1 in binding to a target protein. May in that way participate in a signaling pathway that is crucial for neuronal interaction before and during migration, possibly as part of a calcium ion-dependent signal transduction pathway. May be part with PAFAH1B1/LIS-1 of overlapping, but distinct, signaling pathways that promote neuronal migration. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22359282}. |
| Subellular location SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: Cytoplasm {ECO:0000305}. Cell projection, neuron projection {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9ESI7}. Note=Localizes at neurite tips. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9ESI7}. |
| Tissues TISSUE SPECIFICITY: Highly expressed in neuronal cells of fetal brain (in the majority of cells of the cortical plate, intermediate zone and ventricular zone), but not expressed in other fetal tissues. In the adult, highly expressed in the brain frontal lobe, but very low expression in other regions of brain, and not detected in heart, placenta, lung, liver, skeletal muscles, kidney and pancreas. |
| Structure SUBUNIT: Interacts with tubulin (PubMed:27292316). Interacts with USP9X (PubMed:24607389). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24607389, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27292316}. |
| Post-translational modification PTM: Phosphorylation by MARK1, MARK2 and PKA regulates its ability to bind microtubules (By similarity). Phosphorylation at Ser-265 and Ser-297 seems to occur only in neonatal brain, the levels falling precipitously by postnatal day 21 (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O88809, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9ESI7}.; PTM: Ubiquitinated by MDM2, leading to its degradation by the proteasome. Ubiquitinated by MDM2 and subsequent degradation leads to reduce the dendritic spine density of olfactory bulb granule cells. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O88809}. |
| Involvement in disease DISEASE: Lissencephaly, X-linked 1 (LISX1) [MIM:300067]: A classic lissencephaly characterized by intellectual disability and seizures that are more severe in male patients. Affected boys show an abnormally thick cortex with absent or severely reduced gyri. Clinical manifestations include feeding problems, abnormal muscular tone, seizures and severe to profound psychomotor retardation. Female patients display a less severe phenotype referred to as 'doublecortex'. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11468322, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12552055, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27292316, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9489699, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9489700, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9668176, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9817918}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Subcortical band heterotopia X-linked (SBHX) [MIM:300067]: SBHX is a mild brain malformation of the lissencephaly spectrum. It is characterized by bilateral and symmetric plates or bands of gray matter found in the central white matter between the cortex and cerebral ventricles, cerebral convolutions usually appearing normal. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10369164, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10441340, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10807542, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11175293, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11601509, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12390976, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9618162, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9989615}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Note=A chromosomal aberration involving DCX is found in lissencephaly. Translocation t(X;2)(q22.3;p25.1). |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: O43602 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
| Western blot IHC ICC |
Documents
| # | SDS | Certificate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | |||
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.