| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| host | mouse |
| isotype | IgG |
| clonality | monoclonal |
| concentration | concentrate, predilute |
| applications | IHC |
| reactivity | human |
| available size | 0.1 mL, 0.5 mL, 1 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted |
rabbit anti-Desmin monoclonal antibody (ZR240) 6158
Price range: $160.00 through $528.00
Antibody summary
- Rabbit monoclonal to Desmin
- Suitable for: Immunohistochemistry (formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues)
- Reacts with: Human
- Isotype:IgG
- Control: Skeletal muscle or rhabdomyosarcoma
- Visualization: Cytoplasmic and luminal membrane
- 0.1, 0.5, 1.0 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted
rabbit anti-Desmin monoclonal antibody ZR240 6158
| target relevance |
|---|
| Protein names Desmin |
| Gene names DES,DES |
| Protein family Intermediate filament family |
| Mass 53536Da |
| Function FUNCTION: Muscle-specific type III intermediate filament essential for proper muscular structure and function. Plays a crucial role in maintaining the structure of sarcomeres, inter-connecting the Z-disks and forming the myofibrils, linking them not only to the sarcolemmal cytoskeleton, but also to the nucleus and mitochondria, thus providing strength for the muscle fiber during activity (PubMed:25358400). In adult striated muscle they form a fibrous network connecting myofibrils to each other and to the plasma membrane from the periphery of the Z-line structures (PubMed:24200904, PubMed:25394388, PubMed:26724190). May act as a sarcomeric microtubule-anchoring protein: specifically associates with detyrosinated tubulin-alpha chains, leading to buckled microtubules and mechanical resistance to contraction. Required for nuclear membrane integrity, via anchoring at the cell tip and nuclear envelope, resulting in maintenance of microtubule-derived intracellular mechanical forces (By similarity). Contributes to the transcriptional regulation of the NKX2-5 gene in cardiac progenitor cells during a short period of cardiomyogenesis and in cardiac side population stem cells in the adult. Plays a role in maintaining an optimal conformation of nebulette (NEB) on heart muscle sarcomeres to bind and recruit cardiac alpha-actin (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P31001, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24200904, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25394388, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26724190, ECO:0000303|PubMed:25358400}. |
| Subellular location SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: Cytoplasm, myofibril, sarcomere, Z line {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24200904, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26724190, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30262925}. Cytoplasm {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25394388}. Cell membrane, sarcolemma {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25394388}. Nucleus {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P31001}. Cell tip {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P31001}. Nucleus envelope {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P31001}. Note=Localizes in the intercalated disks which occur at the Z line of cardiomyocytes (PubMed:24200904, PubMed:26724190). Localizes in the nucleus exclusively in differentiating cardiac progenitor cells and premature cardiomyocytes (By similarity). PKP2 is required for correct anchoring of DES at the cell tip and nuclear envelope (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P31001, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24200904, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26724190}. |
| Structure SUBUNIT: Homomer (PubMed:21135508). Interacts with DST (By similarity). Interacts with MTM1 (PubMed:21135508). Interacts with EPPK1; interaction is dependent of higher-order structure of intermediate filament (PubMed:16923132). Interacts with CRYAB (PubMed:28470624). Interacts with NEB (via nebulin repeats 160-164) (PubMed:23615443). Interacts (via rod region) with NEBL (via nebulin repeats 1-5) (PubMed:27733623). Interacts with ASB2 isoform 1; the interaction targets DES for proteasomal degradation (By similarity). Interacts with PLEC isoform 1C (PubMed:24940650). Interacts with PKP1 (PubMed:10852826). Interacts with FLII (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P31001, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10852826, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16923132, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21135508, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23615443, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24940650, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27733623, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28470624}. |
| Post-translational modification PTM: ADP-ribosylation prevents ability to form intermediate filaments. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P48675}.; PTM: Phosphorylation at Ser-7, Ser-28 and Ser-32 by CDK1, phosphorylation at Ser-60 by AURKB and phosphorylation at Thr-76 by ROCK1 contribute to efficient separation of desmin intermediate filaments during mitosis. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P31001}.; PTM: Ubiquitination by a SCF-like complex containing ASB2 isoform 1 leads to proteasomal degradation. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P31001}. |
| Involvement in disease DISEASE: Myopathy, myofibrillar, 1 (MFM1) [MIM:601419]: A form of myofibrillar myopathy, a group of chronic neuromuscular disorders characterized at ultrastructural level by disintegration of the sarcomeric Z disk and myofibrils, and replacement of the normal myofibrillar markings by small dense granules, or larger hyaline masses, or amorphous material. MFM1 is characterized by skeletal muscle weakness associated with cardiac conduction blocks, arrhythmias, restrictive heart failure, and accumulation of desmin-reactive deposits in cardiac and skeletal muscle cells. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10545598, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10717012, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10905661, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11061256, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11668632, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12620971, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12766977, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14648196, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14711882, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14724127, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15495235, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15800015, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16009553, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16376610, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16865695, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17221859, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18061454, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19879535, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20829228, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22106715, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22395865, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23615443, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23687351, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25394388, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27733623, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28470624, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9697706, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9736733}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Mutations in the DES gene are associated with a variable clinical phenotype which encompasses isolated myopathies, pure cardiac phenotypes (including dilated cardiomyopathy, restrictive cardiomyopathy and arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy), cardiac conduction disease, and combinations of these disorders. If both cardiologic and neurologic features occur, they can manifest in any order, as cardiologic features can precede, occur simultaneously with, or follow manifestation of generalized neuromuscular disease (PubMed:19879535). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19879535}.; DISEASE: Cardiomyopathy, dilated, 1I (CMD1I) [MIM:604765]: A disorder characterized by ventricular dilation and impaired systolic function, resulting in congestive heart failure and arrhythmia. Patients are at risk of premature death. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10430757, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24200904, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26724190, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30262925}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Neurogenic scapuloperoneal syndrome Kaeser type (Kaeser syndrome) [MIM:181400]: Autosomal dominant disorder with a peculiar scapuloperoneal distribution of weakness and atrophy. A large clinical variability is observed ranging from scapuloperoneal, limb grindle and distal phenotypes with variable cardiac or respiratory involvement. Facial weakness, dysphagia and gynaecomastia are frequent additional symptoms. Affected men seemingly bear a higher risk of sudden, cardiac death as compared to affected women. Histological and immunohistochemical examination of muscle biopsy specimens reveal a wide spectrum of findings ranging from near normal or unspecific pathology to typical, myofibrillar changes with accumulation of desmin. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17439987, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25394388}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: P17661 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
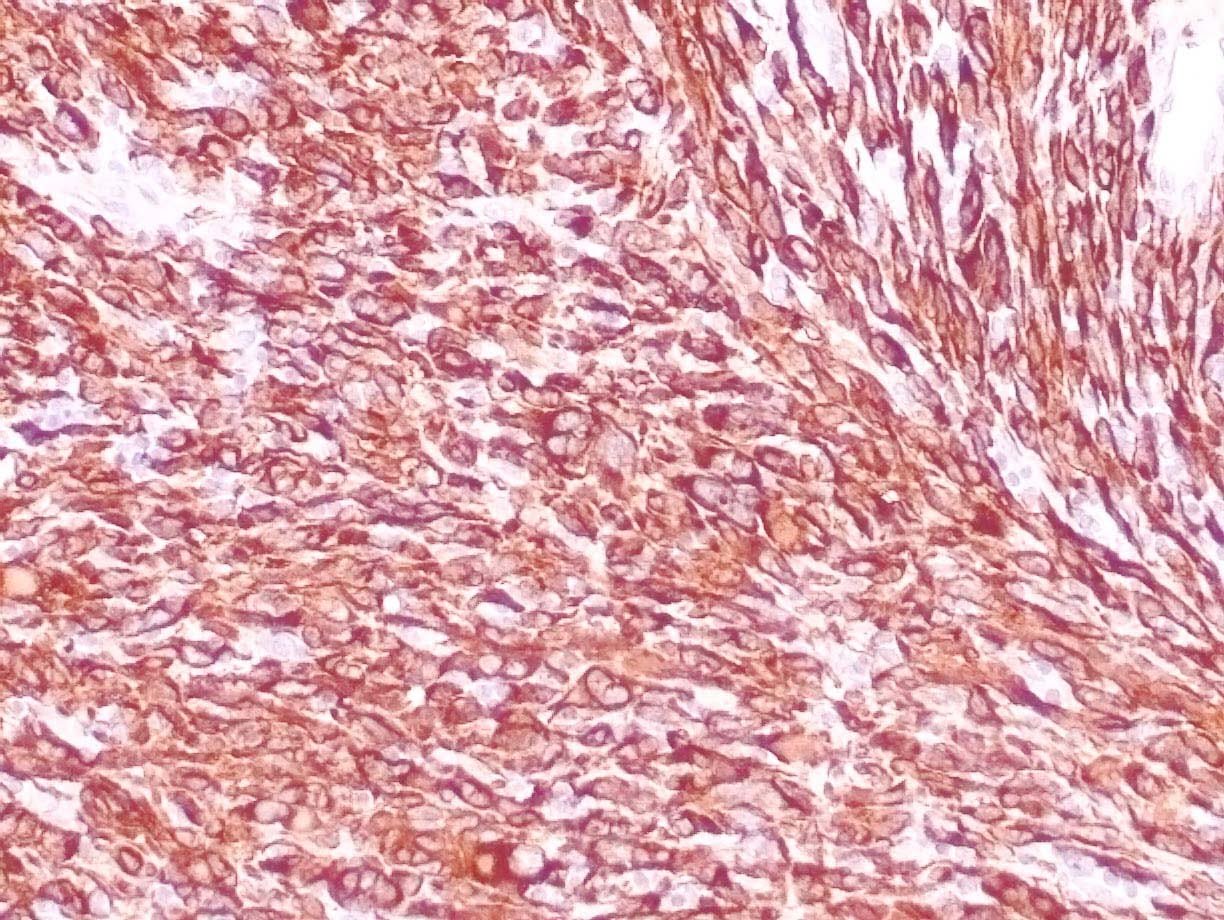 |
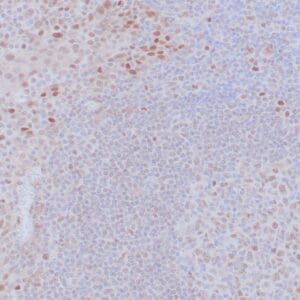
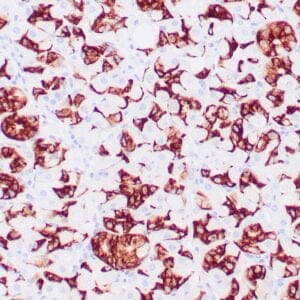
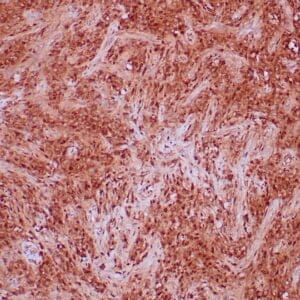
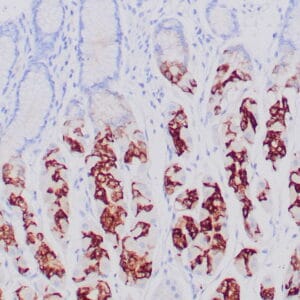
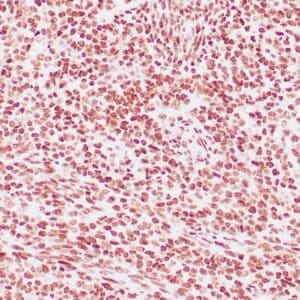
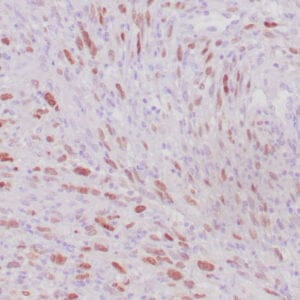
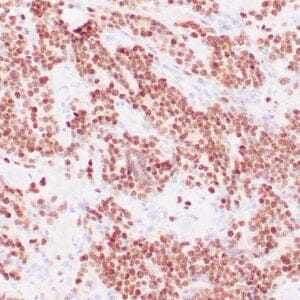
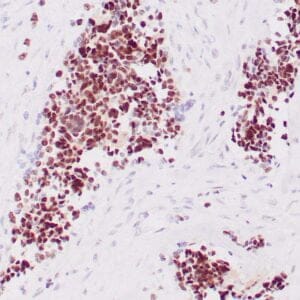
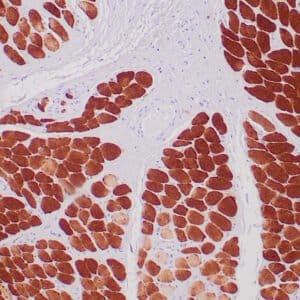
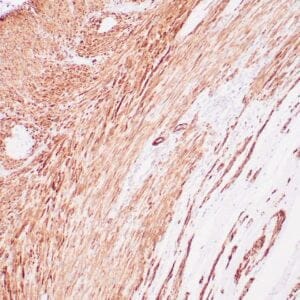
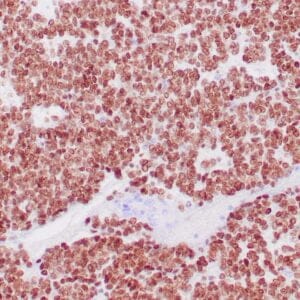
| Human leiomyosarcoma stained with anti-desmin antibody using peroxidase-conjugate and DAB chromogen. Note the cytoplasmic staining of tumor cells. |
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
| IHC |
Documents
| # | SDS | Certificate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | |||
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.