| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| host | mouse |
| isotype | IgG |
| clonality | monoclonal |
| concentration | concentrate, predilute |
| applications | IHC |
| reactivity | human |
| available size | 0.1 mL, 0.5 mL, 1 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted |
rabbit anti-CDK4 monoclonal antibody (ZR394) 6118
Price range: $160.00 through $528.00
Antibody summary
- Rabbit monoclonal to CDK4
- Suitable for: Immunohistochemistry (formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues)
- Reacts with: Human
- Isotype:IgG
- Control: Urothelial carcinoma, well-differentiated liposarcoma
- Visualization: Nucleus and cytoplasm
- 0.1, 0.5, 1.0 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted
rabbit anti-CDK4 monoclonal antibody ZR394 6118
| antibody |
|---|
| Database link: human P11802 |
| Tested applications IHC |
| Recommended dilutions Concentrated 1:100-200 |
| Application Notes Positive control: Urothelial carcinoma, well-differentiated liposarcoma |
| Immunogen Recombinant fragment corresponding to N-terminal of human CDK4 protein |
| Size and concentration 7 mL prediluted or 0.1, 0.5, 1.0 mL and concentrated |
| Form liquid |
| Storage Instructions 2-8°C for short term, for longer term at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. |
| Purity affinity purified |
| Clonality monoclonal |
| Isotype IgG |
| Compatible secondaries goat anti-rabbit IgG, H&L chain specific, peroxidase conjugated, conjugated polyclonal antibody 9512 goat anti-rabbit IgG, H&L chain specific, biotin conjugated polyclonal antibody 2079 goat anti-rabbit IgG, H&L chain specific, FITC conjugated polyclonal antibody 7863 goat anti-rabbit IgG, H&L chain specific, Cross Absorbed polyclonal antibody 2371 goat anti-rabbit IgG, H&L chain specific, biotin conjugated polyclonal antibody, crossabsorbed 1715 goat anti-rabbit IgG, H&L chain specific, FITC conjugated polyclonal antibody, crossabsorbed 1720 |
| Isotype control Rabbit polyclonal - Isotype Control |
| target relevance |
|---|
| Protein names Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 (EC 2.7.11.22) (Cell division protein kinase 4) (PSK-J3) |
| Gene names CDK4,CDK4 |
| Protein family Protein kinase superfamily, CMGC Ser/Thr protein kinase family, CDC2/CDKX subfamily |
| Mass 33730Da |
| Function FUNCTION: Ser/Thr-kinase component of cyclin D-CDK4 (DC) complexes that phosphorylate and inhibit members of the retinoblastoma (RB) protein family including RB1 and regulate the cell-cycle during G(1)/S transition. Phosphorylation of RB1 allows dissociation of the transcription factor E2F from the RB/E2F complexes and the subsequent transcription of E2F target genes which are responsible for the progression through the G(1) phase. Hypophosphorylates RB1 in early G(1) phase. Cyclin D-CDK4 complexes are major integrators of various mitogenenic and antimitogenic signals. Also phosphorylates SMAD3 in a cell-cycle-dependent manner and represses its transcriptional activity. Component of the ternary complex, cyclin D/CDK4/CDKN1B, required for nuclear translocation and activity of the cyclin D-CDK4 complex. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15241418, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18827403, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9003781}. |
| Catalytic activity CATALYTIC ACTIVITY: Reaction=L-seryl-[protein] + ATP = O-phospho-L-seryl-[protein] + ADP + H(+); Xref=Rhea:RHEA:17989, Rhea:RHEA-COMP:9863, Rhea:RHEA-COMP:11604, ChEBI:CHEBI:15378, ChEBI:CHEBI:29999, ChEBI:CHEBI:30616, ChEBI:CHEBI:83421, ChEBI:CHEBI:456216; EC=2.7.11.22; Evidence={ECO:0000269|PubMed:19075005, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19237565, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9106657}; CATALYTIC ACTIVITY: Reaction=L-threonyl-[protein] + ATP = O-phospho-L-threonyl-[protein] + ADP + H(+); Xref=Rhea:RHEA:46608, Rhea:RHEA-COMP:11060, Rhea:RHEA-COMP:11605, ChEBI:CHEBI:15378, ChEBI:CHEBI:30013, ChEBI:CHEBI:30616, ChEBI:CHEBI:61977, ChEBI:CHEBI:456216; EC=2.7.11.22; Evidence={ECO:0000269|PubMed:19075005, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19237565, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9106657}; |
| Subellular location SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: Cytoplasm {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18827403}. Nucleus {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18827403, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20399237, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9106657}. Nucleus membrane {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18827403}. Note=Cytoplasmic when non-complexed. Forms a cyclin D-CDK4 complex in the cytoplasm as cells progress through G(1) phase. The complex accumulates on the nuclear membrane and enters the nucleus on transition from G(1) to S phase. Also present in nucleoli and heterochromatin lumps. Colocalizes with RB1 after release into the nucleus. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18827403}. |
| Structure SUBUNIT: Component of the D-CDK4 complex, composed of CDK4 and some D-type G1 cyclin (CCND1, CCND2 or CCND3). Interacts directly in the complex with CCND1, CCND2 or CCND3. Interacts with SEI1 and ZNF655. Forms a ternary complex, cyclin D-CDK4-CDKN1B, involved in modulating CDK4 enzymatic activity. Interacts directly with CDKN1B (phosphorylated on 'Tyr-88' and 'Tyr-89'); the interaction allows assembly of the cyclin D-CDK4 complex, Thr-172 phosphorylation, nuclear translocation and enhances the cyclin D-CDK4 complex activity. CDK4 activity is either inhibited or enhanced depending on stoichiometry of complex. The non-tyrosine-phosphorylated form of CDKN1B prevents T-loop phosphorylation of CDK4 producing inactive CDK4. Interacts (unphosphorylated form) with CDK2. Also forms ternary complexes with CDKN1A or CDKN2A. Interacts directly with CDKN1A (via its N-terminal); the interaction promotes the assembly of the cyclin D-CDK4 complex, its nuclear translocation and promotes the cyclin D-dependent enzyme activity of CDK4. Interacts with CCND1; the interaction is prevented with the binding of CCND1 to INSM1 during cell cycle progression. Probably forms a complex composed of chaperones HSP90 and HSP70, co-chaperones CDC37, PPP5C, TSC1 and client protein TSC2, CDK4, AKT, RAF1 and NR3C1; this complex does not contain co-chaperones STIP1/HOP and PTGES3/p23 (PubMed:29127155). Interacts with CEBPA (when phosphorylated) (PubMed:15107404). Interacts with FNIP1 and FNIP2 (PubMed:27353360). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P30285, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10580009, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15107404, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15558030, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16782892, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18827403, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19075005, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19124461, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19237555, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19237565, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20399237, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27353360, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29127155, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9106657}. |
| Post-translational modification PTM: Phosphorylation at Thr-172 is required for enzymatic activity. Phosphorylated, in vitro, at this site by CCNH-CDK7, but, in vivo, appears to be phosphorylated by a proline-directed kinase. In the cyclin D-CDK4-CDKN1B complex, this phosphorylation and consequent CDK4 enzyme activity, is dependent on the tyrosine phosphorylation state of CDKN1B. Thus, in proliferating cells, CDK4 within the complex is phosphorylated on Thr-172 in the T-loop. In resting cells, phosphorylation on Thr-172 is prevented by the non-tyrosine-phosphorylated form of CDKN1B. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16782892, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19075005, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19237555, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19237565, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19487459}. |
| Involvement in disease DISEASE: Melanoma, cutaneous malignant 3 (CMM3) [MIM:609048]: A malignant neoplasm of melanocytes, arising de novo or from a pre-existing benign nevus, which occurs most often in the skin but may also involve other sites. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:7652577, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8528263, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9311594, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9425228}. Note=Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: P11802 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
 |
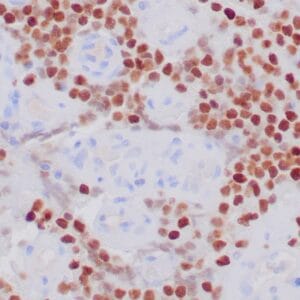
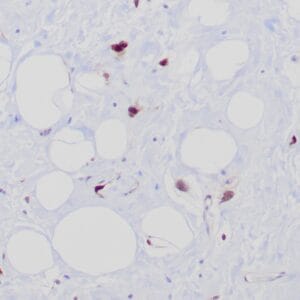
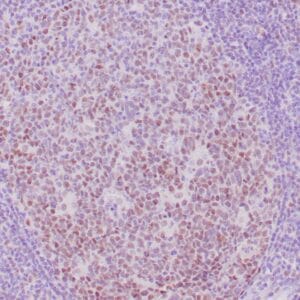
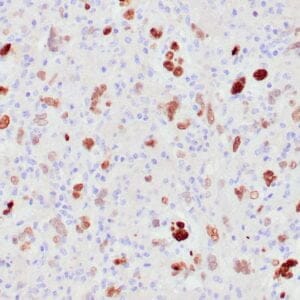
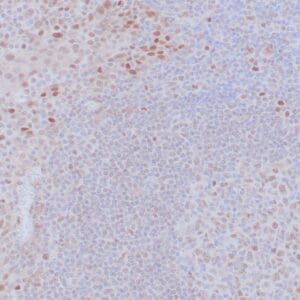
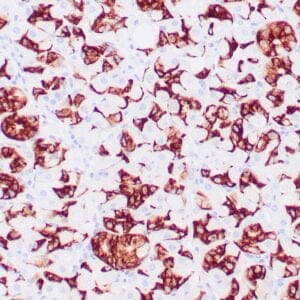
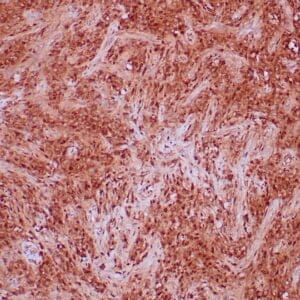
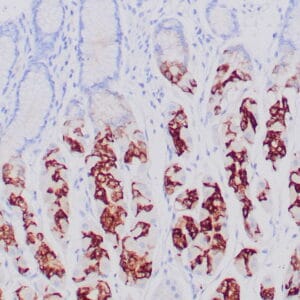
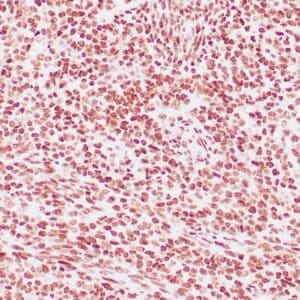
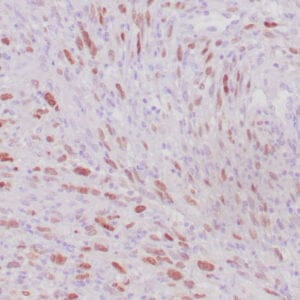
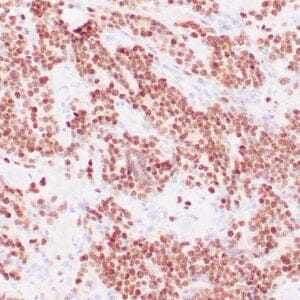
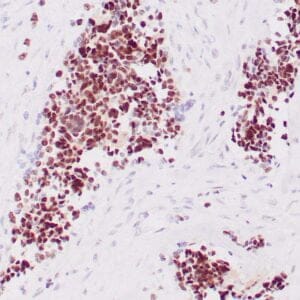
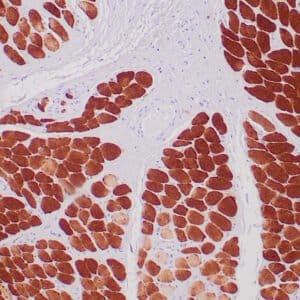
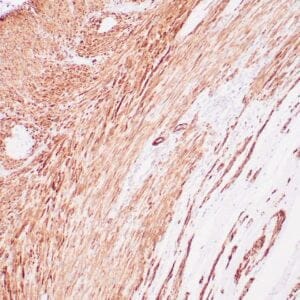
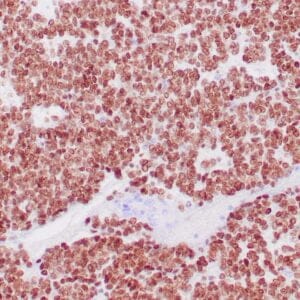
| Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human liposarcoma stained with anti-CDK4 antibody using peroxidase-conjugate and DAB chromogen. Note nuclear/cytoplasmic staining of tumor cells. |
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
| IHC |
Documents
| # | SDS | Certificate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | |||
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.