| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| host | rabbit |
| isotype | IgG |
| clonality | polyclonal |
| concentration | 1 mg/mL |
| applications | ICC/IF, WB |
| reactivity | AMPKα 2 |
| available sizes | 100 µg |
rabbit anti-AMPK α 2 polyclonal antibody 4805
$518.00
Antibody summary
- Rabbit polyclonal to AMPK α 2
- Suitable for: WB,IP
- Isotype: Whole IgG
- 100 µg
rabbit anti-AMPK α 2 polyclonal antibody 4805
| antibody |
|---|
| Tested applications WB,IP |
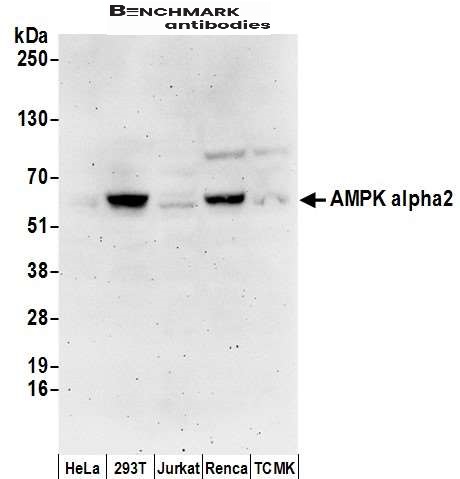
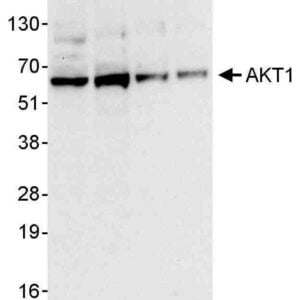
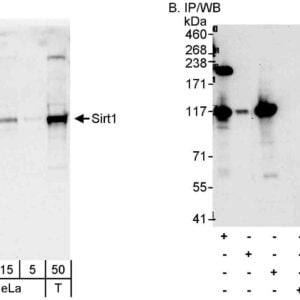
| Recommended dilutions Immunoblotting: use at 0.2-2ug/mLDetection of human and mouse AMPK alpha 2 in whole cell lysates (50 ug) of HeLa, 293T, Jurkat, mouse Renca, and mouse TCMK-1 cells with #13010 at 0.4ug/mL. |
| Immunogen Synthetic peptide representing a portion of the protein encoded within exon 7. |
| Size and concentration 100µg and lot specific |
| Form liquid |
| Storage Instructions This antibody is stable at 2-8°C for 1 year. |
| Storage buffer Tris-citrate/phosphate buffer, pH 7 to 8 contai |
| Purity immunogen affinity purification |
| Clonality polyclonal |
| Isotype IgG |
| Compatible secondaries goat anti-rabbit IgG, H&L chain specific, peroxidase conjugated, conjugated polyclonal antibody 9512 goat anti-rabbit IgG, H&L chain specific, biotin conjugated polyclonal antibody 2079 goat anti-rabbit IgG, H&L chain specific, FITC conjugated polyclonal antibody 7863 goat anti-rabbit IgG, H&L chain specific, Cross Absorbed polyclonal antibody 2371 goat anti-rabbit IgG, H&L chain specific, biotin conjugated polyclonal antibody, crossabsorbed 1715 goat anti-rabbit IgG, H&L chain specific, FITC conjugated polyclonal antibody, crossabsorbed 1720 |
| Isotype control Rabbit polyclonal - Isotype Control |
| target relevance |
|---|
| Protein names 5'-AMP-activated protein kinase catalytic subunit alpha-2 (AMPK subunit alpha-2) (EC 2.7.11.1) (Acetyl-CoA carboxylase kinase) (ACACA kinase) (Hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase kinase) (HMGCR kinase) (EC 2.7.11.31) |
| Gene names PRKAA2,PRKAA2 AMPK AMPK2 |
| Protein family Protein kinase superfamily, CAMK Ser/Thr protein kinase family, SNF1 subfamily |
| Mass 62320Da |
| Function FUNCTION: Catalytic subunit of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), an energy sensor protein kinase that plays a key role in regulating cellular energy metabolism (PubMed:17307971, PubMed:17712357). In response to reduction of intracellular ATP levels, AMPK activates energy-producing pathways and inhibits energy-consuming processes: inhibits protein, carbohydrate and lipid biosynthesis, as well as cell growth and proliferation (PubMed:17307971, PubMed:17712357). AMPK acts via direct phosphorylation of metabolic enzymes, and by longer-term effects via phosphorylation of transcription regulators (PubMed:17307971, PubMed:17712357). Regulates lipid synthesis by phosphorylating and inactivating lipid metabolic enzymes such as ACACA, ACACB, GYS1, HMGCR and LIPE; regulates fatty acid and cholesterol synthesis by phosphorylating acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACACA and ACACB) and hormone-sensitive lipase (LIPE) enzymes, respectively (PubMed:7959015). Promotes lipolysis of lipid droplets by mediating phosphorylation of isoform 1 of CHKA (CHKalpha2) (PubMed:34077757). Regulates insulin-signaling and glycolysis by phosphorylating IRS1, PFKFB2 and PFKFB3 (By similarity). Involved in insulin receptor/INSR internalization (PubMed:25687571). AMPK stimulates glucose uptake in muscle by increasing the translocation of the glucose transporter SLC2A4/GLUT4 to the plasma membrane, possibly by mediating phosphorylation of TBC1D4/AS160 (By similarity). Regulates transcription and chromatin structure by phosphorylating transcription regulators involved in energy metabolism such as CRTC2/TORC2, FOXO3, histone H2B, HDAC5, MEF2C, MLXIPL/ChREBP, EP300, HNF4A, p53/TP53, SREBF1, SREBF2 and PPARGC1A (PubMed:11518699, PubMed:11554766, PubMed:15866171, PubMed:17711846, PubMed:18184930). Acts as a key regulator of glucose homeostasis in liver by phosphorylating CRTC2/TORC2, leading to CRTC2/TORC2 sequestration in the cytoplasm (By similarity). In response to stress, phosphorylates 'Ser-36' of histone H2B (H2BS36ph), leading to promote transcription (By similarity). Acts as a key regulator of cell growth and proliferation by phosphorylating FNIP1, TSC2, RPTOR, WDR24 and ATG1/ULK1: in response to nutrient limitation, negatively regulates the mTORC1 complex by phosphorylating RPTOR component of the mTORC1 complex and by phosphorylating and activating TSC2 (PubMed:14651849, PubMed:20160076, PubMed:21205641). Also phosphorylates and inhibits GATOR2 subunit WDR24 in response to nutrient limitation, leading to suppress glucose-mediated mTORC1 activation (PubMed:36732624). In response to energetic stress, phosphorylates FNIP1, inactivating the non-canonical mTORC1 signaling, thereby promoting nuclear translocation of TFEB and TFE3, and inducing transcription of lysosomal or autophagy genes (PubMed:37079666). In response to nutrient limitation, promotes autophagy by phosphorylating and activating ATG1/ULK1 (PubMed:21205641). In that process, it also activates WDR45/WIPI4 (PubMed:28561066). Phosphorylates CASP6, thereby preventing its autoprocessing and subsequent activation (PubMed:32029622). AMPK also acts as a regulator of circadian rhythm by mediating phosphorylation of CRY1, leading to destabilize it (By similarity). May regulate the Wnt signaling pathway by phosphorylating CTNNB1, leading to stabilize it (By similarity). Also acts as a regulator of cellular polarity by remodeling the actin cytoskeleton; probably by indirectly activating myosin (PubMed:17486097). Also phosphorylates CFTR, EEF2K, KLC1, NOS3 and SLC12A1 (PubMed:12519745, PubMed:20074060). Plays an important role in the differential regulation of pro-autophagy (composed of PIK3C3, BECN1, PIK3R4 and UVRAG or ATG14) and non-autophagy (composed of PIK3C3, BECN1 and PIK3R4) complexes, in response to glucose starvation (By similarity). Can inhibit the non-autophagy complex by phosphorylating PIK3C3 and can activate the pro-autophagy complex by phosphorylating BECN1 (By similarity). Upon glucose starvation, promotes ARF6 activation in a kinase-independent manner leading to cell migration (PubMed:36017701). Upon glucose deprivation mediates the phosphorylation of ACSS2 at 'Ser-659', which exposes the nuclear localization signal of ACSS2, required for its interaction with KPNA1 and nuclear translocation (PubMed:28552616). Upon stress, regulates mitochondrial fragmentation through phosphorylation of MTFR1L (PubMed:36367943). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q09137, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8BRK8, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11518699, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11554766, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12519745, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14651849, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15866171, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17486097, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17711846, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18184930, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20074060, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20160076, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21205641, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25687571, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28552616, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28561066, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32029622, ECO:0000269|PubMed:34077757, ECO:0000269|PubMed:36017701, ECO:0000269|PubMed:36367943, ECO:0000269|PubMed:36732624, ECO:0000269|PubMed:37079666, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7959015, ECO:0000303|PubMed:17307971, ECO:0000303|PubMed:17712357}. |
| Catalytic activity CATALYTIC ACTIVITY: Reaction=L-seryl-[protein] + ATP = O-phospho-L-seryl-[protein] + ADP + H(+); Xref=Rhea:RHEA:17989, Rhea:RHEA-COMP:9863, Rhea:RHEA-COMP:11604, ChEBI:CHEBI:15378, ChEBI:CHEBI:29999, ChEBI:CHEBI:30616, ChEBI:CHEBI:83421, ChEBI:CHEBI:456216; EC=2.7.11.1; Evidence={ECO:0000269|PubMed:28552616, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32029622, ECO:0000269|PubMed:36732624, ECO:0000269|PubMed:37079666}; CATALYTIC ACTIVITY: Reaction=L-threonyl-[protein] + ATP = O-phospho-L-threonyl-[protein] + ADP + H(+); Xref=Rhea:RHEA:46608, Rhea:RHEA-COMP:11060, Rhea:RHEA-COMP:11605, ChEBI:CHEBI:15378, ChEBI:CHEBI:30013, ChEBI:CHEBI:30616, ChEBI:CHEBI:61977, ChEBI:CHEBI:456216; EC=2.7.11.1; Evidence={ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q09137}; CATALYTIC ACTIVITY: Reaction=L-seryl-[acetyl-CoA carboxylase] + ATP = O-phospho-L-seryl-[acetyl-CoA carboxylase] + ADP + H(+); Xref=Rhea:RHEA:20333, Rhea:RHEA-COMP:13722, Rhea:RHEA-COMP:13723, ChEBI:CHEBI:15378, ChEBI:CHEBI:29999, ChEBI:CHEBI:30616, ChEBI:CHEBI:83421, ChEBI:CHEBI:456216; Evidence={ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q09137}; CATALYTIC ACTIVITY: Reaction=L-seryl-[3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase] + ATP = O-phospho-L-seryl-[3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase] + ADP + H(+); Xref=Rhea:RHEA:23172, Rhea:RHEA-COMP:13692, Rhea:RHEA-COMP:13693, ChEBI:CHEBI:15378, ChEBI:CHEBI:29999, ChEBI:CHEBI:30616, ChEBI:CHEBI:83421, ChEBI:CHEBI:456216; EC=2.7.11.31; Evidence={ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q09137}; |
| Subellular location SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: Cytoplasm {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8BRK8}. Nucleus {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15866171}. Note=In response to stress, recruited by p53/TP53 to specific promoters. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15866171}. |
| Structure SUBUNIT: AMPK is a heterotrimer of an alpha catalytic subunit (PRKAA1 or PRKAA2), a beta (PRKAB1 or PRKAB2) and a gamma non-catalytic subunits (PRKAG1, PRKAG2 or PRKAG3) (PubMed:21543851). Interacts with FNIP1 and FNIP2. Associates with internalized insulin receptor/INSR complexes on Golgi/endosomal membranes; PRKAA2/AMPK2 together with ATIC and HACD3/PTPLAD1 is proposed to be part of a signaling network regulating INSR autophosphorylation and endocytosis (PubMed:25687571). Interacts with ARF6 (PubMed:36017701). The phosphorylated form at Thr-172 mediated by CamKK2 interacts with ACSS2 (PubMed:28552616). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21543851, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25687571, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28552616, ECO:0000269|PubMed:36017701}. |
| Post-translational modification PTM: Ubiquitinated. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8BRK8}.; PTM: Phosphorylated at Thr-172 by STK11/LKB1 in complex with STE20-related adapter-alpha (STRADA) pseudo kinase and CAB39. Also phosphorylated at Thr-172 by CAMKK2; triggered by a rise in intracellular calcium ions, without detectable changes in the AMP/ATP ratio. CAMKK1 can also phosphorylate Thr-172, but at much lower level. Dephosphorylated by protein phosphatase 2A and 2C (PP2A and PP2C). Phosphorylated by ULK1; leading to negatively regulate AMPK activity and suggesting the existence of a regulatory feedback loop between ULK1 and AMPK. Dephosphorylated by PPM1A and PPM1B at Thr-172 (mediated by STK11/LKB1). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15980064, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21460634}. |
| Domain DOMAIN: The AIS (autoinhibitory sequence) region shows some sequence similarity with the ubiquitin-associated domains and represses kinase activity. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q13131}. |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: P54646 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
| Western blot |
Documents
| # | SDS | Certificate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | |||
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.



Reviews
There are no reviews yet.