| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| host | mouse |
| isotype | IgG1 |
| clonality | monoclonal |
| concentration | 1 mg/mL |
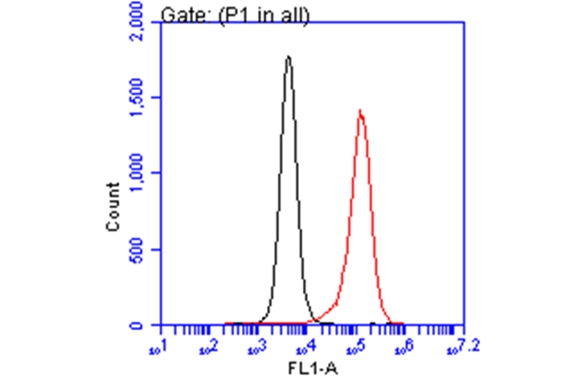
| applications | ICC/IF, WB |
| reactivity | TSG101 |
| available sizes | 100 µL |
mouse anti-TSG101 monoclonal antibody (4A10) 4454
$503.00
Antibody summary
- Mouse monoclonal to TSG101
- Suitable for: WB,ICC/IF,IHC-P,FACS,IP,ELISA,EM,IHC,IHC
- Isotype: IgG1
- 100 µl
mouse anti-TSG101 monoclonal antibody (4A10) 4454
| antibody |
|---|
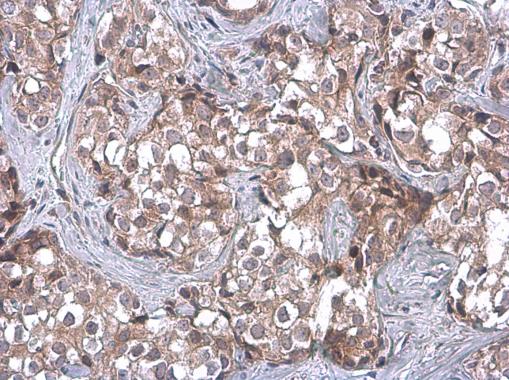
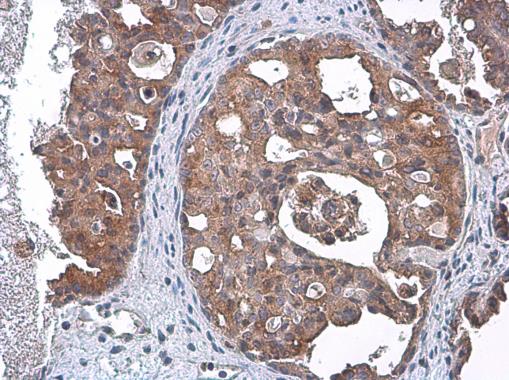
| Tested applications WB,IHC,IHC,ICC/IF |
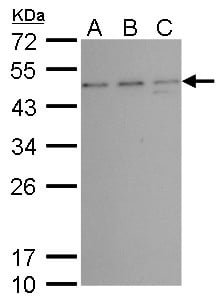
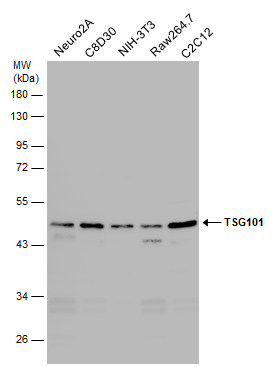
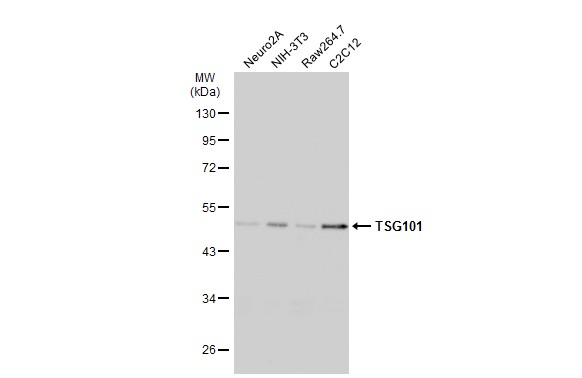
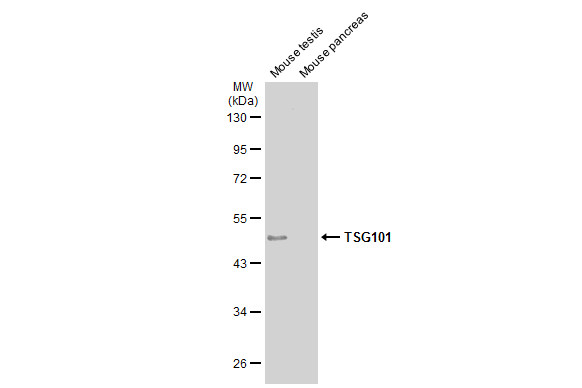
| Recommended dilutions ELISA: use at 1-5ug/ml. Immunoblotting: use at a 1:500-1:3,000 dilution. A band of 46kDa is detected. Detection of TSG101 protein in (A) NIH-3T3 cell lysate, (B) JC cell lysate, and (C) BCL-1 cell lysate with #3352 diluted 1:500. Endusers should determine optimal antibody concentra |
| Immunogen Recombinant protein corresponding to aa 167-374 of TSG101 protein |
| Size and concentration 100µL and lot specific |
| Form liquid |
| Storage Instructions This product is stable for at least one (1) year if stored at -20°C. Store product in appropriate aliquots to avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Storage buffer PBS, pH 7.2. |
| Purity affinity purified |
| Clonality monoclonal |
| Isotype IgG1 |
| Compatible secondaries goat anti-mouse IgG, H&L chain specific, peroxidase conjugated polyclonal antibody 5486 goat anti-mouse IgG, H&L chain specific, biotin conjugated, Conjugate polyclonal antibody 2685 goat anti-mouse IgG, H&L chain specific, FITC conjugated polyclonal antibody 7854 goat anti-mouse IgG, H&L chain specific, peroxidase conjugated polyclonal antibody, crossabsorbed 1706 goat anti-mouse IgG, H&L chain specific, biotin conjugated polyclonal antibody, crossabsorbed 1716 goat anti-mouse IgG, H&L chain specific, FITC conjugated polyclonal antibody, crossabsorbed 1721 |
| Isotype control Mouse monocolonal IgG1 - Isotype Control |
| target relevance |
|---|
| Protein names Tumor susceptibility gene 101 protein (ESCRT-I complex subunit TSG101) |
| Gene names TSG101,TSG101 |
| Protein family Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme family, UEV subfamily |
| Mass 43944Da |
| Function FUNCTION: Component of the ESCRT-I complex, a regulator of vesicular trafficking process. Binds to ubiquitinated cargo proteins and is required for the sorting of endocytic ubiquitinated cargos into multivesicular bodies (MVBs). Mediates the association between the ESCRT-0 and ESCRT-I complex. Required for completion of cytokinesis; the function requires CEP55. May be involved in cell growth and differentiation. Acts as a negative growth regulator. Involved in the budding of many viruses through an interaction with viral proteins that contain a late-budding motif P-[ST]-A-P. This interaction is essential for viral particle budding of numerous retroviruses. Required for the exosomal release of SDCBP, CD63 and syndecan (PubMed:22660413). It may also play a role in the extracellular release of microvesicles that differ from the exosomes (PubMed:22315426). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11916981, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17556548, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17853893, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21070952, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21757351, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22315426, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22660413}. |
| Subellular location SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: Cytoplasm {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17853893}. Early endosome membrane {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23166352}; Peripheral membrane protein {ECO:0000305|PubMed:23166352}; Cytoplasmic side {ECO:0000305|PubMed:23166352}. Late endosome membrane {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11916981, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17229889}; Peripheral membrane protein. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center, centrosome {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17853893}. Midbody, Midbody ring {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17556548, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17853893}. Nucleus {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17229889}. Note=Mainly cytoplasmic. Membrane-associated when active and soluble when inactive. Nuclear localization is cell cycle-dependent. Interaction with CEP55 is required for localization to the midbody during cytokinesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17556548, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17853893}. |
| Tissues TISSUE SPECIFICITY: Heart, brain, placenta, lung, liver, skeletal, kidney and pancreas. |
| Structure SUBUNIT: Component of the ESCRT-I complex (endosomal sorting complex required for transport I) which consists of TSG101, VPS28, a VPS37 protein (VPS37A to -D) and MVB12A or MVB12B in a 1:1:1:1 stoichiometry (PubMed:18005716). Interacts with VPS37A, VPS37B and VPS37C (PubMed:15218037, PubMed:15509564). Interacts with DMAP1 (PubMed:10888872). Interacts with ubiquitin (PubMed:11595185). Interacts with stathmin, GMCL and AATF (By similarity). Component of an ESCRT-I complex (endosomal sorting complex required for transport I) which consists of TSG101, VPS28, VPS37A and UBAP1 in a 1:1:1:1 stoichiometry (PubMed:21757351). Interacts with HGS; the interaction mediates the association with the ESCRT-0 complex. Interacts with GGA1 and GGA3 (PubMed:15039775, PubMed:15143060). Interacts (via UEV domain) with PDCD6IP/AIP1 (PubMed:14505570, PubMed:14519844). Interacts with VPS28, SNF8 and VPS36 (PubMed:14505570). Self-associates (PubMed:14505570, PubMed:14519844). Interacts with MVB12A; the association appears to be mediated by the TSG101-VPS37 binary subcomplex. Interacts with VPS37D. Interacts with LRSAM1. Interacts with CEP55; the interaction is required for cytokinesis but not for viral budding (PubMed:17853893). Interacts with PDCD6 (PubMed:18256029). Interacts with LITAF (PubMed:23166352). Interacts with MGRN1 (PubMed:17229889). Interacts with ARRDC1; recruits TSG101 to the plasma membrane (PubMed:21191027, PubMed:22315426). {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q6IRE4, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10888872, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14505570, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15039775, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15053872, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15143060, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15218037, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15509564, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15858022, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17229889, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17556548, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17853893, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18005716, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18256029, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19520058, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19703557, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21191027, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21757351, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22315426, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23166352}.; SUBUNIT: (Microbial infection) Interacts with HIV-1 p6. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11427703, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11595185, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12900394, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21070952, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21643473}.; SUBUNIT: (Microbial infection) Interacts with human spumavirus Gag. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15858022}.; SUBUNIT: (Microbial infection) Interacts with HTLV-1 Gag. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:14581525}.; SUBUNIT: (Microbial infection) Interacts with Ebola virus VP40. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12559917}.; SUBUNIT: (Microbial infection) Interacts with EIAV p9; the interaction has been shown in vitro. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:14519844}.; SUBUNIT: (Microbial infection) Interacts with Lassa virus protein Z. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16571837}.; SUBUNIT: (Microbial infection) Interacts with hepatitis E virus protein ORF3. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21068219}. |
| Post-translational modification PTM: Monoubiquitinated at multiple sites by LRSAM1 and by MGRN1. Ubiquitination inactivates it, possibly by regulating its shuttling between an active membrane-bound protein and an inactive soluble form. Ubiquitination by MGRN1 requires the presence of UBE2D1. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15256501, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17229889, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19703557}. |
| Domain DOMAIN: The UEV domain is required for the interaction of the complex with ubiquitin. It also mediates the interaction with PTAP/PSAP motifs of HIV-1 P6 protein and human spumaretrovirus Gag protein.; DOMAIN: The coiled coil domain may interact with stathmin.; DOMAIN: The UEV domain binds ubiquitin and P-[ST]-A-P peptide motif independently. |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: Q99816 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 38339765 | Bioengineered small extracellular vesicles deliver multiple SARS-CoV-2 antigenic fragments and drive a broad immunological response. | Hannah K Jackson, Heather M Long, Juan Carlos Yam-Puc, Roberta Palmulli, Tracey A Haigh, Pehuén Pereyra Gerber, Jin S Lee, Nicholas J Matheson, Lesley Young, John Trowsdale, Mathew Lo, Graham S Taylor, James E Thaventhiran, James R Edgar | J Extracell Vesicles 13:e12412 |
| 38339765 | Bioengineered small extracellular vesicles deliver multiple SARS-CoV-2 antigenic fragments and drive a broad immunological response. | Hannah K Jackson, Heather M Long, Juan Carlos Yam-Puc, Roberta Palmulli, Tracey A Haigh, Pehuén Pereyra Gerber, Jin S Lee, Nicholas J Matheson, Lesley Young, John Trowsdale, Mathew Lo, Graham S Taylor, James E Thaventhiran, James R Edgar | J Extracell Vesicles 13:e12412 |
| 38338867 | CD99 Modulates the Proteomic Landscape of Ewing Sarcoma Cells and Related Extracellular Vesicles. | Alessandra De Feo, Marcello Manfredi, Caterina Mancarella, Joaquín J Maqueda, Veronica De Giorgis, Ymera Pignochino, Marika Sciandra, Camilla Cristalli, Massimo Donadelli, Katia Scotlandi | Int J Mol Sci 25:N/A |
| 38338867 | CD99 Modulates the Proteomic Landscape of Ewing Sarcoma Cells and Related Extracellular Vesicles. | Alessandra De Feo, Marcello Manfredi, Caterina Mancarella, Joaquín J Maqueda, Veronica De Giorgis, Ymera Pignochino, Marika Sciandra, Camilla Cristalli, Massimo Donadelli, Katia Scotlandi | Int J Mol Sci 25:N/A |
| 38225453 | Deep proteomic analysis of obstetric antiphospholipid syndrome by DIA-MS of extracellular vesicle enriched fractions. | Wenmin Tian, Dongxue Shi, Yinmei Zhang, Hongli Wang, Haohao Tang, Zhongyu Han, Catherine C L Wong, Liyan Cui, Jiajia Zheng, Yang Chen | Commun Biol 7:99 |
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
| Western blot IHC ICC |
Documents
| # | SDS | Certificate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | |||
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.















Reviews
There are no reviews yet.