| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| host | mouse |
| isotype | IgG1 + IgG1 |
| clonality | monoclonal |
| concentration | concentrate, predilute |
| applications | IHC |
| reactivity | human |
| available size | 0.1 mL, 0.5 mL, 1 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted |
mouse anti-Thyroglobulin monoclonal antibody (2H11+6E1) 6383
Price range: $160.00 through $528.00
Antibody summary
- Mouse monoclonal to Thyroglobulin
- Suitable for: Immunohistochemistry (formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues)
- Reacts with: Human
- Isotype:IgG1 + IgG1
- Control: Thyroid
- Visualization: Cytoplasmic
- 0.1, 0.5, 1.0 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted
mouse anti-Thyroglobulin monoclonal antibody 2H11+6E1 6383
| target relevance |
|---|
| Protein names Thyroglobulin (Tg) |
| Gene names TG,TG |
| Protein family Type-B carboxylesterase/lipase family |
| Mass 304790Da |
| Function FUNCTION: Acts as a substrate for the production of iodinated thyroid hormones thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) (PubMed:17532758, PubMed:32025030). The synthesis of T3 and T4 involves iodination of selected tyrosine residues of TG/thyroglobulin followed by their oxidative coupling in the thyroid follicle lumen (PubMed:32025030). Following TG re-internalization and lysosomal-mediated proteolysis, T3 and T4 are released from the polypeptide backbone leading to their secretion into the bloodstream (PubMed:32025030). One dimer produces 7 thyroid hormone molecules (PubMed:32025030). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17532758, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32025030}. |
| Subellular location SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: Secreted {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11082042, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19509106, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8626858}. Note=Secreted into the thyroid follicle lumen (PubMed:19509106). Localizes to colloid globules, a structure formed in the thyroid follicle lumen consisting of cross-linked TG arranged in concentric layers (PubMed:11082042, PubMed:8626858). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11082042, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19509106, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8626858}. |
| Tissues TISSUE SPECIFICITY: Specifically expressed in the thyroid gland. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11082042, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19509106, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8626858}. |
| Structure SUBUNIT: Monomer (PubMed:32025030). Homodimer (via ChEL region); occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum and is required for export to the Golgi apparatus (PubMed:32025030). Homooligomer; disulfide-linked; stored in this form in the thyroid follicle lumen (PubMed:8626858). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:32025030, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8626858}. |
| Post-translational modification PTM: Iodinated on tyrosine residues by TPO (PubMed:2760035, PubMed:32025030). There are 4 pairs of iodinated tyrosines used for coupling: acceptor Tyr-24 is coupled to donor Tyr-149 or Tyr-234, acceptor Tyr-2573 is coupled to donor Tyr-2540, acceptor Tyr-2766 in monomer 1 is coupled to donor Tyr-2766 in monomer 2 and acceptor Tyr-1310 in monomer 1 is coupled to donor Tyr-108 in monomer 2 (PubMed:32025030). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:2760035, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32025030}.; PTM: Sulfated tyrosines are desulfated during iodination. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10448091}.; PTM: Undergoes sequential proteolysis by cathepsins to release thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) hormones. In the thyroid follicle lumen, cross-linked TG (storage form) is solubilized by limited proteolysis mediated by cathepsins CTSB and/or CTSL. Partially cleaved TG is further processed by CTSK/cathepsin K and/or CTSL resulting in the release of T4. Following endocytosis, further processing occurs leading to the release of T3 and more T4 hormones. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O08710}. |
| Domain DOMAIN: The cholinesterase-like (ChEL) region is required for dimerization and export from the endoplasmic reticulum. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O08710}. |
| Involvement in disease DISEASE: Thyroid dyshormonogenesis 3 (TDH3) [MIM:274700]: A disorder due to thyroid dyshormonogenesis, causing large goiters of elastic and soft consistency in the majority of patients. Although the degree of thyroid dysfunction varies considerably among patients with defective thyroglobulin synthesis, patients usually have a relatively high serum free triiodothyronine (T3) concentration with disproportionately low free tetraiodothyronine (T4) level. The maintenance of relatively high free T3 levels prevents profound tissue hypothyroidism except in brain and pituitary, which are dependent on T4 supply, resulting in neurologic and intellectual defects in some cases. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10199792, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16477365, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17244789, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17532758, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19509106, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27305979}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Autoimmune thyroid disease 3 (AITD3) [MIM:608175]: A complex autoimmune disorder comprising two related diseases affecting the thyroid: Graves disease and Hashimoto thyroiditis. In both disorders, thyroid-reactive T-cells are formed and infiltrate the thyroid gland. In Graves disease, the majority of the T-cells undergo a Th2 differentiation and activate B-cells to produce antibodies against the TSH receptor, which stimulate the thyroid and cause clinical hyperthyroidism. In contrast, Hashimoto thyroiditis is characterized by Th1 switching of the thyroid-infiltrating T-cells, which induces apoptosis of thyroid follicular cells and clinical hypothyroidism. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10199792, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14657345}. Note=Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: P01266 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
 |
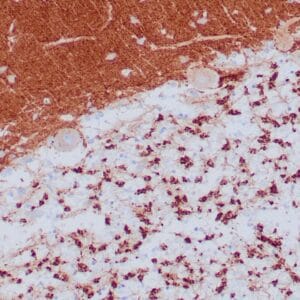
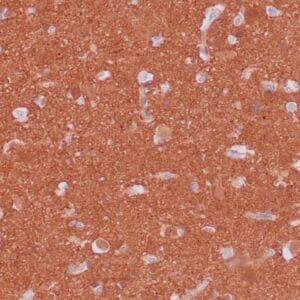
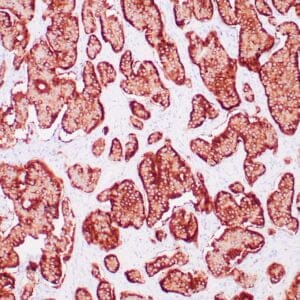
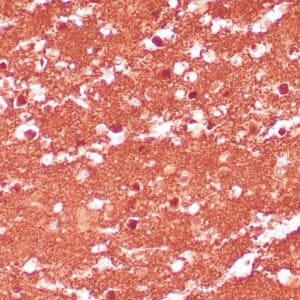
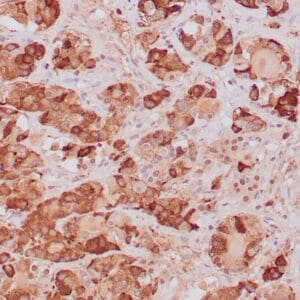
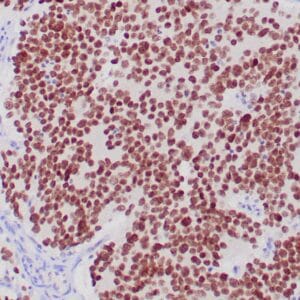
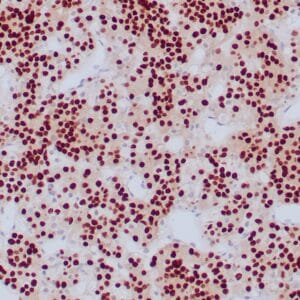
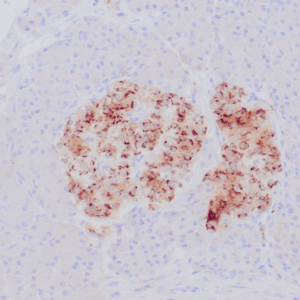
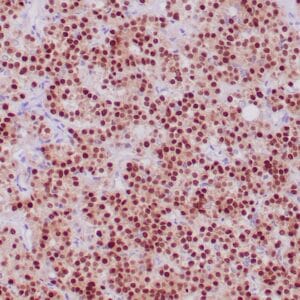
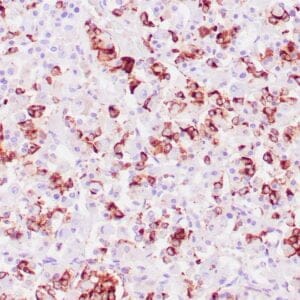
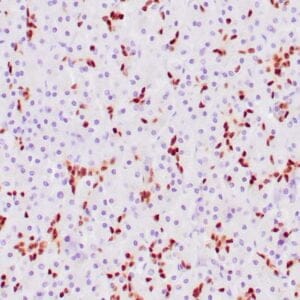
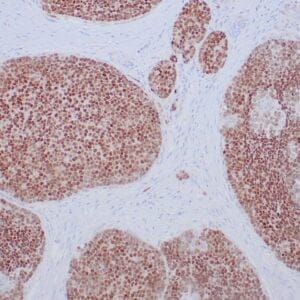
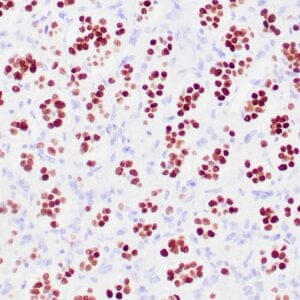
| Human thyroid gland stained with anti-thyroglobulin antibody using peroxidase-conjugate and DAB chromogen. Note the cytoplasmic of follicular cells. |
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
| IHC |
Documents
| # | SDS | Certificate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | |||
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.