| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| host | mouse |
| isotype | IgG1 / IgG1 |
| clonality | monoclonal |
| concentration | concentrate, predilute |
| applications | IHC |
| reactivity | human |
| available size | 0.1 mL, 0.5 mL, 1 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted |
mouse anti-MiTF (Microphthalmia) monoclonal antibody (C5&D5) 6256
Price range: $160.00 through $528.00
Antibody summary
- Mouse monoclonal to MiTF (Microphthalmia)
- Suitable for: Immunohistochemistry (formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues)
- Reacts with: Human
- Isotype:IgG1 / IgG1
- Control: Melanoma
- Visualization: Nuclear
- 0.1, 0.5, 1.0 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted
mouse anti-MiTF (Microphthalmia) monoclonal antibody C5&D5 6256
| target relevance |
|---|
| Protein names Microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (Class E basic helix-loop-helix protein 32) (bHLHe32) |
| Gene names MITF,MITF BHLHE32 |
| Protein family MiT/TFE family |
| Mass 58795Da |
| Function FUNCTION: Transcription factor that acts as a master regulator of melanocyte survival and differentiation as well as melanosome biogenesis (PubMed:10587587, PubMed:22647378, PubMed:27889061, PubMed:9647758). Binds to M-boxes (5'-TCATGTG-3') and symmetrical DNA sequences (E-boxes) (5'-CACGTG-3') found in the promoter of pigmentation genes, such as tyrosinase (TYR) (PubMed:10587587, PubMed:22647378, PubMed:27889061, PubMed:9647758). Involved in the cellular response to amino acid availability by acting downstream of MTOR: in the presence of nutrients, MITF phosphorylation by MTOR promotes its inactivation (PubMed:36608670). Upon starvation or lysosomal stress, inhibition of MTOR induces MITF dephosphorylation, resulting in transcription factor activity (PubMed:36608670). Plays an important role in melanocyte development by regulating the expression of tyrosinase (TYR) and tyrosinase-related protein 1 (TYRP1) (PubMed:10587587, PubMed:22647378, PubMed:27889061, PubMed:9647758). Plays a critical role in the differentiation of various cell types, such as neural crest-derived melanocytes, mast cells, osteoclasts and optic cup-derived retinal pigment epithelium (PubMed:10587587, PubMed:22647378, PubMed:27889061, PubMed:9647758). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10587587, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22647378, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27889061, ECO:0000269|PubMed:36608670, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9647758}. |
| Subellular location SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: Nucleus {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16822840, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27889061, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28842328, ECO:0000269|PubMed:36608670}. Cytoplasm {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16822840, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28842328, ECO:0000269|PubMed:36608670}. Lysosome membrane {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23401004, ECO:0000269|PubMed:36608670}. Note=When nutrients are present, recruited to the lysosomal membrane via association with GDP-bound RagC/RRAGC (or RagD/RRAGD): it is then phosphorylated by MTOR (PubMed:23401004, PubMed:36608670). Phosphorylation by MTOR promotes ubiquitination and degradation (PubMed:36608670). Conversely, inhibition of mTORC1, starvation and lysosomal disruption, promotes dephosphorylation and translocation to the nucleus (PubMed:36608670). Phosphorylation by MARK3/cTAK1 promotes association with 14-3-3/YWHA adapters and retention in the cytosol (PubMed:16822840). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16822840, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23401004, ECO:0000269|PubMed:36608670}. |
| Tissues TISSUE SPECIFICITY: Expressed in melanocytes (at protein level). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28842328}.; TISSUE SPECIFICITY: [Isoform A2]: Expressed in the retinal pigment epithelium, brain, and placenta (PubMed:9647758). Expressed in the kidney (PubMed:10578055, PubMed:9647758). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10578055, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9647758}.; TISSUE SPECIFICITY: [Isoform C2]: Expressed in the kidney and retinal pigment epithelium. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10578055}.; TISSUE SPECIFICITY: [Isoform H1]: Expressed in the kidney. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10578055, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9647758}.; TISSUE SPECIFICITY: [Isoform H2]: Expressed in the kidney. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10578055, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9647758}.; TISSUE SPECIFICITY: [Isoform M1]: Expressed in melanocytes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20163701}.; TISSUE SPECIFICITY: [Isoform Mdel]: Expressed in melanocytes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20163701}. |
| Structure SUBUNIT: Homodimer or heterodimer; dimerization is mediated via the coiled coil region (PubMed:24631970). Efficient DNA binding requires dimerization with another bHLH protein (PubMed:14975237). Binds DNA in the form of homodimer or heterodimer with either TFE3, TFEB or TFEC (PubMed:15507434). Interacts with small GTPases Rag (RagA/RRAGA, RagB/RRAGB, RagC/RRAGC and/or RagD/RRAGD); promoting its recruitment to lysosomal membrane in the presence of nutrients (PubMed:23401004, PubMed:36608670). Interacts with KARS1 (PubMed:14975237). Identified in a complex with HINT1 and CTNNB1 (PubMed:22647378). Interacts with VSX2 (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q08874, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14975237, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15507434, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22647378, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23401004, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24631970, ECO:0000269|PubMed:36608670}. |
| Post-translational modification PTM: When nutrients are present, phosphorylation by MTOR at Ser-5 via non-canonical mTORC1 pathway promotes ubiquitination by the SCF(BTRC) complex, followed by degradation (PubMed:36608670). Phosphorylation at Ser-405 significantly enhances the ability to bind the tyrosinase promoter (PubMed:10587587). Phosphorylation by MARK3/cTAK1 at Ser-280 promotes association with 14-3-3/YWHA adapters and retention in the cytosol (PubMed:16822840). Phosphorylated at Ser-180 and Ser-516 following KIT signaling, triggering a short live activation: Phosphorylation at Ser-180 and Ser-516 by MAPK and RPS6KA1, respectively, activate the transcription factor activity but also promote ubiquitination and subsequent degradation by the proteasome (PubMed:10673502). Phosphorylated in response to blue light (415nm) (PubMed:28842328). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10587587, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10673502, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16822840, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28842328, ECO:0000269|PubMed:36608670}.; PTM: Ubiquitinated by the SCF(BTRC) and SCF(FBXW11) complexes following phosphorylation ar Ser-5 by MTOR, leading to its degradation by the proteasome (PubMed:36608670). Ubiquitinated following phosphorylation at Ser-180, leading to subsequent degradation by the proteasome (PubMed:10673502). Deubiquitinated by USP13, preventing its degradation (PubMed:10673502). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10673502, ECO:0000269|PubMed:36608670}. |
| Domain DOMAIN: The leucine zipper region is part of a larger coiled coil. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:24631970}. |
| Involvement in disease DISEASE: Waardenburg syndrome 2A (WS2A) [MIM:193510]: WS2 is a genetically heterogeneous, autosomal dominant disorder characterized by sensorineural deafness, pigmentary disturbances, and absence of dystopia canthorum. The frequency of deafness is higher in WS2 than in WS1. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28236341, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8589691, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9647758}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Tietz albinism-deafness syndrome (TADS) [MIM:103500]: An autosomal dominant disorder characterized by generalized hypopigmentation and congenital, bilateral, profound sensorineural deafness. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10851256}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Melanoma, cutaneous malignant 8 (CMM8) [MIM:614456]: A malignant neoplasm of melanocytes, arising de novo or from a pre-existing benign nevus, which occurs most often in the skin but may also involve other sites. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22012259, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22080950}. Note=Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Coloboma, osteopetrosis, microphthalmia, macrocephaly, albinism, and deafness (COMMAD) [MIM:617306]: An autosomal recessive syndrome characterized by severe microphthalmia, profound congenital sensorineural hearing loss, lack of pigment in the hair, skin, and eyes, macrocephaly, facial dysmorphism, and osteopetrosis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27889061}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. An allelic combination involving at least one dominant-negative mutation, inherited in a recessive manner, represents the underlying molecular mechanism leading to COMMAD syndrome. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27889061}.; DISEASE: Note=Variations affecting this gene are associated with susceptibility to pheochromocytomas and paragangliomas, rare neural crest-derived tumors with an approximate incidence of 1:300,000/year. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27680874}. |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: O75030 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
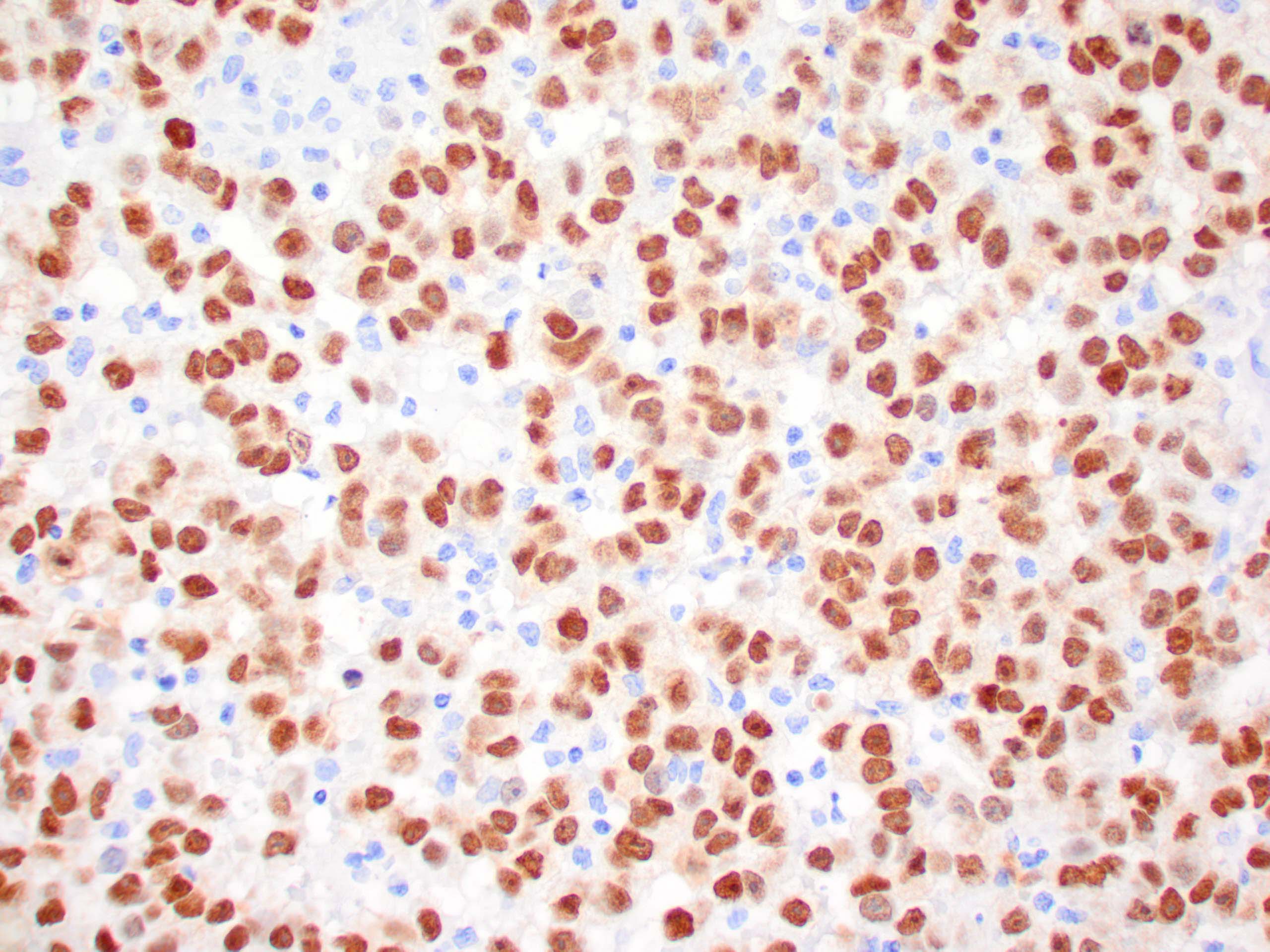 |
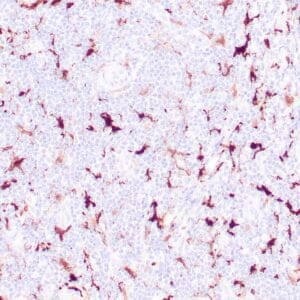
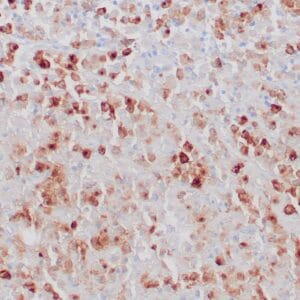
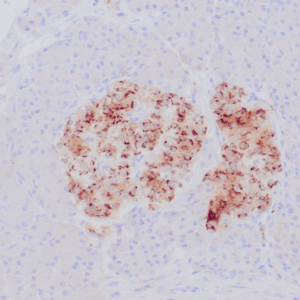
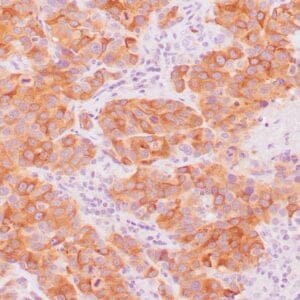
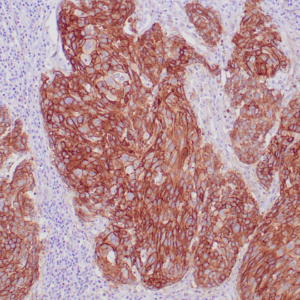
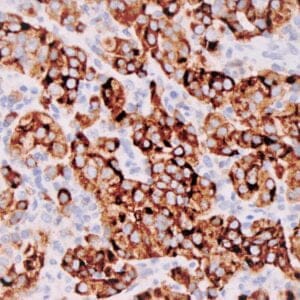
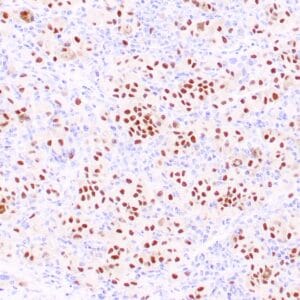
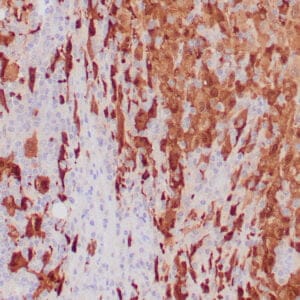
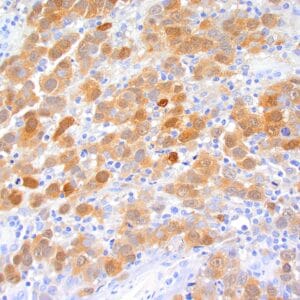
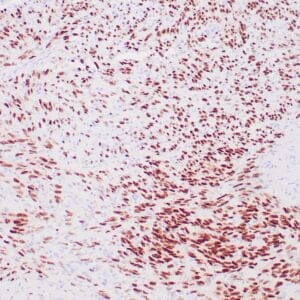
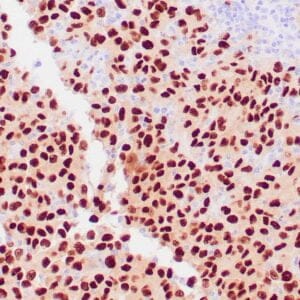
| Human melanoma stained with MiTF C5/D5 antibodies using peroxidase-conjugate and DAB chromogen. Note nuclear staining of tumor cells. |
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
| IHC |
Documents
| # | SDS | Certificate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | |||
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.