| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| host | mouse |
| isotype | IgG3 |
| clonality | monoclonal |
| concentration | concentrate, predilute |
| applications | IHC |
| reactivity | human |
| available size | 0.1 mL, 0.5 mL, 1 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted |
mouse anti-Cytokeratin 14 monoclonal antibody (LL002) 6135
Price range: $160.00 through $528.00
Antibody summary
- Mouse monoclonal to Cytokeratin 14
- Suitable for: Immunohistochemistry (formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues)
- Reacts with: Human
- Isotype:IgG3
- Control: Skin, tonsil or squamous cell carcinoma
- Visualization: Cytoplasmic
- 0.1, 0.5, 1.0 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted
mouse anti-Cytokeratin 14 monoclonal antibody LL002 6135
| antibody |
|---|
| Database link: human P02533 |
| Tested applications IHC |
| Recommended dilutions Concentrated 1:100-300 |
| Application Notes Positive control: Skin, tonsil or squamous cell carcinoma |
| Immunogen A synthetic peptide of 15 amino acid residues from the C-terminus of human keratin 14 |
| Size and concentration 7 mL prediluted or 0.1, 0.5, 1.0 mL and concentrated |
| Form liquid |
| Storage Instructions 2-8°C for short term, for longer term at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. |
| Purity affinity purified |
| Clonality monoclonal |
| Isotype IgG3 |
| Compatible secondaries goat anti-mouse IgG, H&L chain specific, peroxidase conjugated polyclonal antibody 5486 goat anti-mouse IgG, H&L chain specific, biotin conjugated, Conjugate polyclonal antibody 2685 goat anti-mouse IgG, H&L chain specific, FITC conjugated polyclonal antibody 7854 goat anti-mouse IgG, H&L chain specific, peroxidase conjugated polyclonal antibody, crossabsorbed 1706 goat anti-mouse IgG, H&L chain specific, biotin conjugated polyclonal antibody, crossabsorbed 1716 goat anti-mouse IgG, H&L chain specific, FITC conjugated polyclonal antibody, crossabsorbed 1721 |
| Isotype control Mouse monoclonal IgG3 - Isotype Control |
| target relevance |
|---|
| Protein names Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 14 (Cytokeratin-14) (CK-14) (Keratin-14) (K14) |
| Gene names KRT14,KRT14 |
| Protein family Intermediate filament family |
| Mass 51561Da |
| Function FUNCTION: The nonhelical tail domain is involved in promoting KRT5-KRT14 filaments to self-organize into large bundles and enhances the mechanical properties involved in resilience of keratin intermediate filaments in vitro. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11724817}. |
| Subellular location SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: Cytoplasm {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11724817, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31995743, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32179842}. Nucleus {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11724817}. Note=Expressed in both as a filamentous pattern. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11724817}. |
| Tissues TISSUE SPECIFICITY: Expressed in the corneal epithelium (at protein level) (PubMed:26758872). Detected in the basal layer, lowered within the more apically located layers specifically in the stratum spinosum, stratum granulosum but is not detected in stratum corneum. Strongly expressed in the outer root sheath of anagen follicles but not in the germinative matrix, inner root sheath or hair (PubMed:9457912). Found in keratinocytes surrounding the club hair during telogen (PubMed:9457912). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26758872, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9457912}. |
| Structure SUBUNIT: Heterotetramer of two type I and two type II keratins (By similarity). Forms a disulfide-linked heterodimer (via 2B domains) with KRT5 (via 2B domains) (PubMed:22705788, PubMed:24940650). Forms a heterodimer with KRT1; the interaction is more abundant in the absence of KRT5 (By similarity). Interacts with PLEC isoform 1C, when in a heterodimer with KRT5 (PubMed:24940650). Interacts with TRADD and with keratin filaments (PubMed:11684708). Associates with other type I keratins (PubMed:11724817). Interacts with EPPK1 (By similarity). Interacts with KLHL24 (PubMed:27798626). Interacts with PKP1 (via N-terminus) and PKP2 (PubMed:10852826). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q61781, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10852826, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11684708, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11724817, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22705788, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24940650, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27798626}. |
| Post-translational modification PTM: A disulfide bond is formed between rather than within filaments and promotes the formation of a keratin filament cage around the nucleus. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q61781}.; PTM: Ubiquitinated by the BCR(KLHL24) E3 ubiquitin ligase complex. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27798626}. |
| Involvement in disease DISEASE: Epidermolysis bullosa simplex 1A, generalized severe (EBS1A) [MIM:131760]: A form of epidermolysis bullosa simplex, a group of skin fragility disorders characterized by skin blistering due to cleavage within the basal layer of keratinocytes, and erosions caused by minor mechanical trauma. There is a broad spectrum of clinical severity ranging from minor blistering on the feet, to subtypes with extracutaneous involvement and a lethal outcome. EBS1A is an autosomal dominant form characterized by generalized intraepidermal skin blistering that begins and is very prominent at birth. EBS1A may be life-threatening in the first year of life. Tendency to blistering diminishes in adolescence. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10583131, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10730767, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10733662, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10820403, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11710919, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12603865, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12655565, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12707098, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14987259, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16786515, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16882168, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1717157, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21375516, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26432462, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7506097, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7561171, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7688405, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8601736, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9804355, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9989794, ECO:0000269|Ref.37}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Epidermolysis bullosa simplex 1C, localized (EBS1C) [MIM:131800]: A form of epidermolysis bullosa simplex, a group of skin fragility disorders characterized by skin blistering due to cleavage within the basal layer of keratinocytes, and erosions caused by minor mechanical trauma. There is a broad spectrum of clinical severity ranging from minor blistering on the feet, to subtypes with extracutaneous involvement and a lethal outcome. EBS1C is an autosomal dominant form with intraepidermal blistering mainly restricted to hands and feet beginning in infancy. Nails may be thick and dystrophic. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10733662, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12603865, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12655565, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12707098, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14987259, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16786515, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16882168, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21375516, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26432462, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7506606, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7561171, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9284105, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9804357, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9989794}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Epidermolysis bullosa simplex 1B, generalized intermediate (EBS1B) [MIM:131900]: A form of epidermolysis bullosa simplex, a group of skin fragility disorders characterized by skin blistering due to cleavage within the basal layer of keratinocytes, and erosions caused by minor mechanical trauma. There is a broad spectrum of clinical severity ranging from minor blistering on the feet, to subtypes with extracutaneous involvement and a lethal outcome. EBS1B is an autosomal dominant form characterized by generalized intraepidermal blistering beginning at birth. The tendency to blistering diminishes in adolescence, when it may become localized to hands and feet. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10733662, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10820403, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11710919, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16786515, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1720261, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7526926, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7682883, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9989794, ECO:0000269|Ref.10, ECO:0000269|Ref.37}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Epidermolysis bullosa simplex 1D, generalized, intermediate or severe, autosomal recessive (EBS1D) [MIM:601001]: A form of epidermolysis bullosa simplex, a group of skin fragility disorders characterized by skin blistering due to cleavage within the basal layer of keratinocytes, and erosions caused by minor mechanical trauma. There is a broad spectrum of clinical severity ranging from minor blistering on the feet, to subtypes with extracutaneous involvement and a lethal outcome. EBS1D is an autosomal recessive form characterized by blistering beginning at birth or early childhood. In some patients hands and feet are primarily affected, and in others blistering anywhere on the body may occur. In some patients the condition improves with age. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12707098, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22832485, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7526933}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Naegeli-Franceschetti-Jadassohn syndrome (NFJS) [MIM:161000]: A rare autosomal dominant form of ectodermal dysplasia. The cardinal features are absence of dermatoglyphics (fingerprints), reticular cutaneous hyperpigmentation (starting at about the age of 2 years without a preceding inflammatory stage), palmoplantar keratoderma, hypohidrosis with diminished sweat gland function and discomfort provoked by heat, nail dystrophy, and tooth enamel defects. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16960809}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Dermatopathia pigmentosa reticularis (DPR) [MIM:125595]: A rare ectodermal dysplasia characterized by lifelong persistent reticulate hyperpigmentation, non-cicatricial alopecia, and nail dystrophy. Variable features include adermatoglyphia, hypohidrosis or hyperhidrosis, and palmoplantar hyperkeratosis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16960809}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: P02533 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
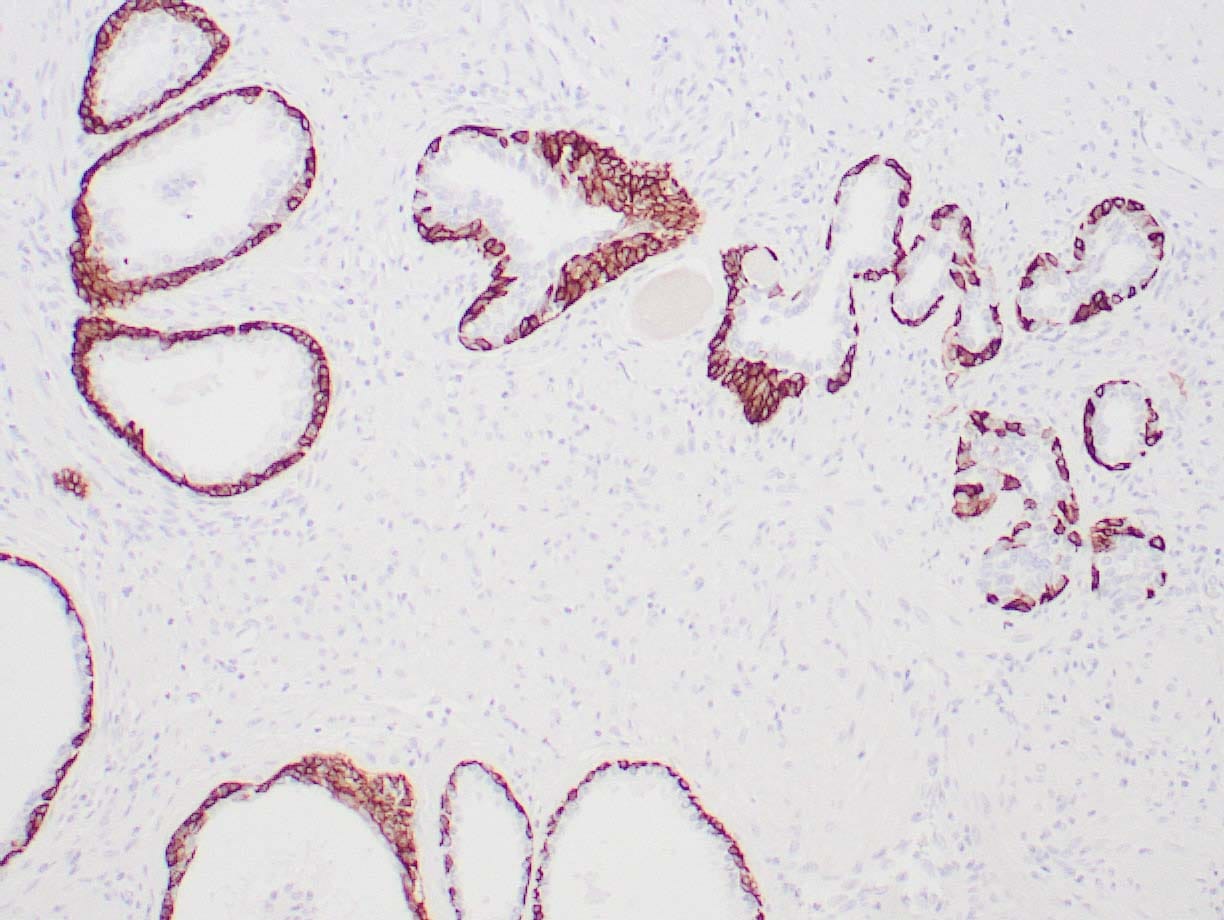 |
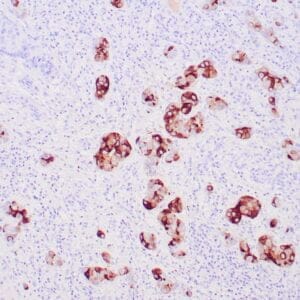
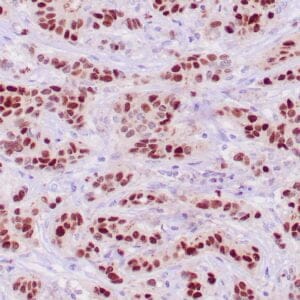
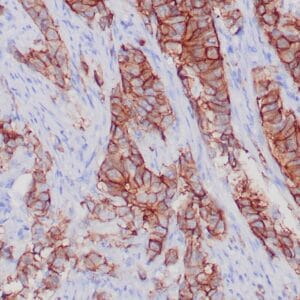
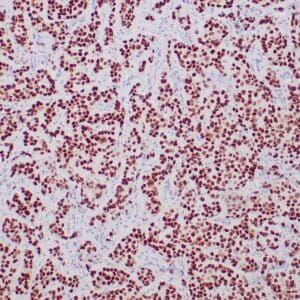
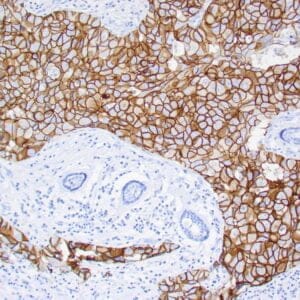
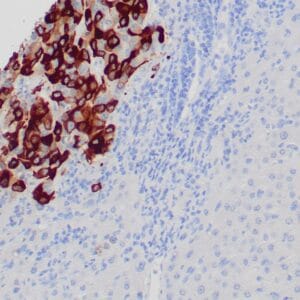
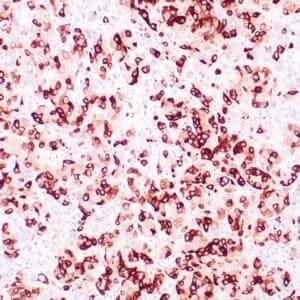
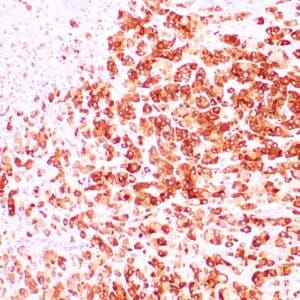
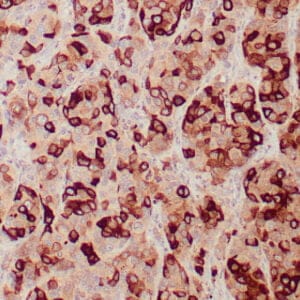
| Human breast stained with Keratin 14 using peroxidase-conjugate and DAB chromogen. Note the cytoplasmic staining of myoepithelial cells. |
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
| IHC |
Documents
| # | SDS | Certificate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | |||
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.