| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| host | mouse |
| isotype | IgG1 |
| clonality | monoclonal |
| concentration | concentrate, predilute |
| applications | IHC |
| reactivity | human |
| available size | 0.1 mL, 0.5 mL, 1 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted |
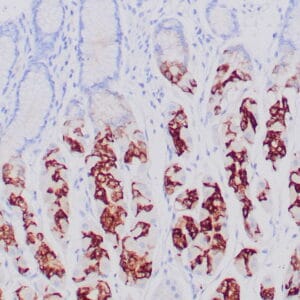
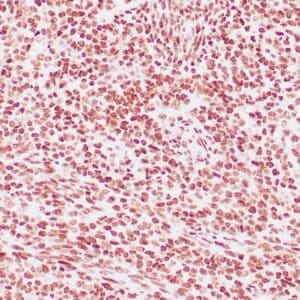
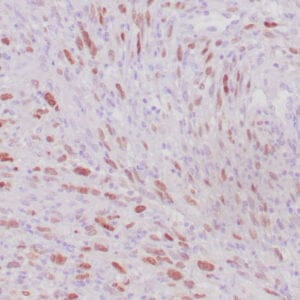
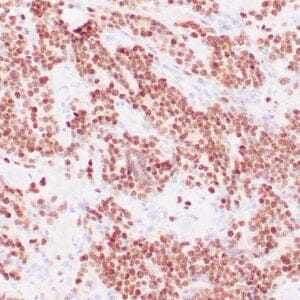
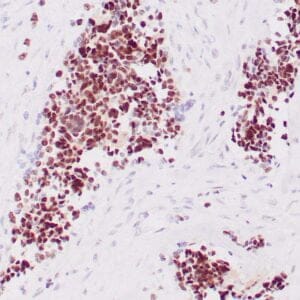
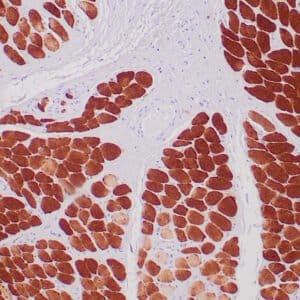
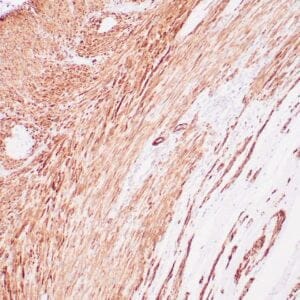
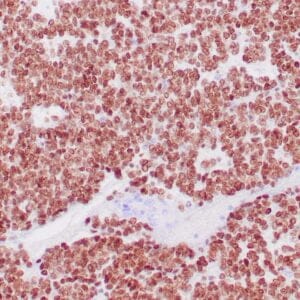
mouse anti-ALDH1A1 monoclonal antibody (ZM71) 6015
Price range: $160.00 through $528.00
Antibody summary
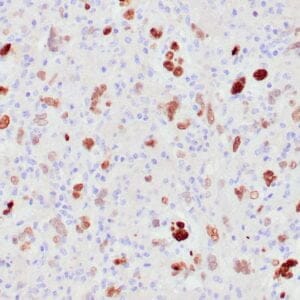
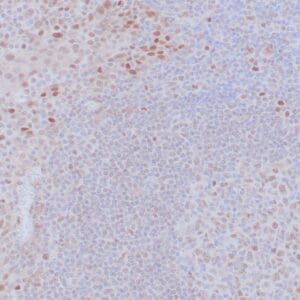
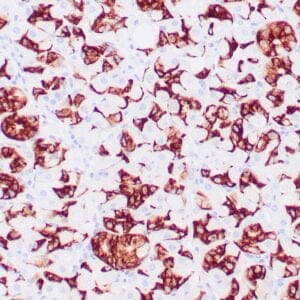
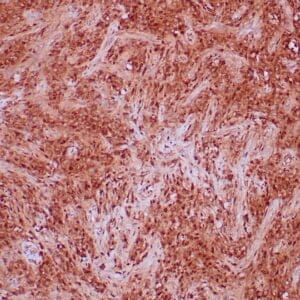
- Mouse monoclonal to ALDH1A1
- Suitable for: Immunohistochemistry (formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues)
- Reacts with: Human
- Isotype:IgG1
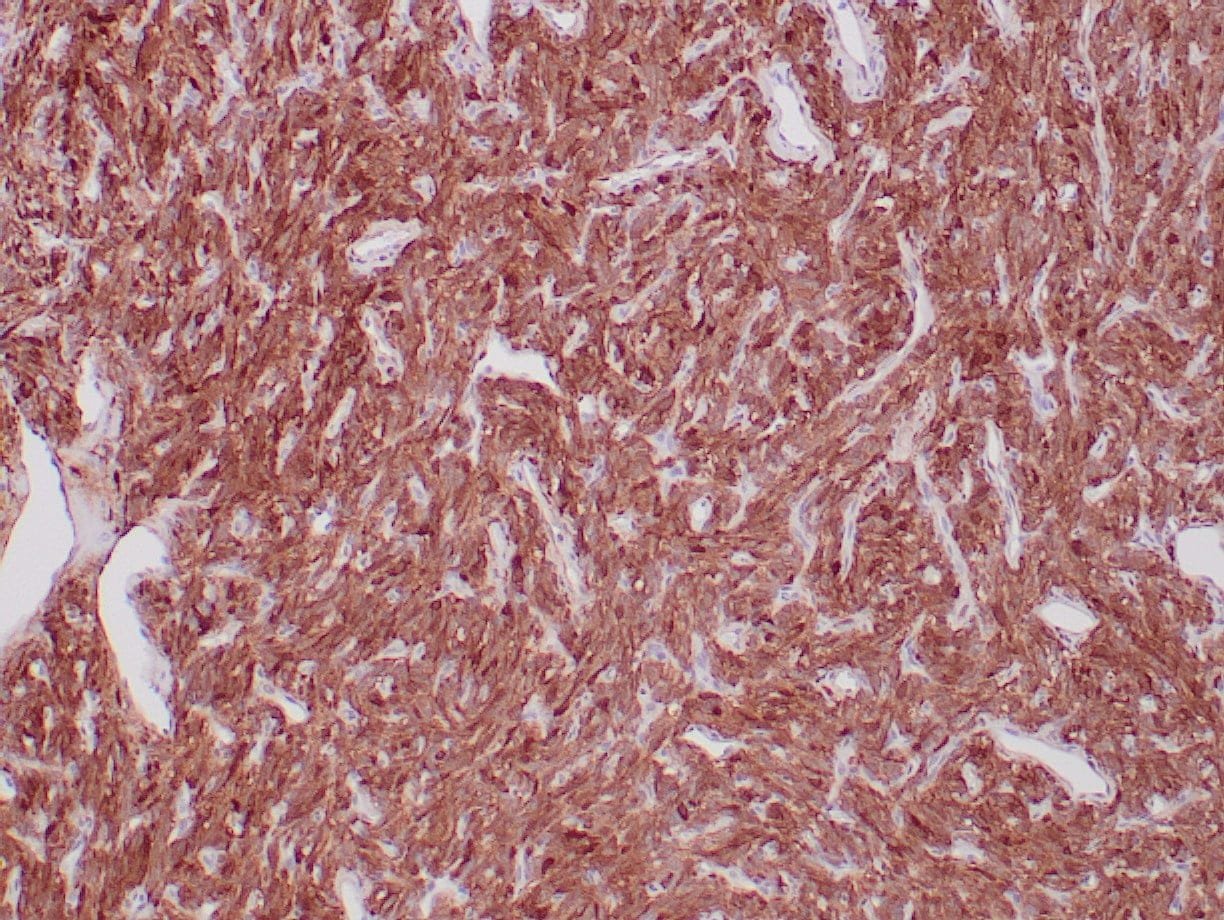
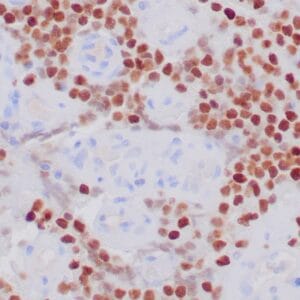
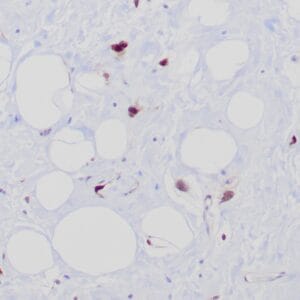
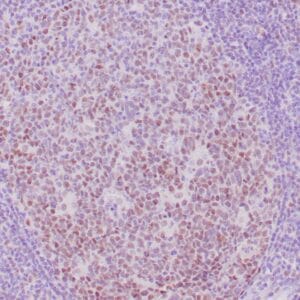
- Control: Solitary fibrous tumor
- Visualization: Cytoplasmic and nuclear
- 0.1, 0.5, 1.0 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted
mouse anti-ALDH1A1 monoclonal antibody ZM71 6015
| target relevance |
|---|
| Protein names Aldehyde dehydrogenase 1A1 (EC 1.2.1.19) (EC 1.2.1.28) (EC 1.2.1.3) (EC 1.2.1.36) (3-deoxyglucosone dehydrogenase) (ALDH-E1) (ALHDII) (Aldehyde dehydrogenase family 1 member A1) (Aldehyde dehydrogenase, cytosolic) (Retinal dehydrogenase 1) (RALDH 1) (RalDH1) |
| Gene names ALDH1A1,ALDH1A1 ALDC ALDH1 PUMB1 |
| Protein family Aldehyde dehydrogenase family |
| Mass 54862Da |
| Function FUNCTION: Cytosolic dehydrogenase that catalyzes the irreversible oxidation of a wide range of aldehydes to their corresponding carboxylic acid (PubMed:12941160, PubMed:15623782, PubMed:17175089, PubMed:19296407, PubMed:25450233, PubMed:26373694). Functions downstream of retinol dehydrogenases and catalyzes the oxidation of retinaldehyde into retinoic acid, the second step in the oxidation of retinol/vitamin A into retinoic acid (By similarity). This pathway is crucial to control the levels of retinol and retinoic acid, two important molecules which excess can be teratogenic and cytotoxic (By similarity). Also oxidizes aldehydes resulting from lipid peroxidation like (E)-4-hydroxynon-2-enal/HNE, malonaldehyde and hexanal that form protein adducts and are highly cytotoxic. By participating for instance to the clearance of (E)-4-hydroxynon-2-enal/HNE in the lens epithelium prevents the formation of HNE-protein adducts and lens opacification (PubMed:12941160, PubMed:15623782, PubMed:19296407). Also functions downstream of fructosamine-3-kinase in the fructosamine degradation pathway by catalyzing the oxidation of 3-deoxyglucosone, the carbohydrate product of fructosamine 3-phosphate decomposition, which is itself a potent glycating agent that may react with lysine and arginine side-chains of proteins (PubMed:17175089). Also has an aminobutyraldehyde dehydrogenase activity and is probably part of an alternative pathway for the biosynthesis of GABA/4-aminobutanoate in midbrain, thereby playing a role in GABAergic synaptic transmission (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P24549, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12941160, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15623782, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17175089, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19296407, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25450233, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26373694}. |
| Catalytic activity CATALYTIC ACTIVITY: Reaction=an aldehyde + NAD(+) + H2O = a carboxylate + NADH + 2 H(+); Xref=Rhea:RHEA:16185, ChEBI:CHEBI:15377, ChEBI:CHEBI:15378, ChEBI:CHEBI:17478, ChEBI:CHEBI:29067, ChEBI:CHEBI:57540, ChEBI:CHEBI:57945; EC=1.2.1.3; Evidence={ECO:0000269|PubMed:12941160, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15623782, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17175089, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19296407}; PhysiologicalDirection=left-to-right; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:16186; Evidence={ECO:0000305|PubMed:19296407}; CATALYTIC ACTIVITY: Reaction=all-trans-retinal + NAD(+) + H2O = all-trans-retinoate + NADH + 2 H(+); Xref=Rhea:RHEA:42080, ChEBI:CHEBI:15377, ChEBI:CHEBI:15378, ChEBI:CHEBI:17898, ChEBI:CHEBI:35291, ChEBI:CHEBI:57540, ChEBI:CHEBI:57945; EC=1.2.1.36; Evidence={ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P51647}; PhysiologicalDirection=left-to-right; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:42081; Evidence={ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P51647}; CATALYTIC ACTIVITY: Reaction=9-cis-retinal + NAD(+) + H2O = 9-cis-retinoate + NADH + 2 H(+); Xref=Rhea:RHEA:42084, ChEBI:CHEBI:15377, ChEBI:CHEBI:15378, ChEBI:CHEBI:57540, ChEBI:CHEBI:57945, ChEBI:CHEBI:78273, ChEBI:CHEBI:78630; Evidence={ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P51647}; PhysiologicalDirection=left-to-right; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:42085; Evidence={ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P51647}; CATALYTIC ACTIVITY: Reaction=11-cis-retinal + NAD(+) + H2O = 11-cis-retinoate + NADH + 2 H(+); Xref=Rhea:RHEA:47132, ChEBI:CHEBI:15377, ChEBI:CHEBI:15378, ChEBI:CHEBI:16066, ChEBI:CHEBI:57540, ChEBI:CHEBI:57945, ChEBI:CHEBI:87435; Evidence={ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P51647}; PhysiologicalDirection=left-to-right; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:47133; Evidence={ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P51647}; CATALYTIC ACTIVITY: Reaction=13-cis-retinal + NAD(+) + H2O = 13-cis-retinoate + NADH + 2 H(+); Xref=Rhea:RHEA:67332, ChEBI:CHEBI:15377, ChEBI:CHEBI:15378, ChEBI:CHEBI:45487, ChEBI:CHEBI:57540, ChEBI:CHEBI:57945, ChEBI:CHEBI:169952; Evidence={ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8HYE4}; PhysiologicalDirection=left-to-right; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:67333; Evidence={ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8HYE4}; CATALYTIC ACTIVITY: Reaction=3-deoxyglucosone + NAD(+) + H2O = 2-dehydro-3-deoxy-D-gluconate + NADH + 2 H(+); Xref=Rhea:RHEA:67244, ChEBI:CHEBI:15377, ChEBI:CHEBI:15378, ChEBI:CHEBI:57540, ChEBI:CHEBI:57945, ChEBI:CHEBI:57990, ChEBI:CHEBI:60777; Evidence={ECO:0000269|PubMed:17175089}; PhysiologicalDirection=left-to-right; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:67245; Evidence={ECO:0000305|PubMed:17175089}; CATALYTIC ACTIVITY: Reaction=(E)-4-hydroxynon-2-enal + NAD(+) + H2O = (E)-4-hydroxynon-2-enoate + NADH + 2 H(+); Xref=Rhea:RHEA:67248, ChEBI:CHEBI:15377, ChEBI:CHEBI:15378, ChEBI:CHEBI:57540, ChEBI:CHEBI:57945, ChEBI:CHEBI:58968, ChEBI:CHEBI:142920; Evidence={ECO:0000269|PubMed:12941160, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15623782, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19296407}; PhysiologicalDirection=left-to-right; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:67249; Evidence={ECO:0000269|PubMed:15623782}; CATALYTIC ACTIVITY: Reaction=malonaldehyde + NAD(+) + H2O = 3-oxopropanoate + NADH + 2 H(+); Xref=Rhea:RHEA:67252, ChEBI:CHEBI:15377, ChEBI:CHEBI:15378, ChEBI:CHEBI:33190, ChEBI:CHEBI:57540, ChEBI:CHEBI:57945, ChEBI:CHEBI:566274; Evidence={ECO:0000269|PubMed:12941160, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19296407}; PhysiologicalDirection=left-to-right; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:67253; Evidence={ECO:0000305|PubMed:19296407}; CATALYTIC ACTIVITY: Reaction=hexanal + NAD(+) + H2O = hexanoate + NADH + 2 H(+); Xref=Rhea:RHEA:67276, ChEBI:CHEBI:15377, ChEBI:CHEBI:15378, ChEBI:CHEBI:17120, ChEBI:CHEBI:57540, ChEBI:CHEBI:57945, ChEBI:CHEBI:88528; Evidence={ECO:0000269|PubMed:12941160}; PhysiologicalDirection=left-to-right; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:67277; Evidence={ECO:0000305|PubMed:12941160}; CATALYTIC ACTIVITY: Reaction=propanal + NAD(+) + H2O = propanoate + NADH + 2 H(+); Xref=Rhea:RHEA:67256, ChEBI:CHEBI:15377, ChEBI:CHEBI:15378, ChEBI:CHEBI:17153, ChEBI:CHEBI:17272, ChEBI:CHEBI:57540, ChEBI:CHEBI:57945; Evidence={ECO:0000269|PubMed:12941160, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19296407}; PhysiologicalDirection=left-to-right; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:67257; Evidence={ECO:0000305|PubMed:19296407}; CATALYTIC ACTIVITY: Reaction=acetaldehyde + NAD(+) + H2O = acetate + NADH + 2 H(+); Xref=Rhea:RHEA:25294, ChEBI:CHEBI:15343, ChEBI:CHEBI:15377, ChEBI:CHEBI:15378, ChEBI:CHEBI:30089, ChEBI:CHEBI:57540, ChEBI:CHEBI:57945; EC=1.2.1.3; Evidence={ECO:0000269|PubMed:19296407}; PhysiologicalDirection=left-to-right; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:25295; Evidence={ECO:0000305|PubMed:19296407}; CATALYTIC ACTIVITY: Reaction=benzaldehyde + NAD(+) + H2O = benzoate + NADH + 2 H(+); Xref=Rhea:RHEA:11840, ChEBI:CHEBI:15377, ChEBI:CHEBI:15378, ChEBI:CHEBI:16150, ChEBI:CHEBI:17169, ChEBI:CHEBI:57540, ChEBI:CHEBI:57945; EC=1.2.1.28; Evidence={ECO:0000269|PubMed:17175089, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19296407}; PhysiologicalDirection=left-to-right; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:11841; Evidence={ECO:0000305|PubMed:19296407}; CATALYTIC ACTIVITY: Reaction=4-aminobutanal + NAD(+) + H2O = 4-aminobutanoate + NADH + 2 H(+); Xref=Rhea:RHEA:19105, ChEBI:CHEBI:15377, ChEBI:CHEBI:15378, ChEBI:CHEBI:57540, ChEBI:CHEBI:57945, ChEBI:CHEBI:58264, ChEBI:CHEBI:59888; EC=1.2.1.19; Evidence={ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P24549}; PhysiologicalDirection=left-to-right; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:19106; Evidence={ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P24549}; |
| Pathway PATHWAY: Cofactor metabolism; retinol metabolism. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P51647}. |
| Subellular location SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: Cytoplasm, cytosol {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12941160}. Cell projection, axon {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P24549}. |
| Tissues TISSUE SPECIFICITY: Expressed by erythrocytes (at protein level). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17175089}. |
| Structure SUBUNIT: Homotetramer (By similarity). Interacts with PRMT3; the interaction is direct, inhibits ALDH1A1 aldehyde dehydrogenase activity and is independent of the methyltransferase activity of PRMT3 (PubMed:33495566). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P51977, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33495566}. |
| Post-translational modification PTM: The N-terminus is blocked most probably by acetylation. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P15437}. |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: P00352 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
| IHC |
Documents
| # | SDS | Certificate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | |||
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.