| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| host | mouse |
| isotype | IgG2a |
| clonality | monoclonal |
| concentration | concentrate, predilute |
| applications | IHC |
| reactivity | human |
| available size | 0.1 mL, 0.5 mL, 1 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted |
mouse anti-Thrombomodulin/ CD141 monoclonal antibody (ZM105) 6380
Price range: $160.00 through $528.00
Antibody summary
- Mouse monoclonal to Thrombomodulin/ CD141
- Suitable for: Immunohistochemistry (formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues)
- Reacts with: Human
- Isotype:IgG2a
- Control: Mesothelioma
- Visualization: Cytoplasmic
- 0.1, 0.5, 1.0 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted
mouse anti-Thrombomodulin/ CD141 monoclonal antibody ZM105 6380
| target relevance |
|---|
| Protein names Thrombomodulin (TM) (Fetomodulin) (CD antigen CD141) |
| Gene names THBD,THBD THRM |
| Mass 60329Da |
| Function FUNCTION: Endothelial cell receptor that plays a critical role in regulating several physiological processes including hemostasis, coagulation, fibrinolysis, inflammation, and angiogenesis (PubMed:10761923). Acts as a cofactor for thrombin activation of protein C/PROC on the surface of vascular endothelial cells leading to initiation of the activated protein C anticoagulant pathway (PubMed:29323190, PubMed:33836597, PubMed:9395524). Also accelerates the activation of the plasma carboxypeptidase B2/CPB2, which catalyzes removal of C-terminal basic amino acids from its substrates including kinins or anaphylatoxins leading to fibrinolysis inhibition (PubMed:26663133). Plays critical protective roles in changing the cleavage specificity of protease-activated receptor 1/PAR1, inhibiting endothelial cell permeability and inflammation (By similarity). Suppresses inflammation distinctly from its anticoagulant cofactor activity by sequestering HMGB1 thereby preventing it from engaging cellular receptors such as RAGE and contributing to the inflammatory response (PubMed:15841214). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P15306, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10761923, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15841214, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26663133, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29323190, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33836597, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9395524}. |
| Subellular location SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: Membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. |
| Tissues TISSUE SPECIFICITY: Endothelial cells are unique in synthesizing thrombomodulin. |
| Structure SUBUNIT: Interacts with ITGAL, ITGAM and ITGB2. Interacts with thrombin/F2; this interaction switches the specificity of thrombin from a procoagulant to an anticoagulant and antifibrinolytic protease (PubMed:10761923). Interacts with ANGP1 and ANGP2; these interactions significantly inhibit the generation of activated PC and TAFIa/CPB2 by the thrombin/thrombomodulin complex (PubMed:29323190). Interacts with PF4; this interaction enhances generation of activated protein C (PubMed:9395524). Interacts with HMGB1; this interaction inhibits HMGB1 inflammatory activity (PubMed:15841214). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10761923, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15841214, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27055590, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29323190, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9395524}. |
| Post-translational modification PTM: N-glycosylated. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:8216207}.; PTM: The iron and 2-oxoglutarate dependent 3-hydroxylation of aspartate and asparagine is (R) stereospecific within EGF domains. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:8390446}. |
| Domain DOMAIN: Extracellular region (481-515) contains a binding side for alpha-L/beta-2 and alpha-M/beta-2 integrin. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27055590}. |
| Involvement in disease DISEASE: Thrombophilia due to thrombomodulin defect (THPH12) [MIM:614486]: A hemostatic disorder characterized by a tendency to thrombosis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12139752, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7811989, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9198186}. Note=The disease may be caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. The role of thrombomodulin in thrombosis is controversial. It is likely that genetic or environmental risk factors in addition to THBD variation are involved in the pathogenesis of venous thrombosis.; DISEASE: Hemolytic uremic syndrome, atypical, 6 (AHUS6) [MIM:612926]: An atypical form of hemolytic uremic syndrome. It is a complex genetic disease characterized by microangiopathic hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, renal failure and absence of episodes of enterocolitis and diarrhea. In contrast to typical hemolytic uremic syndrome, atypical forms have a poorer prognosis, with higher death rates and frequent progression to end-stage renal disease. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19625716, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20513133}. Note=Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Other genes may play a role in modifying the phenotype. |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: P07204 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
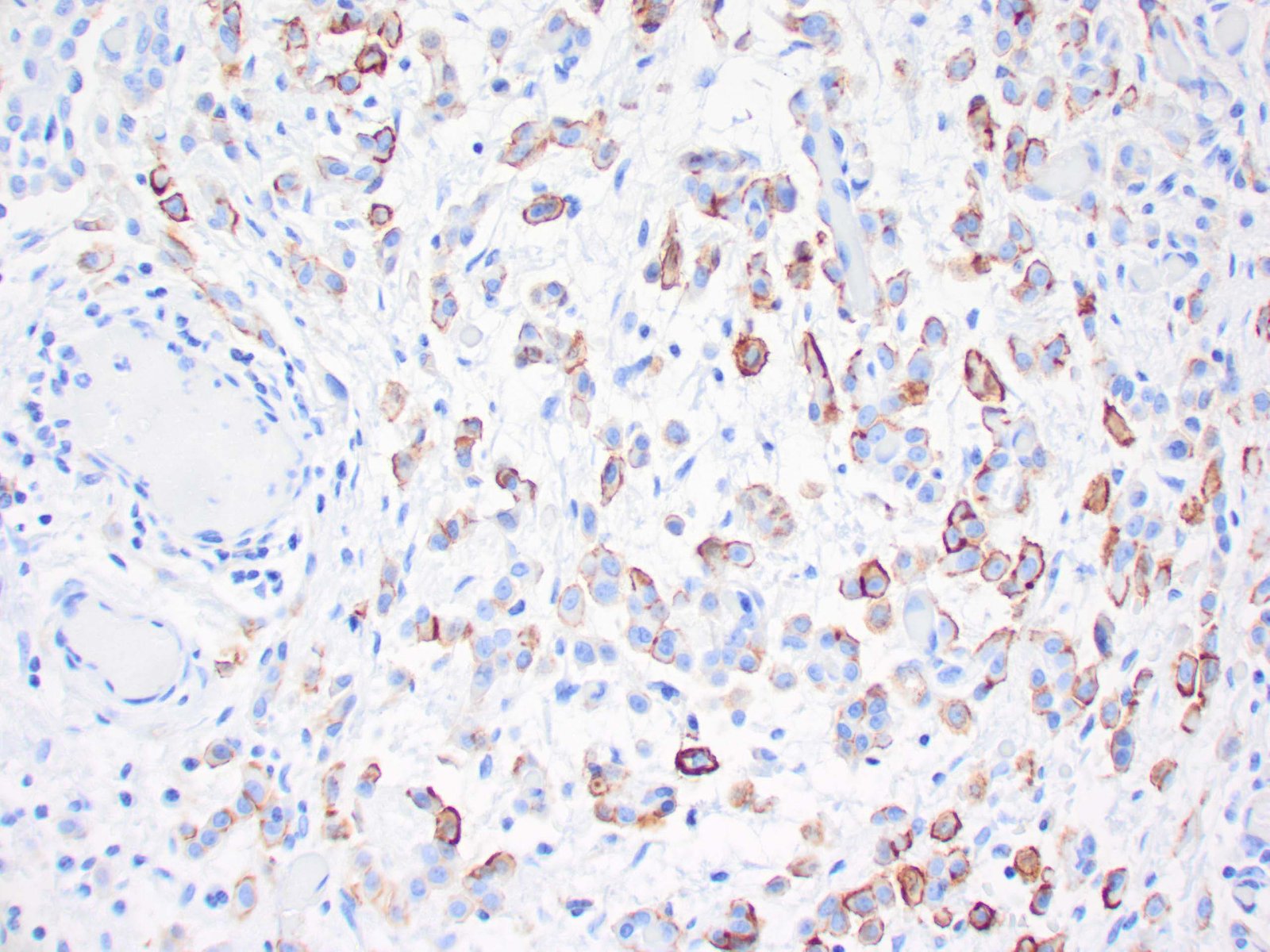 |
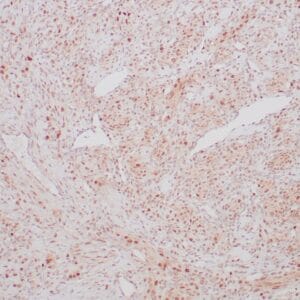
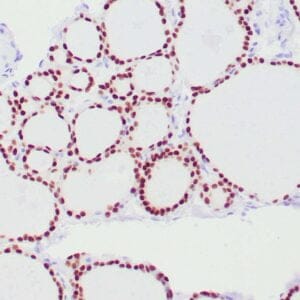
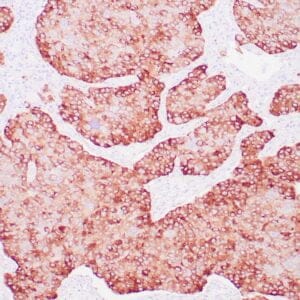
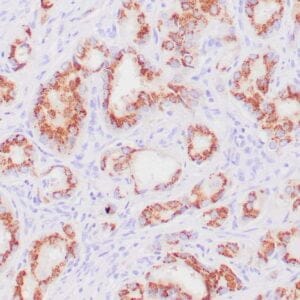
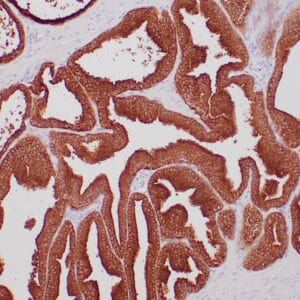
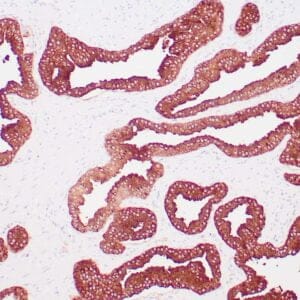
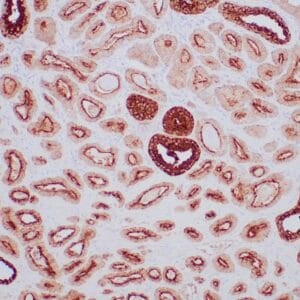
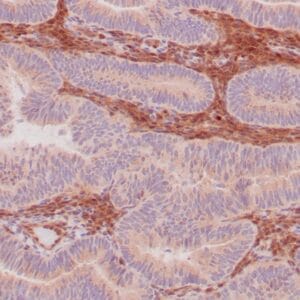
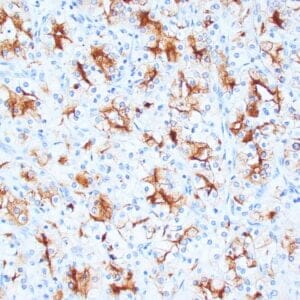
| Human urothelial carcinoma stained with anti-Thrombomodulin antibody using peroxidase-conjugate and DAB chromogen. Note the cytoplasmic staining of tumor cells. |
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
| IHC |
Documents
| # | SDS | Certificate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | |||
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.