| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| host | rabbit |
| isotype | IgG |
| clonality | polyclonal |
| concentration | 1 mg/mL |
| applications | ICC/IF, WB |
| reactivity | RIP3 |
| available sizes | 100 µg |
rabbit anti-RIP3 polyclonal antibody 3801
$445.00
Antibody summary
- Rabbit polyclonal to RIP3
- Suitable for: ELISA,IF,IHC-P,WB,IP
- Isotype: IgG
- 100 µg
rabbit anti-RIP3 polyclonal antibody 3801
| antibody |
|---|
| Tested applications IHC,IHC,ICC/IF,ELISA |
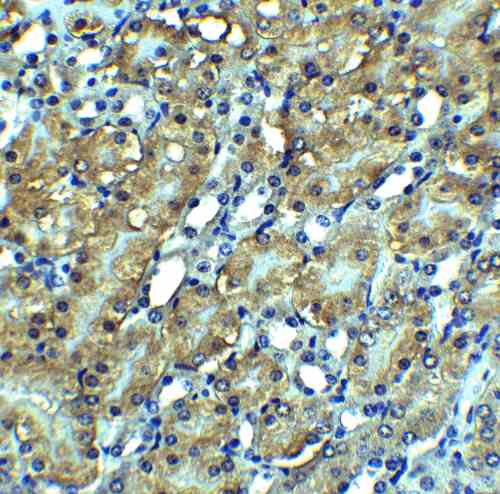
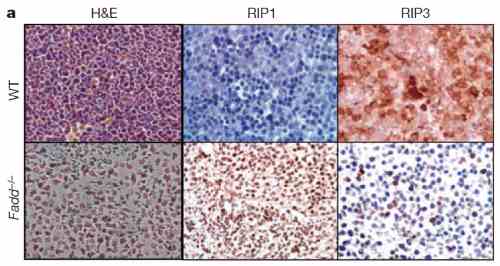
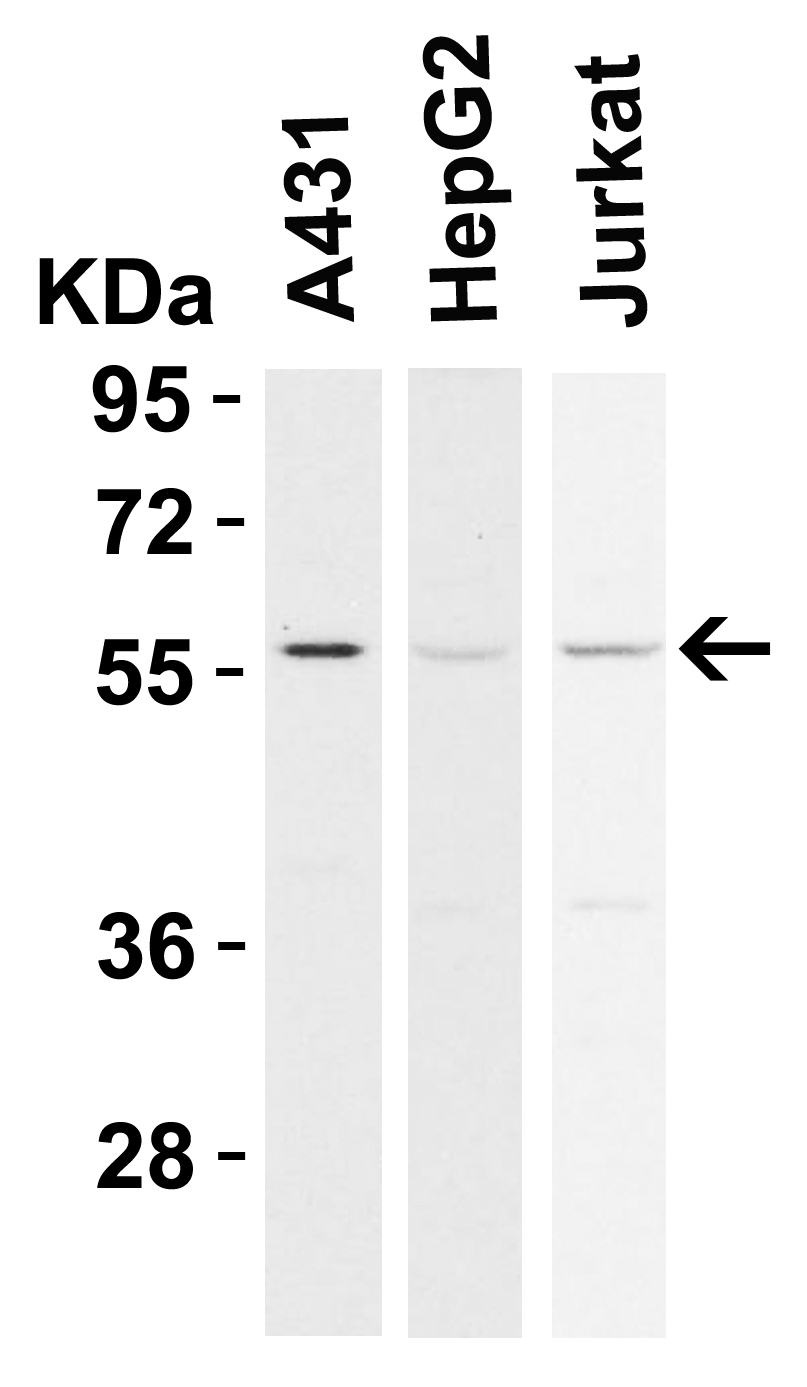
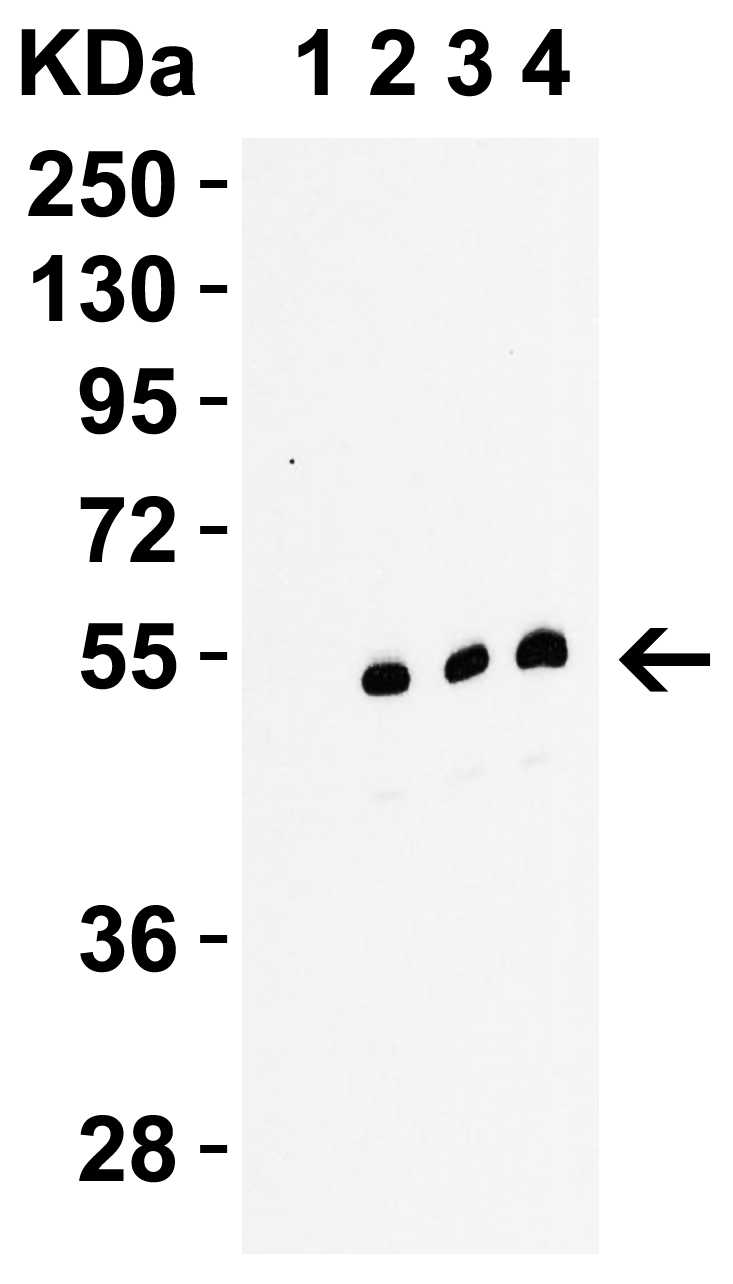
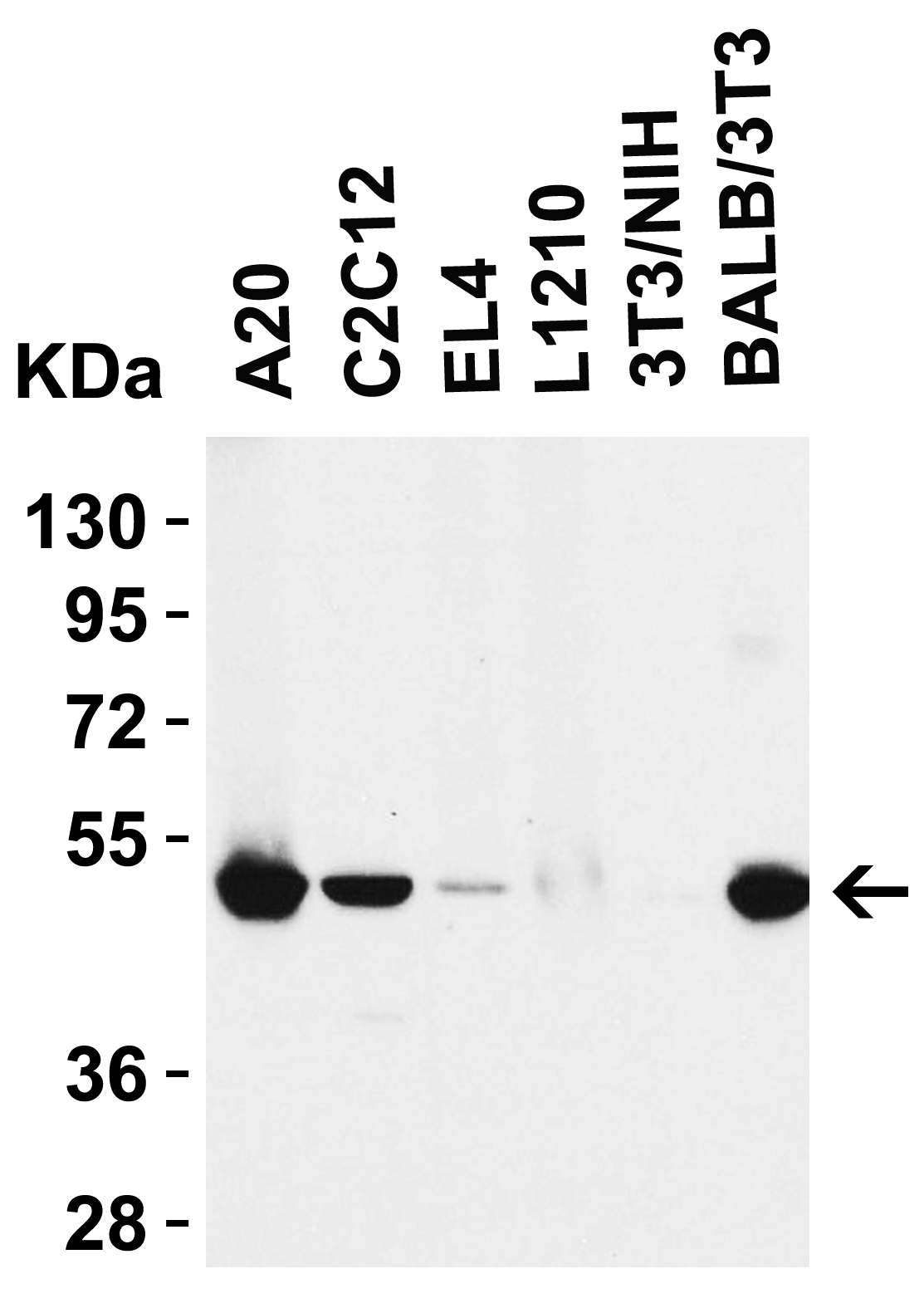
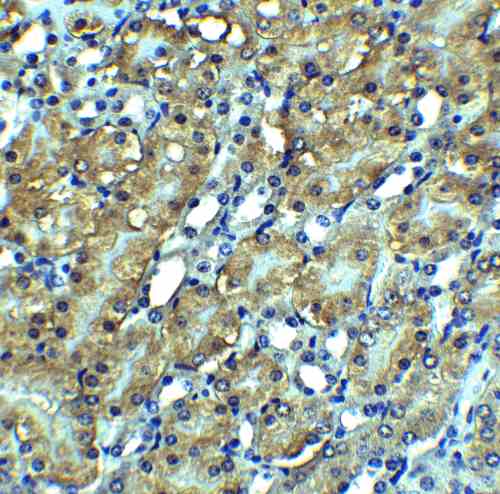
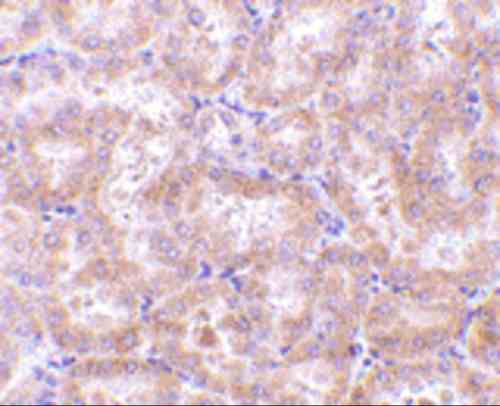
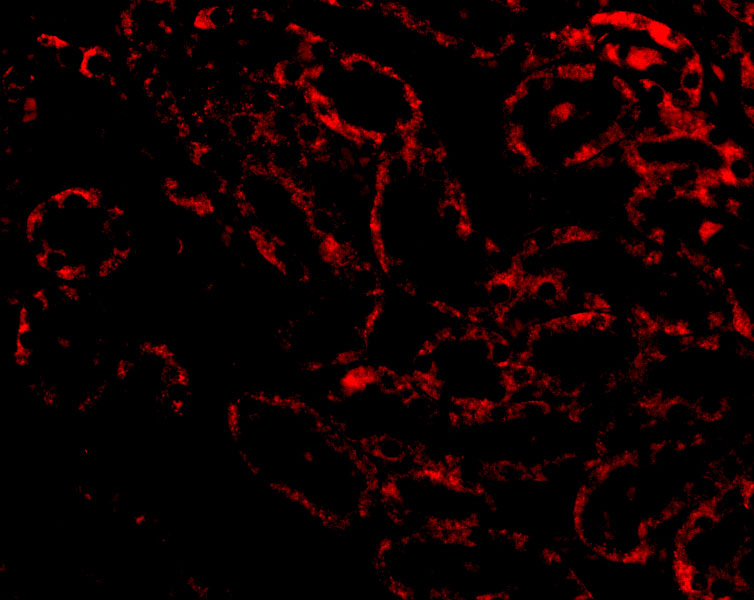
| Recommended dilutions Immunoblotting: use at 1ug/mL. Positive control: NIH/3T3 cell lysate. Immunohistochemistry: use at 5ug/mL. These are recommended concentrations. Enduser should determine optimal concentrations for their applications. |
| Immunogen Synthetic peptide corresponding to aa 473-486 of mouse RIP3 (accession no. AAF03133). |
| Size and concentration 100µg and lot specific |
| Form liquid |
| Storage Instructions This antibody is stable for at least one (1) year at -20°C. Avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Storage buffer PBS, pH 7.4. |
| Purity peptide affinity purification |
| Clonality polyclonal |
| Isotype IgG |
| Compatible secondaries goat anti-rabbit IgG, H&L chain specific, peroxidase conjugated, conjugated polyclonal antibody 9512 goat anti-rabbit IgG, H&L chain specific, biotin conjugated polyclonal antibody 2079 goat anti-rabbit IgG, H&L chain specific, FITC conjugated polyclonal antibody 7863 goat anti-rabbit IgG, H&L chain specific, Cross Absorbed polyclonal antibody 2371 goat anti-rabbit IgG, H&L chain specific, biotin conjugated polyclonal antibody, crossabsorbed 1715 goat anti-rabbit IgG, H&L chain specific, FITC conjugated polyclonal antibody, crossabsorbed 1720 |
| Isotype control Rabbit polyclonal - Isotype Control |
| target relevance |
|---|
| Protein names Receptor-interacting serine/threonine-protein kinase 3 (EC 2.7.11.1) (RIP-like protein kinase 3) (Receptor-interacting protein 3) (RIP-3) (mRIP3) |
| Gene names Ripk3,Ripk3 Rip3 |
| Protein family Protein kinase superfamily, TKL Ser/Thr protein kinase family |
| Mass 53322Da |
| Function FUNCTION: Serine/threonine-protein kinase that activates necroptosis and apoptosis, two parallel forms of cell death (PubMed:27321907, PubMed:27746097, PubMed:27917412, PubMed:28607035, PubMed:32200799, PubMed:32296175). Necroptosis, a programmed cell death process in response to death-inducing TNF-alpha family members, is triggered by RIPK3 following activation by ZBP1 (PubMed:19590578, PubMed:22423968, PubMed:24012422, PubMed:24019532, PubMed:24095729, PubMed:24557836, PubMed:27321907, PubMed:27746097, PubMed:27819681, PubMed:27819682, PubMed:32200799, PubMed:32296175). Activated RIPK3 forms a necrosis-inducing complex and mediates phosphorylation of MLKL, promoting MLKL localization to the plasma membrane and execution of programmed necrosis characterized by calcium influx and plasma membrane damage (PubMed:24813849, PubMed:24813850, PubMed:27321907). In addition to TNF-induced necroptosis, necroptosis can also take place in the nucleus in response to orthomyxoviruses infection: following ZBP1 activation, which senses double-stranded Z-RNA structures, nuclear RIPK3 catalyzes phosphorylation and activation of MLKL, promoting disruption of the nuclear envelope and leakage of cellular DNA into the cytosol (PubMed:32200799, PubMed:32296175). Also regulates apoptosis: apoptosis depends on RIPK1, FADD and CASP8, and is independent of MLKL and RIPK3 kinase activity (PubMed:27321907). Phosphorylates RIPK1: RIPK1 and RIPK3 undergo reciprocal auto- and trans-phosphorylation (By similarity). In some cell types, also able to restrict viral replication by promoting cell death-independent responses (PubMed:30635240). In response to flavivirus infection in neurons, promotes a cell death-independent pathway that restricts viral replication: together with ZBP1, promotes a death-independent transcriptional program that modifies the cellular metabolism via up-regulation expression of the enzyme ACOD1/IRG1 and production of the metabolite itaconate (PubMed:30635240). Itaconate inhibits the activity of succinate dehydrogenase, generating a metabolic state in neurons that suppresses replication of viral genomes (PubMed:30635240). RIPK3 binds to and enhances the activity of three metabolic enzymes: GLUL, GLUD1, and PYGL (By similarity). These metabolic enzymes may eventually stimulate the tricarboxylic acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation, which could result in enhanced ROS production (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9Y572, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19590578, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22423968, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24012422, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24019532, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24095729, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24557836, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24813849, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24813850, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27321907, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27746097, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27819681, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27819682, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27917412, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28607035, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30635240, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32200799, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32296175}. |
| Catalytic activity CATALYTIC ACTIVITY: Reaction=L-seryl-[protein] + ATP = O-phospho-L-seryl-[protein] + ADP + H(+); Xref=Rhea:RHEA:17989, Rhea:RHEA-COMP:9863, Rhea:RHEA-COMP:11604, ChEBI:CHEBI:15378, ChEBI:CHEBI:29999, ChEBI:CHEBI:30616, ChEBI:CHEBI:83421, ChEBI:CHEBI:456216; EC=2.7.11.1; Evidence={ECO:0000269|PubMed:10490590, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24095729, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32200799, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32296175}; CATALYTIC ACTIVITY: Reaction=L-threonyl-[protein] + ATP = O-phospho-L-threonyl-[protein] + ADP + H(+); Xref=Rhea:RHEA:46608, Rhea:RHEA-COMP:11060, Rhea:RHEA-COMP:11605, ChEBI:CHEBI:15378, ChEBI:CHEBI:30013, ChEBI:CHEBI:30616, ChEBI:CHEBI:61977, ChEBI:CHEBI:456216; EC=2.7.11.1; Evidence={ECO:0000269|PubMed:10490590, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24095729, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32200799, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32296175}; |
| Subellular location SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: Cytoplasm, cytosol {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28607035, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32200799, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32296175}. Nucleus {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28607035, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32200799, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32296175}. Note=Mainly cytoplasmic (PubMed:32200799, PubMed:32296175). Present in the nucleus in response to influenza A virus (IAV) infection (PubMed:32200799). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:32200799, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32296175}. |
| Tissues TISSUE SPECIFICITY: Expressed in embryo and in adult spleen, liver, testis, heart, brain and lung. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10490590}. |
| Structure SUBUNIT: Interacts (via RIP homotypic interaction motif) with RIPK1 (via RIP homotypic interaction motif); this interaction induces RIPK1 phosphorylation and formation of a RIPK1-RIPK3 necrosis-inducing complex (PubMed:27321907, PubMed:27819681, PubMed:28842570, PubMed:31519887). Interacts with MLKL; the interaction is direct and triggers necroptosis (PubMed:24012422, PubMed:27321907). Interacts with ZBP1 (via RIP homotypic interaction motif); interaction with ZBP1 activates RIPK3, triggering necroptosis (PubMed:19590578, PubMed:22423968, PubMed:27746097, PubMed:27819681, PubMed:27819682, PubMed:28607035, PubMed:32200799). Upon TNF-induced necrosis, the RIPK1-RIPK3 dimer further interacts with PGAM5 and MLKL; the formation of this complex leads to PGAM5 phosphorylation and increase in PGAM5 phosphatase activity (By similarity). Binds TRAF2 and is recruited to the TNFR-1 signaling complex (By similarity). Interacts with PYGL, GLUL and GLUD1; these interactions result in activation of these metabolic enzymes (By similarity). Interacts with BIRC2/c-IAP1, BIRC3/c-IAP2 and XIAP/BIRC4 (By similarity). Interacts with ARHGEF2 (By similarity). Interacts with PELI1 (via atypical FHA domain); the phosphorylated form at Thr-187 binds preferentially to PELI1 (PubMed:29883609). Interacts with BUB1B, TRAF2 and STUB1 (By similarity). Interacts with CASP6 (By similarity). Component of the AIM2 PANoptosome complex, a multiprotein complex that drives inflammatory cell death (PANoptosis) (PubMed:34471287). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9Y572, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19590578, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22423968, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24012422, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27321907, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27746097, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27819681, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27819682, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28607035, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28842570, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29883609, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31519887, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32200799, ECO:0000269|PubMed:34471287}.; SUBUNIT: (Microbial infection) Interacts (via RIP homotypic interaction motif) with murid herpesvirus protein RIR1; this interaction disrupts RIP3-RIP1 interactions characteristic of TNF-alpha induced necroptosis, thereby suppressing this death pathway. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18442983, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30498077}. |
| Post-translational modification PTM: RIPK1 and RIPK3 undergo reciprocal auto- and trans-phosphorylation (By similarity). Autophosphorylated following interaction with ZBP1 (PubMed:27819681). Phosphorylation of Ser-204 plays a role in the necroptotic function of RIPK3 (By similarity). Autophosphorylates at Thr-231 and Ser-232 following activation by ZBP1: phosphorylation at these sites is a hallmark of necroptosis and is required for binding MLKL (PubMed:23612963, PubMed:27819682). Phosphorylation at Thr-187 is important for its kinase activity, interaction with PELI1 and for its ability to mediate TNF-induced necroptosis (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9Y572, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23612963, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27819681, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27819682}.; PTM: Polyubiquitinated with 'Lys-48' and 'Lys-63'-linked chains by BIRC2/c-IAP1 and BIRC3/c-IAP2, leading to activation of NF-kappa-B. Ubiquitinated by STUB1 leading to its subsequent proteasome-dependent degradation. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9Y572}. |
| Domain DOMAIN: The RIP homotypic interaction motif (RHIM) mediates interaction with the RHIM motif of RIPK1. Both motifs form a hetero-amyloid serpentine fold, stabilized by hydrophobic packing and featuring an unusual Cys-Ser ladder of alternating Ser (from RIPK1) and Cys (from RIPK3). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9Y572}. |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: Q9QZL0 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
| Western blot IHC ICC |
Documents
| # | SDS | Certificate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | |||
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.







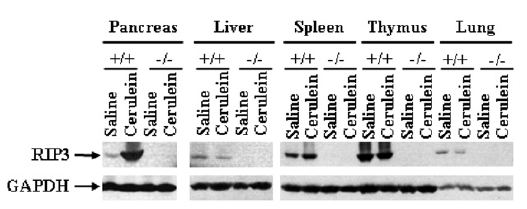
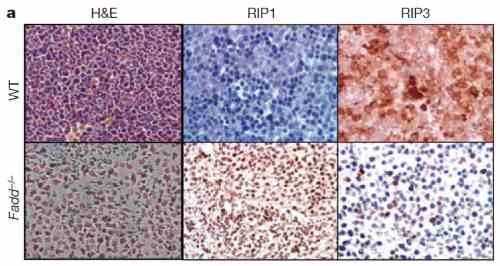
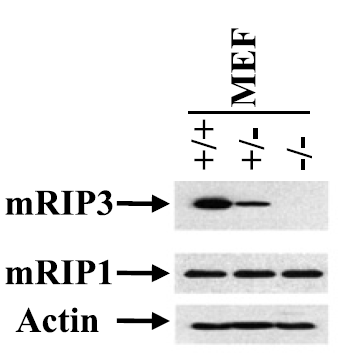







Reviews
There are no reviews yet.