| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| host | mouse |
| isotype | IgG |
| clonality | monoclonal |
| concentration | concentrate, predilute |
| applications | IHC |
| reactivity | human |
| available size | 0.1 mL, 0.5 mL, 1 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted |
rabbit anti-PR monoclonal antibody (ZR4) 6434
Price range: $160.00 through $528.00
Antibody summary
- Rabbit monoclonal to PR
- Suitable for: Immunohistochemistry (formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues)
- Reacts with: Human
- Isotype:IgG
- Control: Breast carcinomas
- Visualization: Nuclear
- 0.1, 0.5, 1.0 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted
rabbit anti-PR monoclonal antibody ZR4 6434
| target relevance |
|---|
| Protein names Progesterone receptor (PR) (Nuclear receptor subfamily 3 group C member 3) |
| Gene names PGR,PGR NR3C3 |
| Protein family Nuclear hormone receptor family, NR3 subfamily |
| Mass 98981Da |
| Function FUNCTION: The steroid hormones and their receptors are involved in the regulation of eukaryotic gene expression and affect cellular proliferation and differentiation in target tissues. Depending on the isoform, progesterone receptor functions as a transcriptional activator or repressor. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10757795, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1587864, ECO:0000269|PubMed:37478846, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9407067, ECO:0000305}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform A]: Ligand-dependent transdominant repressor of steroid hormone receptor transcriptional activity including repression of its isoform B, MR and ER. Transrepressional activity may involve recruitment of corepressor NCOR2. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:7969170, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8180103, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8264658, ECO:0000305, ECO:0000305|PubMed:10757795}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform B]: Transcriptional activator of several progesteron-dependent promoters in a variety of cell types. Involved in activation of SRC-dependent MAPK signaling on hormone stimulation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:7969170}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 4]: Increases mitochondrial membrane potential and cellular respiration upon stimulation by progesterone. |
| Subellular location SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: Nucleus. Cytoplasm. Note=Nucleoplasmic shuttling is both hormone- and cell cycle-dependent. On hormone stimulation, retained in the cytoplasm in the G(1) and G(2)/M phases.; SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: [Isoform A]: Nucleus. Cytoplasm. Note=Mainly nuclear.; SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: [Isoform 4]: Mitochondrion outer membrane {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23518922}. |
| Tissues TISSUE SPECIFICITY: In reproductive tissues the expression of isoform A and isoform B varies as a consequence of developmental and hormonal status. Isoform A and isoform B are expressed in comparable levels in uterine glandular epithelium during the proliferative phase of the menstrual cycle. Expression of isoform B but not of isoform A persists in the glands during mid-secretory phase. In the stroma, isoform A is the predominant form throughout the cycle. Heterogeneous isoform expression between the glands of the endometrium basalis and functionalis is implying region-specific responses to hormonal stimuli. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11041221}. |
| Structure SUBUNIT: Interacts with SMARD1 and UNC45A. Interacts with CUEDC2; the interaction promotes ubiquitination, decreases sumoylation, and represses transcriptional activity. Interacts with PIAS3; the interaction promotes sumoylation of PR in a hormone-dependent manner, inhibits DNA-binding, and alters nuclear export. Interacts with SP1; the interaction requires ligand-induced phosphorylation on Ser-345 by ERK1/2 MAPK. Interacts with PRMT2. Isoform A interacts with NCOR2. Isoform B (but not isoform A) interacts with NCOA2 and NCOA1. Isoform B (but not isoform A) interacts with KLF9. Interacts with GTF2B (PubMed:1517211). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q00175, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10757795, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12039952, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12917342, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1517211, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16478993, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17020914, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17347654, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18202149}. |
| Post-translational modification PTM: Phosphorylated on multiple serine sites. Several of these sites are hormone-dependent. Phosphorylation on Ser-294 occurs preferentially on isoform B, is highly hormone-dependent and modulates ubiquitination and sumoylation on Lys-388. Phosphorylation on Ser-102 and Ser-345 also requires induction by hormone. Basal phosphorylation on Ser-81, Ser-162, Ser-190 and Ser-400 is increased in response to progesterone and can be phosphorylated in vitro by the CDK2-A1 complex. Increased levels of phosphorylation on Ser-400 also in the presence of EGF, heregulin, IGF, PMA and FBS. Phosphorylation at this site by CDK2 is ligand-independent, and increases nuclear translocation and transcriptional activity. Phosphorylation at Ser-162 and Ser-294, but not at Ser-190, is impaired during the G(2)/M phase of the cell cycle. Phosphorylation on Ser-345 by ERK1/2 MAPK is required for interaction with SP1. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10628747, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10655479, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11110801, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15572662, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15798179, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17020914, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17173941, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17347654, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17717077, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18202149, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7476977, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8702648, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9171245}.; PTM: Sumoylation is hormone-dependent and represses transcriptional activity. Sumoylation on all three sites is enhanced by PIAS3. Desumoylated by SENP1. Sumoylation on Lys-388, the main site of sumoylation, is repressed by ubiquitination on the same site, and modulated by phosphorylation at Ser-294. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10628747, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10655479, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15798179, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17020914, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17173941, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17347654, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17717077, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18202149, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8702648}.; PTM: Ubiquitination is hormone-dependent and represses sumoylation on the same site (PubMed:10628747, PubMed:10655479, PubMed:15798179, PubMed:17173941, PubMed:17717077, PubMed:18202149, PubMed:8702648). Promoted by MAPK-mediated phosphorylation on Ser-294 (PubMed:10628747, PubMed:10655479, PubMed:15798179, PubMed:17173941, PubMed:17717077, PubMed:18202149, PubMed:8702648). Ubiquitinated by UBR5, leading to its degradation: UBR5 specifically recognizes and binds ligand-bound PGR when it is not associated with coactivators (NCOAs) (PubMed:37478846). In presence of NCOAs, the UBR5-degron is not accessible, preventing its ubiquitination and degradation (PubMed:37478846). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10628747, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10655479, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15798179, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17173941, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17717077, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18202149, ECO:0000269|PubMed:37478846, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8702648}.; PTM: Palmitoylated by ZDHHC7 and ZDHHC21. Palmitoylation is required for plasma membrane targeting and for rapid intracellular signaling via ERK and AKT kinases and cAMP generation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22031296}. |
| Domain DOMAIN: Composed of three domains: a modulating N-terminal domain, a DNA-binding domain and a C-terminal ligand-binding domain. |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: P06401 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
 |
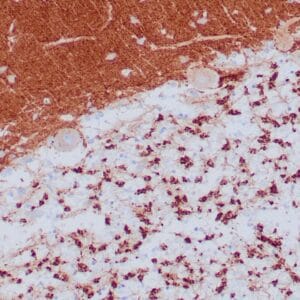
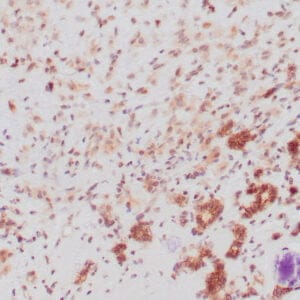
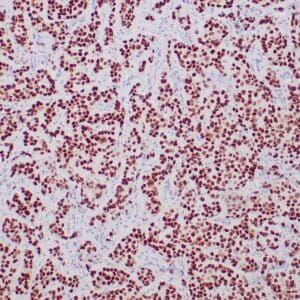
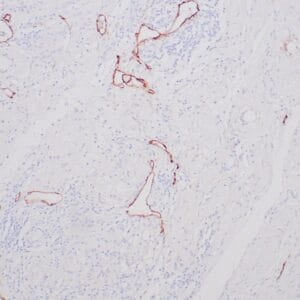
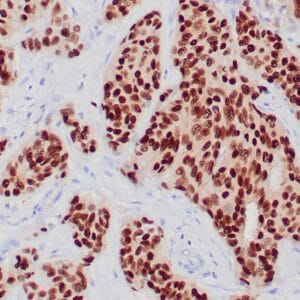
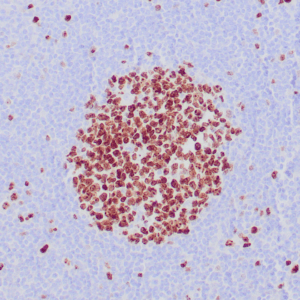
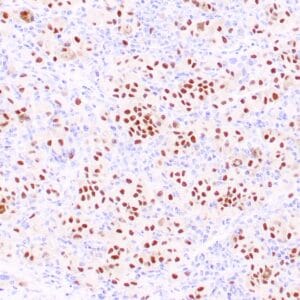
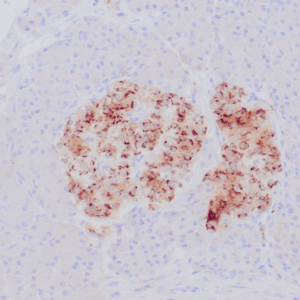
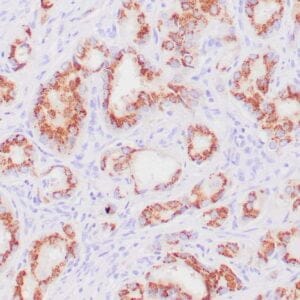
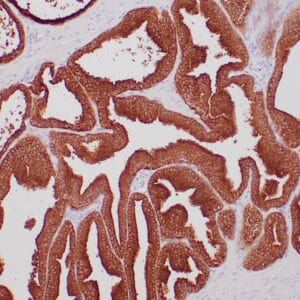
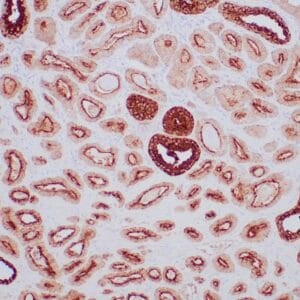
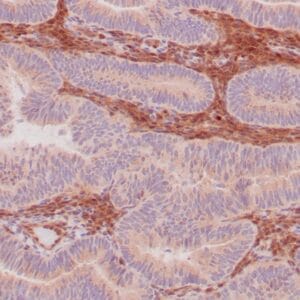
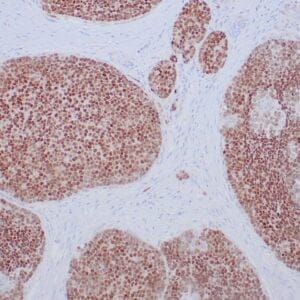
| Human breast carcinoma stained with anti-PR antibody using peroxidase-conjugate and DAB chromogen. Note the nuclear staining of tumor cells. |
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
| IHC |
Documents
| # | SDS | Certificate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | |||
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.