| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| host | rabbit |
| isotype | IgG |
| clonality | polyclonal |
| concentration | 1 mg/mL |
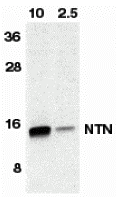
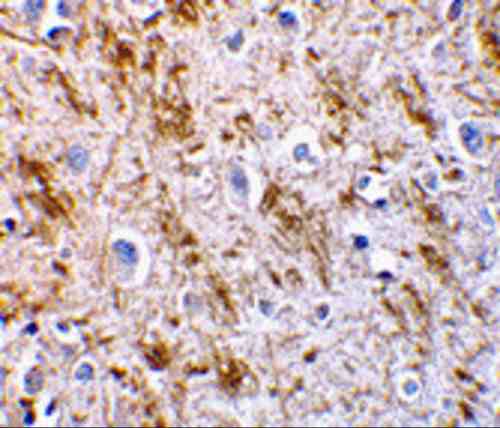
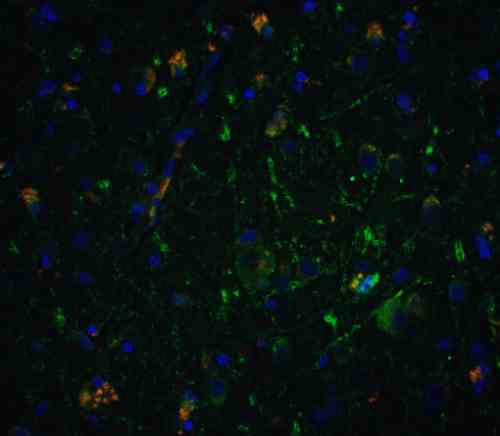
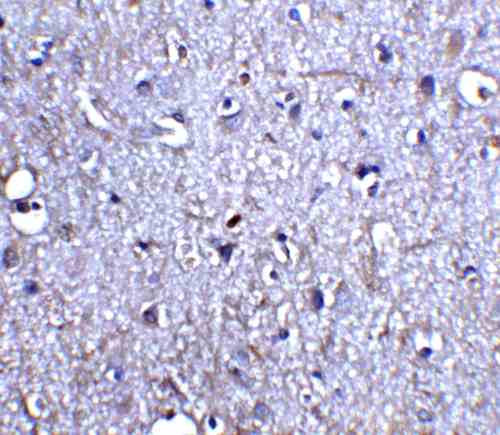
| applications | ICC/IF, WB |
| reactivity | Neurturin |
| available sizes | 100 µg |
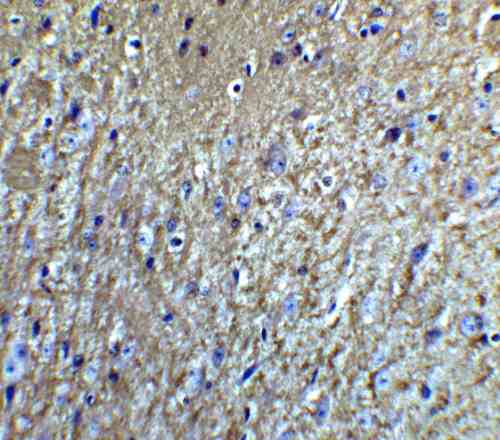
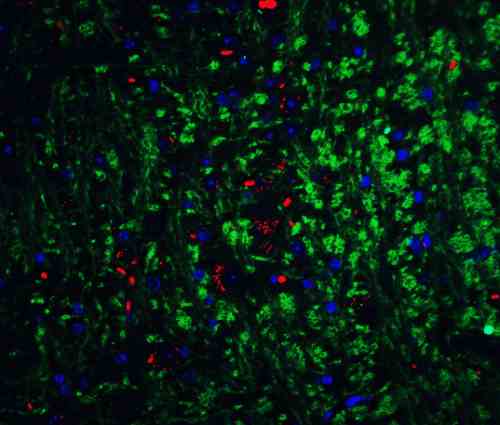
rabbit anti-Neurturin polyclonal antibody 6199
$445.00
Antibody summary
- Rabbit polyclonal to Neurturin
- Suitable for: ELISA,WB,IHC-P,IF
- Isotype: IgG
- 100 µg
rabbit anti-Neurturin polyclonal antibody 6199
| target relevance |
|---|
| Protein names Neurturin |
| Gene names NRTN,NRTN |
| Protein family TGF-beta family, GDNF subfamily |
| Mass 22405Da |
| Function FUNCTION: Growth factor that supports the survival of sympathetic neurons in culture (PubMed:8945474). May regulate the development and maintenance of the CNS (PubMed:8945474). Involved in the development of the neural crest (PubMed:15242795). Might control the size of non-neuronal cell population such as haemopoietic cells (PubMed:8945474). Acts by binding to its coreceptor, GFRA2, leading to autophosphorylation and activation of the RET receptor (PubMed:10829012, PubMed:29414779, PubMed:31535977). Heparan sulfate-binding is required for signaling (PubMed:29414779). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10829012, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15242795, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29414779, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31535977, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8945474}. |
| Subellular location SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: Secreted {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P97463}. |
| Structure SUBUNIT: Homodimer; disulfide-linked (PubMed:29414779, PubMed:31535977). Interacts with GFRA2 coreceptor and RET: forms a 2:2:2 ternary complex composed of NRTN ligand, GFRA2 and RET receptor (PubMed:31535977). Also forms a 4:4:4 tetrameric complex composed of 4 copies of NRTN ligand, GFRA2 and RET receptor, which prevents endocytosis of RET (PubMed:31535977). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:29414779, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31535977}. |
| Involvement in disease DISEASE: Note=Genetic variations in NRTN may contribute to Hirschsprung disease, in association with mutations of RET gene, and possibly mutations in other loci. Hirschsprung disease is a disorder of neural crest development is characterized by the absence of intramural ganglion cells in the hindgut, often resulting in intestinal obstruction. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9700200}. |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: Q99748 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
| Western blot IHC ICC |
Documents
| # | SDS | Certificate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | |||
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.













Reviews
There are no reviews yet.