| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| host | mouse |
| isotype | IgG |
| clonality | monoclonal |
| concentration | concentrate, predilute |
| applications | IHC |
| reactivity | human |
| available size | 0.1 mL, 0.5 mL, 1 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted |
rabbit anti-MyoD1 monoclonal antibody (ZR262) 6277
Price range: $160.00 through $528.00
Antibody summary
- Rabbit monoclonal to MyoD1
- Suitable for: Immunohistochemistry (formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues)
- Reacts with: Human
- Isotype:IgG
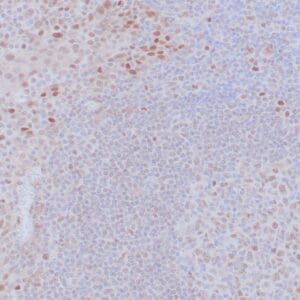
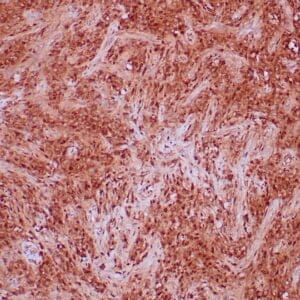
- Control: Rhabdomyosarcoma
- Visualization: Nuclear and cytoplasmic
- 0.1, 0.5, 1.0 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted
rabbit anti-MyoD1 monoclonal antibody ZR262 6277
| target relevance |
|---|
| Protein names Myoblast determination protein 1 (Class C basic helix-loop-helix protein 1) (bHLHc1) (Myogenic factor 3) (Myf-3) |
| Gene names MYOD1,MYOD1 BHLHC1 MYF3 MYOD |
| Mass 34501Da |
| Function FUNCTION: Acts as a transcriptional activator that promotes transcription of muscle-specific target genes and plays a role in muscle differentiation. Together with MYF5 and MYOG, co-occupies muscle-specific gene promoter core region during myogenesis. Induces fibroblasts to differentiate into myoblasts. Interacts with and is inhibited by the twist protein. This interaction probably involves the basic domains of both proteins (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
| Subellular location SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: Nucleus. |
| Structure SUBUNIT: Efficient DNA binding requires dimerization with another bHLH protein. Seems to form active heterodimers with ITF-2. Interacts with SUV39H1. Interacts with DDX5. Interacts with CHD2. Interacts with TSC22D3 (By similarity). Interacts with SETD3 (By similarity). Interacts with P-TEFB complex; promotes the transcriptional activity of MYOD1 through its CDK9-mediated phosphorylation (By similarity) (PubMed:12037670). Interacts with CSRP3. Interacts with NUPR1 (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P10085, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12037670, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16858404, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24860983}. |
| Post-translational modification PTM: Phosphorylated by CDK9. This phosphorylation promotes its function in muscle differentiation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12037670}.; PTM: Acetylated by a complex containing EP300 and PCAF. The acetylation is essential to activate target genes. Conversely, its deacetylation by SIRT1 inhibits its function (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}.; PTM: Ubiquitinated on the N-terminus; which is required for proteasomal degradation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9774340}.; PTM: Methylation at Lys-104 by EHMT2/G9a inhibits myogenic activity. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22215600}. |
| Involvement in disease DISEASE: Congenital myopathy 17 (CMYO17) [MIM:618975]: An autosomal recessive muscular disorder characterized by hypotonia and respiratory insufficiency apparent soon after birth, high diaphragmatic dome on imaging, poor overall growth, pectus excavatum, dysmorphic facies, and renal anomalies in some affected individuals. Additional variable features include delayed motor development, mildly decreased endurance, distal arthrogryposis, and lung hypoplasia resulting in early death. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26733463, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30403323, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31260566}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: P15172 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
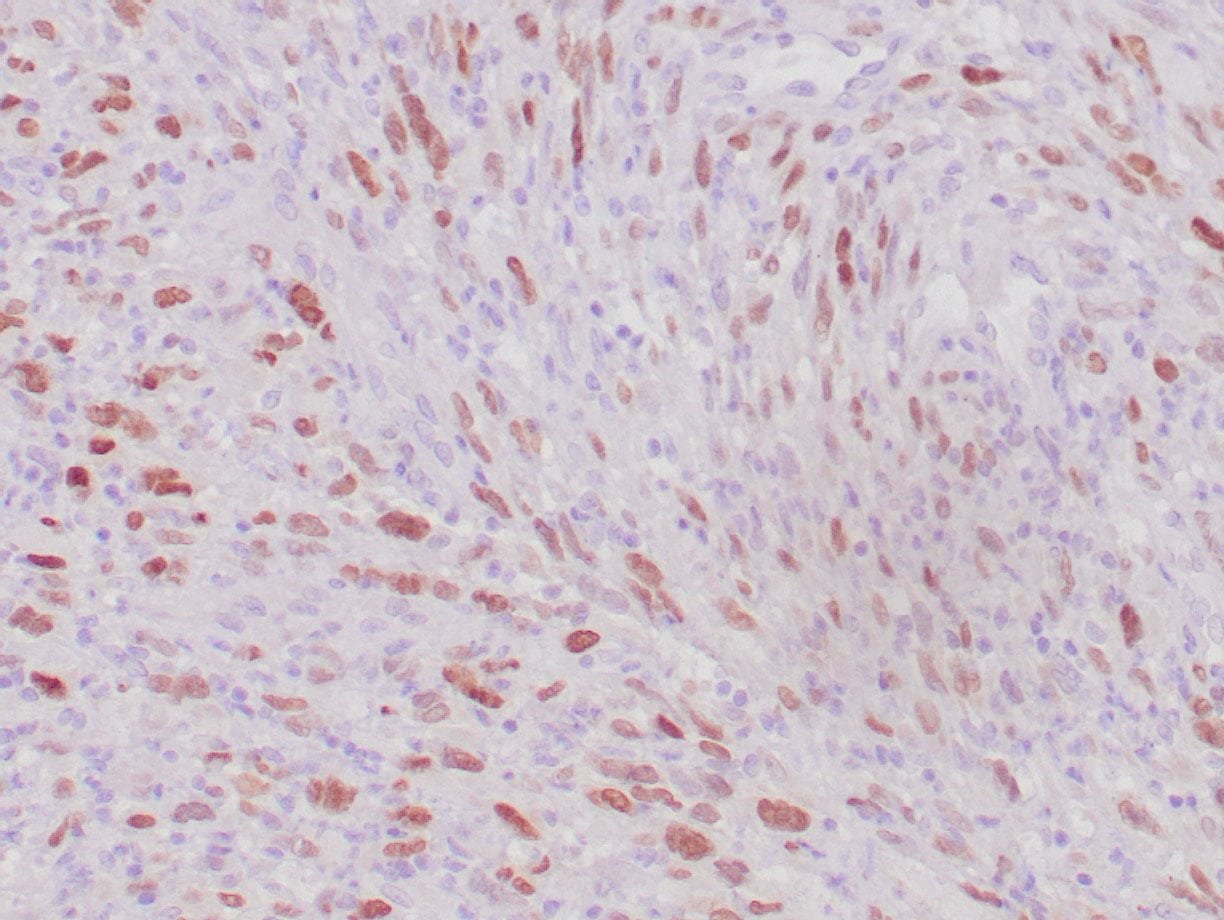 |
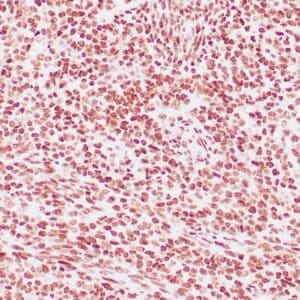
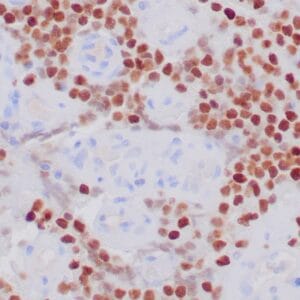
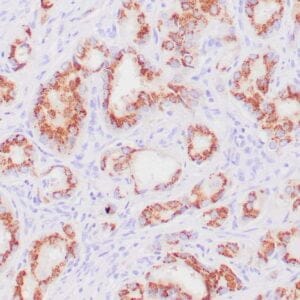
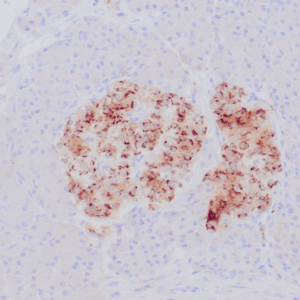
| Human rhabdomyosarcoma stained with anti-MyoD1 antibody using peroxidase-conjugate and DAB chromogen. Note the nuclear staining of sarcoma cells. |
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
| IHC |
Documents
| # | SDS | Certificate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | |||
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.