| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| host | mouse |
| isotype | IgG2a |
| clonality | monoclonal |
| concentration | 1 mg/mL |
| applications | ICC/IF, WB |
| reactivity | RPA32 |
| available sizes | 100 µg |
mouse anti-RPA32 monoclonal antibody (12F3.3) 6624
$503.00
Antibody summary
- Mouse monoclonal to RPA32
- Suitable for: WB,ICC/IF,IP
- Isotype: IgG2a
- 100 µg
mouse anti-RPA32 monoclonal antibody (12F3.3) 6624
| antibody |
|---|
| Tested applications WB,ICC/IF,IP |
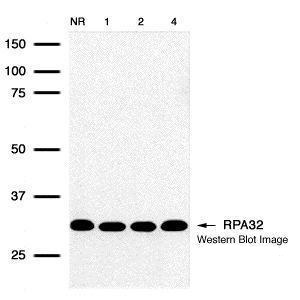
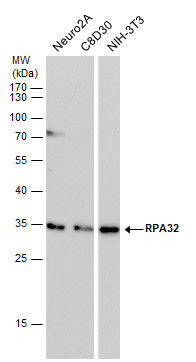
| Recommended dilutions Immunoblotting, Immunoprecipitation: use at 0.2-1 ug/mL. Positive control: HeLa, Raji, and 3T3 cells and recombinant protein. |
| Immunogen N-terminally 6x-His tagged fusion protein corresponding to full-length human RPA32 expressed in E. coli. |
| Size and concentration 100µg and lot specific |
| Form liquid |
| Storage Instructions This antibody is stable for at least one (1) year at -70°C. Avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Storage buffer PBS, pH 7.4 |
| Purity protein affinity purification |
| Clonality monoclonal |
| Isotype IgG2a |
| Compatible secondaries goat anti-mouse IgG, H&L chain specific, peroxidase conjugated polyclonal antibody 5486 goat anti-mouse IgG, H&L chain specific, biotin conjugated, Conjugate polyclonal antibody 2685 goat anti-mouse IgG, H&L chain specific, FITC conjugated polyclonal antibody 7854 goat anti-mouse IgG, H&L chain specific, peroxidase conjugated polyclonal antibody, crossabsorbed 1706 goat anti-mouse IgG, H&L chain specific, biotin conjugated polyclonal antibody, crossabsorbed 1716 goat anti-mouse IgG, H&L chain specific, FITC conjugated polyclonal antibody, crossabsorbed 1721 |
| Isotype control Mouse monocolonal IgG2a - Isotype Control |
| target relevance |
|---|
| Protein names Replication protein A 32 kDa subunit (RP-A p32) (Replication factor A protein 2) (RF-A protein 2) (Replication protein A 34 kDa subunit) (RP-A p34) |
| Gene names RPA2,RPA2 REPA2 RPA32 RPA34 |
| Protein family Replication factor A protein 2 family |
| Mass 29247Da |
| Function FUNCTION: As part of the heterotrimeric replication protein A complex (RPA/RP-A), binds and stabilizes single-stranded DNA intermediates that form during DNA replication or upon DNA stress. It prevents their reannealing and in parallel, recruits and activates different proteins and complexes involved in DNA metabolism. Thereby, it plays an essential role both in DNA replication and the cellular response to DNA damage. In the cellular response to DNA damage, the RPA complex controls DNA repair and DNA damage checkpoint activation. Through recruitment of ATRIP activates the ATR kinase a master regulator of the DNA damage response. It is required for the recruitment of the DNA double-strand break repair factors RAD51 and RAD52 to chromatin in response to DNA damage. Also recruits to sites of DNA damage proteins like XPA and XPG that are involved in nucleotide excision repair and is required for this mechanism of DNA repair. Also plays a role in base excision repair (BER) probably through interaction with UNG. Also recruits SMARCAL1/HARP, which is involved in replication fork restart, to sites of DNA damage. May also play a role in telomere maintenance. RPA stimulates 5'-3' helicase activity of BRIP1/FANCJ (PubMed:17596542). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15205463, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17596542, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17765923, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17959650, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19116208, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20154705, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21504906, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2406247, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24332808, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7697716, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7700386, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8702565, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9430682, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9765279}. |
| Subellular location SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: Nucleus {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10982866, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12814551, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17596542, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20154705, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21504906}. Nucleus, PML body {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12814551}. Note=Redistributes to discrete nuclear foci upon DNA damage in an ATR-dependent manner. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12814551}. |
| Structure SUBUNIT: Component of the replication protein A complex (RPA/RP-A), a heterotrimeric complex composed of RPA1, RPA2 and RPA3 (PubMed:10449415, PubMed:19116208, PubMed:2406247). Interacts with PRPF19; the PRP19-CDC5L complex is recruited to the sites of DNA repair where it ubiquitinates the replication protein A complex (RPA) (PubMed:24332808). Interacts with SERTAD3 (PubMed:10982866). Interacts with TIPIN (PubMed:17141802, PubMed:17296725). Interacts with TIMELESS (PubMed:17141802). Interacts with PPP4R2; the interaction is direct, DNA damage-dependent and mediates the recruitment of the PP4 catalytic subunit PPP4C (PubMed:20154705). Interacts (hyperphosphorylated) with RAD51 (PubMed:20154705). Interacts with SMARCAL1; the interaction is direct and mediates the recruitment to the RPA complex of SMARCAL1 (PubMed:19793861, PubMed:19793862, PubMed:19793863). Interacts with RAD52 and XPA; those interactions are direct and associate RAD52 and XPA to the RPA complex (PubMed:11081631, PubMed:17765923, PubMed:7700386, PubMed:8702565). Interacts with FBH1 (PubMed:23319600). Interacts with ETAA1; the interaction is direct and promotes ETAA1 recruitment at stalled replication forks (PubMed:27601467, PubMed:27723717, PubMed:27723720). Interacts with RFWD3 (PubMed:21504906, PubMed:21558276, PubMed:26474068, PubMed:28575657). Interacts with DDI2 (PubMed:29290612). Interacts (in unphosphorylated form via N-terminus) with EIF4EBP3; the interaction enhances EIF4EBP3-mediated inhibition of EIF4E-mediated mRNA nuclear export (PubMed:22684010). Interacts with BRIP1/FANCJ via the RPA1 subunit; following DNA damage they colocalize in foci in the nucleus (PubMed:17596542). Interacts with nuclear UNG (isoform 2); this interaction mediates UNG recruitment to RPA-coated single-stranded DNA at stalled replication forks. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10449415, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10982866, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11081631, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17141802, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17296725, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17596542, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17765923, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19793861, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19793862, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19793863, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20154705, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21504906, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21558276, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22521144, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22684010, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23319600, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2406247, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24332808, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26474068, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27601467, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27723717, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27723720, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28575657, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29290612, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7700386, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8702565}. |
| Post-translational modification PTM: Differentially phosphorylated throughout the cell cycle, becoming phosphorylated at the G1-S transition and dephosphorylated in late mitosis. Mainly phosphorylated at Ser-23 and Ser-29, by cyclin A-CDK2 and cyclin B-CDK1, respectively during DNA replication and mitosis. Dephosphorylation may require the serine/threonine-protein phosphatase 4. Phosphorylation at Ser-23 and Ser-29 is a prerequisite for further phosphorylation. Becomes hyperphosphorylated on additional residues including Ser-4, Ser-8, Thr-21 and Ser-33 in response to DNA damage. Hyperphosphorylation is mediated by ATM, ATR and PRKDC. Primarily recruited to DNA repair nuclear foci as a hypophosphorylated form it undergoes subsequent hyperphosphorylation, catalyzed by ATR. Hyperphosphorylation is required for RAD51 recruitment to chromatin and efficient DNA repair. Phosphorylation at Thr-21 depends upon RFWD3 presence. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12814551, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1318195, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20154705, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21558276, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21731742, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26474068, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8246944, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9139719, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9295339}.; PTM: DNA damage-induced 'Lys-63'-linked polyubiquitination by PRPF19 mediates ATRIP recruitment to the RPA complex at sites of DNA damage and activation of ATR (PubMed:24332808). Ubiquitinated by RFWD3 at stalled replication forks in response to DNA damage: ubiquitination by RFWD3 does not lead to degradation by the proteasome and promotes removal of the RPA complex from stalled replication forks, promoting homologous recombination (PubMed:26474068). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24332808, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26474068}. |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: P15927 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
| Western blot IHC ICC |
Documents
| # | SDS | Certificate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | |||
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.
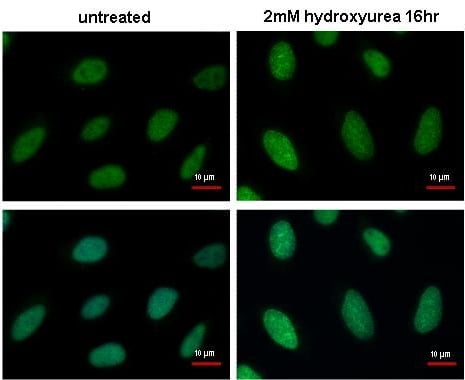
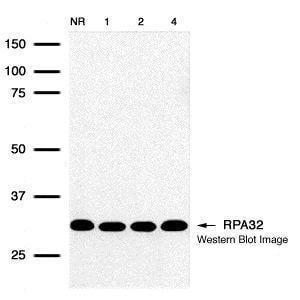
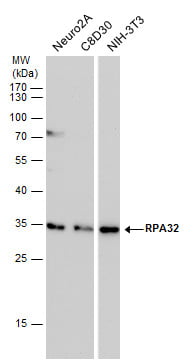
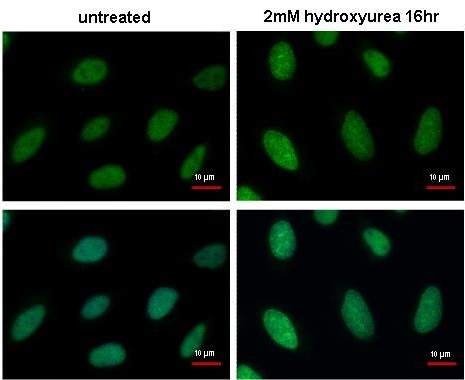







Reviews
There are no reviews yet.