| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| host | mouse |
| isotype | IgG1 |
| clonality | monoclonal |
| concentration | concentrate, predilute |
| applications | IHC |
| reactivity | human |
| available size | 0.1 mL, 0.5 mL, 1 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted |
mouse anti-Podoplanin monoclonal antibody (D2-40) 6341
Price range: $160.00 through $528.00
Antibody summary
- Mouse monoclonal to Podoplanin
- Suitable for: Immunohistochemistry (formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues)
- Reacts with: Human
- Isotype:IgG1
- Control: Germ cell tumor
- Visualization: Cytoplasmic
- 0.1, 0.5, 1.0 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted
mouse anti-Podoplanin monoclonal antibody D2-40 6341
| target relevance |
|---|
| Protein names Podoplanin (Aggrus) (Glycoprotein 36) (Gp36) (PA2.26 antigen) (T1-alpha) (T1A) [Cleaved into: 29kDa cytosolic podoplanin intracellular domain (PICD)] |
| Gene names PDPN,PDPN GP36 PSEC0003 PSEC0025 |
| Protein family Podoplanin family |
| Mass 16698Da |
| Function FUNCTION: Mediates effects on cell migration and adhesion through its different partners. During development plays a role in blood and lymphatic vessels separation by binding CLEC1B, triggering CLEC1B activation in platelets and leading to platelet activation and/or aggregation (PubMed:14522983, PubMed:15231832, PubMed:17222411, PubMed:17616532, PubMed:18215137). Interaction with CD9, on the contrary, attenuates platelet aggregation induced by PDPN (PubMed:18541721). Through MSN or EZR interaction promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) leading to ERZ phosphorylation and triggering RHOA activation leading to cell migration increase and invasiveness (PubMed:17046996, PubMed:21376833). Interaction with CD44 promotes directional cell migration in epithelial and tumor cells (PubMed:20962267). In lymph nodes (LNs), controls fibroblastic reticular cells (FRCs) adhesion to the extracellular matrix (ECM) and contraction of the actomyosin by maintaining ERM proteins (EZR; MSN and RDX) and MYL9 activation through association with unknown transmembrane proteins. Engagement of CLEC1B by PDPN promotes FRCs relaxation by blocking lateral membrane interactions leading to reduction of ERM proteins (EZR; MSN and RDX) and MYL9 activation (By similarity). Through binding with LGALS8 may participate in connection of the lymphatic endothelium to the surrounding extracellular matrix (PubMed:19268462). In keratinocytes, induces changes in cell morphology showing an elongated shape, numerous membrane protrusions, major reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton, increased motility and decreased cell adhesion (PubMed:15515019). Controls invadopodia stability and maturation leading to efficient degradation of the extracellular matrix (ECM) in tumor cells through modulation of RHOC activity in order to activate ROCK1/ROCK2 and LIMK1/LIMK2 and inactivation of CFL1 (PubMed:25486435). Required for normal lung cell proliferation and alveolus formation at birth (By similarity). Does not function as a water channel or as a regulator of aquaporin-type water channels (PubMed:9651190). Does not have any effect on folic acid or amino acid transport (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q62011, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14522983, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15231832, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15515019, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17046996, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17222411, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17616532, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18215137, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18541721, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19268462, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20962267, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21376833, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25486435, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9651190}. |
| Subellular location SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: [Podoplanin]: Membrane {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17046996, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20962267, ECO:0000305|PubMed:18215137}; Single-pass type I membrane protein {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q62011}. Cell projection, lamellipodium membrane {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17046996, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20962267}; Single-pass type I membrane protein {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q62011}. Cell projection, filopodium membrane {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17046996}; Single-pass type I membrane protein {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q62011}. Cell projection, microvillus membrane {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17046996}; Single-pass type I membrane protein {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q62011}. Cell projection, ruffle membrane {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17046996}; Single-pass type I membrane protein {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q62011}. Membrane raft {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21376833}. Apical cell membrane {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20962267}. Basolateral cell membrane {ECO:0000269|PubMed:14978162}. Cell projection, invadopodium {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25486435}. Note=Localized to actin-rich microvilli and plasma membrane projections such as filopodia, lamellipodia and ruffles (By similarity). Association to the lipid rafts is required for PDPN-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) (PubMed:21376833). Colocalizes with CD9 in tetraspanin microdomains (PubMed:18541721). Localized at invadopodium adhesion rings in tumor cell. Association to the lipid rafts is essential for PDPN recruitment to invadopodia and ECM degradation (PubMed:25486435). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q62011, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18541721, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21376833, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25486435}.; SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: [29kDa cytosolic podoplanin intracellular domain]: Cytoplasm, cytosol {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24275092}. |
| Tissues TISSUE SPECIFICITY: Highly expressed in placenta, lung, skeletal muscle and brain. Weakly expressed in brain, kidney and liver. In placenta, expressed on the apical plasma membrane of endothelium. In lung, expressed in alveolar epithelium. Up-regulated in colorectal tumors and expressed in 25% of early oral squamous cell carcinomas. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10393083, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14522983, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15515019}. |
| Structure SUBUNIT: Homodimer (PubMed:21376833). Interacts with CLEC1B; the interaction is independent of CLEC1B glycosylation and activates CLEC1B; the interaction is dependent of sialic acid on O-glycans (PubMed:17616532, PubMed:18215137, PubMed:25458834). Interacts with CD9; this interaction is homophilic and attenuates platelet aggregation and pulmonary metastasis induced by PDPN (PubMed:18541721). Interacts with LGALS8; the interaction is glycosylation-dependent; may participate in connection of the lymphatic endothelium to the surrounding extracellular matrix (PubMed:19268462). Interacts with HSPA9 (PubMed:23541579). Interacts (via extracellular domain) with CD44; this interaction is required for PDPN-mediated directional migration and regulation of lamellipodia extension/stabilization during cell spreading and migration (PubMed:20962267). Interacts (via cytoplasmic domain) with MSN and EZR; activates RHOA and promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition (PubMed:17046996). Interacts with CCL21; relocalized PDPN to the basolateral membrane (PubMed:14978162). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:14978162, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17046996, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17616532, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18215137, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18541721, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19268462, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20962267, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21376833, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23541579, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25458834}. |
| Post-translational modification PTM: Extensively O-glycosylated. Contains sialic acid residues. O-glycosylation is necessary for platelet aggregation activity. Disialylated at Thr-52; sialic acid is critical for platelet-aggregating activity and for CLEC1B interaction (PubMed:17222411, PubMed:25458834). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10393083, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15231832, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15515019, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17222411, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25458834}.; PTM: The N-terminus is blocked. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q64294}.; PTM: Cleaved by a metalloprotease within its extracellular (EC) domain, generating a membrane-bound C-terminal fragment (PCTF33) and an extracellular fragment. The resulting membrane-bound C-terminal fragment (PCTF33) is further processed between Val-150 and Val-151 by PSEN1/gamma-secretase generating the intracellular domain of podoplanin (PICD). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24275092}. |
| Domain DOMAIN: The cytoplasmic domain controls FRC elongation but is dispensable for contraction (By similarity). The cytoplasmic domain is essential for recruitment to invadopodia and ECM degradation (PubMed:25486435). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q62011, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25486435}. |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: Q86YL7 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
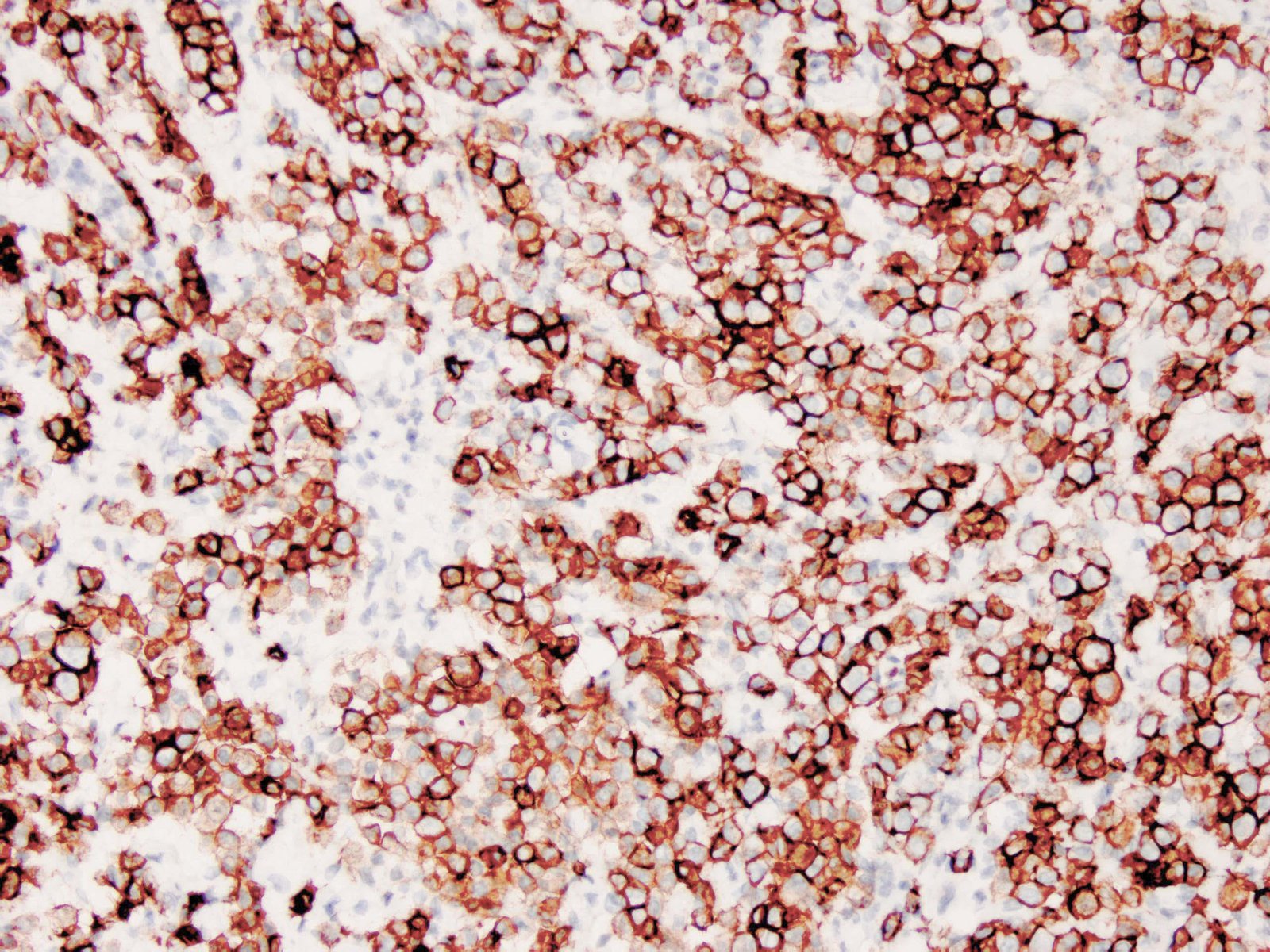 |
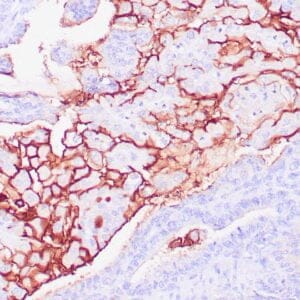
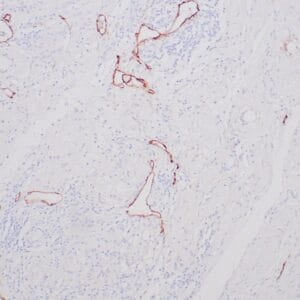
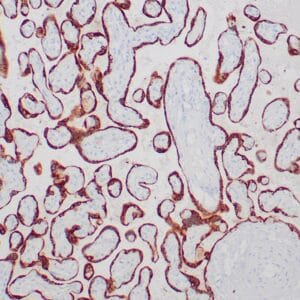
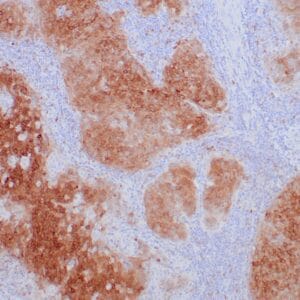
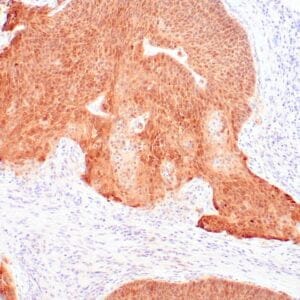
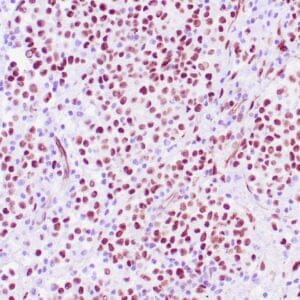
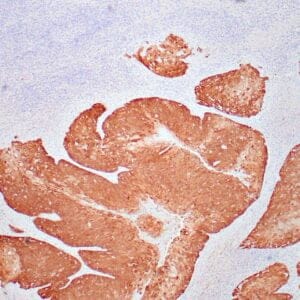
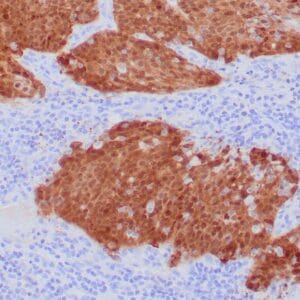
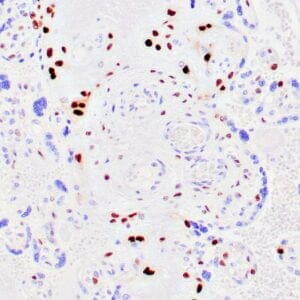
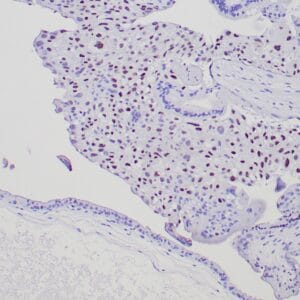
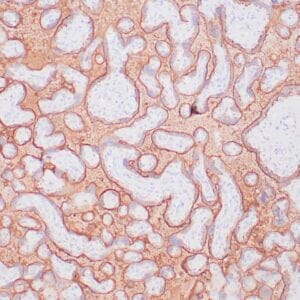
| Human testicular seminoma stained with anti-D2-40 antibody using peroxidase-conjugate and DAB chromogen. Note cytoplasmic staining of tumor cells and endothelial cells of lymphatic channels. |
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
| IHC |
Documents
| # | SDS | Certificate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | |||
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.
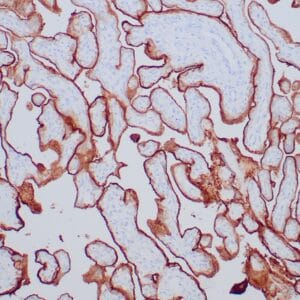
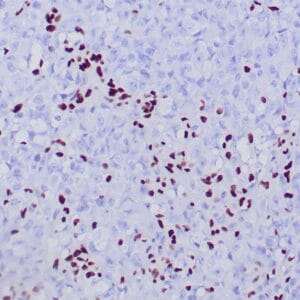
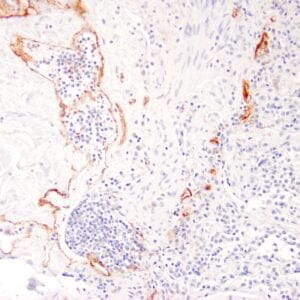

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.