| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| host | mouse |
| isotype | IgG1 |
| clonality | monoclonal |
| concentration | 1 mg/mL |
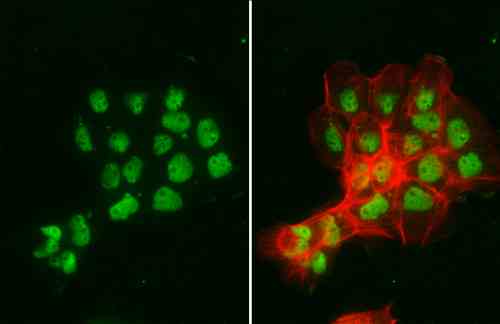
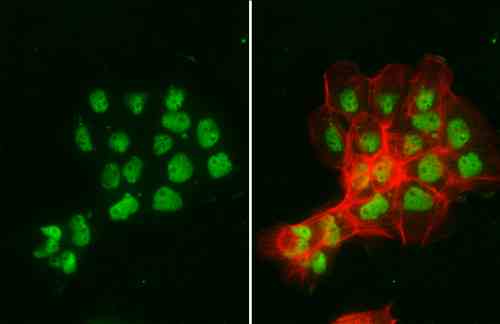
| applications | ICC/IF, WB |
| reactivity | p95/Nibrin |
| available sizes | 100 µg |
mouse anti-p95 monoclonal antibody (1D7) 1319
$503.00
Antibody summary
- Mouse monoclonal to p95
- Suitable for: WB,ICC/IF,IP
- Isotype: IgG1
- 100 µg
mouse anti-p95 monoclonal antibody (1D7) 1319
| antibody |
|---|
| Tested applications WB,ICC/IF,IP |
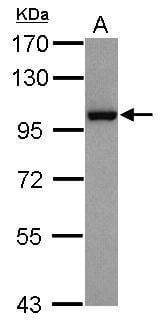
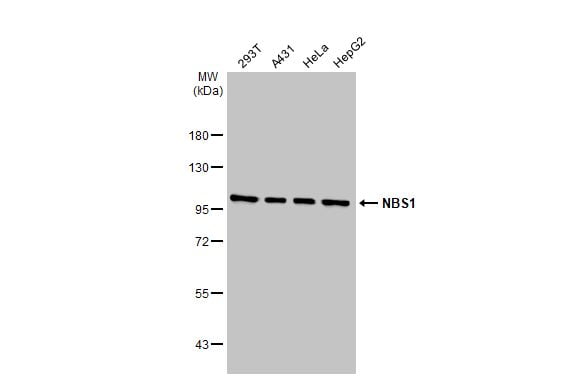
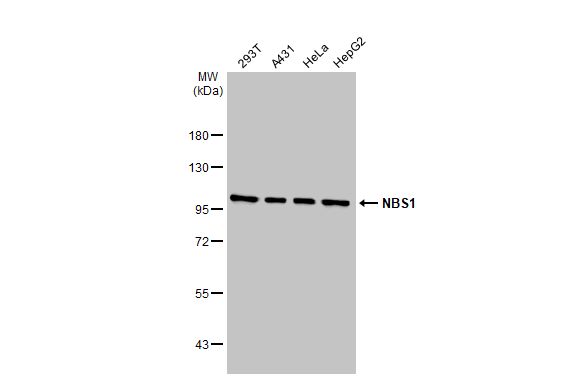
| Recommended dilutions Immunoblotting, Immunoprecipitation:: use at 1-2 ug/mL. In immunoblots, a band of 95 kD is detected. Positive controls: MCF-7, HeLa, or Raji cells. |
| Immunogen Fusion protein containing the complete coding region of human p95/nibrin expressed in E. coli. |
| Size and concentration 100µg and lot specific |
| Form liquid |
| Storage Instructions This antibody is stable for at least one (1) year at -70°C. Avoid multiple freeze- thaw cycles. |
| Storage buffer PBS, pH 7.4. |
| Purity protein affinity purification |
| Clonality monoclonal |
| Isotype IgG1 |
| Compatible secondaries goat anti-mouse IgG, H&L chain specific, peroxidase conjugated polyclonal antibody 5486 goat anti-mouse IgG, H&L chain specific, biotin conjugated, Conjugate polyclonal antibody 2685 goat anti-mouse IgG, H&L chain specific, FITC conjugated polyclonal antibody 7854 goat anti-mouse IgG, H&L chain specific, peroxidase conjugated polyclonal antibody, crossabsorbed 1706 goat anti-mouse IgG, H&L chain specific, biotin conjugated polyclonal antibody, crossabsorbed 1716 goat anti-mouse IgG, H&L chain specific, FITC conjugated polyclonal antibody, crossabsorbed 1721 |
| Isotype control Mouse monocolonal IgG1 - Isotype Control |
| target relevance |
|---|
| Protein names Nibrin (Cell cycle regulatory protein p95) (Nijmegen breakage syndrome protein 1) (hNbs1) |
| Gene names NBN,NBN NBS NBS1 P95 |
| Protein family Nibrin family |
| Mass 84959Da |
| Function FUNCTION: Component of the MRN complex, which plays a central role in double-strand break (DSB) repair, DNA recombination, maintenance of telomere integrity and meiosis (PubMed:10888888, PubMed:15616588, PubMed:18411307, PubMed:18583988, PubMed:18678890, PubMed:19759395, PubMed:23115235, PubMed:28216226, PubMed:28867292, PubMed:9705271). The MRN complex is involved in the repair of DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) via homologous recombination (HR), an error-free mechanism which primarily occurs during S and G2 phases (PubMed:19759395, PubMed:28867292, PubMed:9705271). The complex (1) mediates the end resection of damaged DNA, which generates proper single-stranded DNA, a key initial steps in HR, and is (2) required for the recruitment of other repair factors and efficient activation of ATM and ATR upon DNA damage (PubMed:19759395, PubMed:9705271). The MRN complex possesses single-strand endonuclease activity and double-strand-specific 3'-5' exonuclease activity, which are provided by MRE11, to initiate end resection, which is required for single-strand invasion and recombination (PubMed:19759395, PubMed:28867292, PubMed:9705271). Within the MRN complex, NBN acts as a protein-protein adapter, which specifically recognizes and binds phosphorylated proteins, promoting their recruitment to DNA damage sites (PubMed:12419185, PubMed:15616588, PubMed:18411307, PubMed:18582474, PubMed:18583988, PubMed:18678890, PubMed:19759395, PubMed:19804756, PubMed:23762398, PubMed:24534091, PubMed:27814491, PubMed:27889449, PubMed:33836577). Recruits MRE11 and RAD50 components of the MRN complex to DSBs in response to DNA damage (PubMed:12419185, PubMed:18411307, PubMed:18583988, PubMed:18678890, PubMed:24534091, PubMed:26438602). Promotes the recruitment of PI3/PI4-kinase family members ATM, ATR, and probably DNA-PKcs to the DNA damage sites, activating their functions (PubMed:15064416, PubMed:15616588, PubMed:15790808, PubMed:16622404, PubMed:22464731, PubMed:30952868, PubMed:35076389). Mediates the recruitment of phosphorylated RBBP8/CtIP to DSBs, leading to cooperation between the MRN complex and RBBP8/CtIP to initiate end resection (PubMed:19759395, PubMed:27814491, PubMed:27889449, PubMed:33836577). RBBP8/CtIP specifically promotes the endonuclease activity of the MRN complex to clear DNA ends containing protein adducts (PubMed:27814491, PubMed:27889449, PubMed:30787182, PubMed:33836577). The MRN complex is also required for the processing of R-loops (PubMed:31537797). NBN also functions in telomere length maintenance via its interaction with TERF2: interaction with TERF2 during G1 phase preventing recruitment of DCLRE1B/Apollo to telomeres (PubMed:10888888, PubMed:28216226). NBN also promotes DNA repair choice at dysfunctional telomeres: NBN phosphorylation by CK2 promotes non-homologous end joining repair at telomeres, while unphosphorylated NBN promotes microhomology-mediated end-joining (MMEJ) repair (PubMed:28216226). Enhances AKT1 phosphorylation possibly by association with the mTORC2 complex (PubMed:23762398). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10888888, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12419185, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15064416, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15616588, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15790808, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16622404, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18411307, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18582474, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18583988, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18678890, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19759395, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19804756, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22464731, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23115235, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23762398, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24534091, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26438602, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27814491, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27889449, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28216226, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28867292, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30787182, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30952868, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31537797, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33836577, ECO:0000269|PubMed:35076389, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9705271}. |
| Subellular location SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: Nucleus {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10783165, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26215093}. Chromosome {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12419185, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18411307, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18582474, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18583988, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18678890, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19338747, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23115235, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24534091, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26215093, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26438602}. Nucleus, PML body {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12470659, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15916964}. Chromosome, telomere {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10888888, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28216226}. Note=Localizes to discrete nuclear foci after treatment with genotoxic agents (PubMed:10783165, PubMed:26215093, PubMed:26438602). Localizes to DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs); recruited to DNA damage sites via association with phosphorylated proteins, such as phosphorylated H2AX, phosphorylated MDC1 and phosphorylated RAD17 (PubMed:12419185, PubMed:18411307, PubMed:18582474, PubMed:18583988, PubMed:18678890, PubMed:19338747, PubMed:23115235, PubMed:24534091, PubMed:26438602). Acetylation of 'Lys-5' of histone H2AX (H2AXK5ac) promotes NBN/NBS1 assembly at the sites of DNA damage (PubMed:26438602). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10783165, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12419185, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18411307, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18582474, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18583988, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18678890, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23115235, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24534091, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26215093, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26438602}. |
| Tissues TISSUE SPECIFICITY: Ubiquitous (PubMed:9590180). Expressed at high levels in testis (PubMed:9590180). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9590180}. |
| Structure SUBUNIT: Component of the MRN complex composed of two heterodimers RAD50 and MRE11 associated with a single NBN (PubMed:11238951, PubMed:26215093, PubMed:28867292, PubMed:36577401, PubMed:9590181, PubMed:9705271). The MRN complexes dimerize on DNA to form joined MRN-MRN oligomers required for DNA double-strand break repair (PubMed:36577401). As part of the MRN complex, interacts with MCM9; the interaction recruits the complex to DNA repair sites (PubMed:26215093). Component of the BASC complex, at least composed of BRCA1, MSH2, MSH6, MLH1, ATM, BLM, RAD50, MRE11 and NBN (PubMed:10783165). Interacts with histone H2AX; this requires phosphorylation of H2AX on 'Ser-139' and promotes NBN recruitment to DNA damage sites (PubMed:12419185, PubMed:19338747). Interacts with (phosphorylated) MDC1; promoting NBN recruitment to DNA damage sites (PubMed:18411307, PubMed:18582474, PubMed:18583988, PubMed:18678890). Interacts with (phosphorylated) RAD17; promoting NBN recruitment to DNA damage sites (PubMed:24534091). Interacts (via FxF/Y motif) with ATM (PubMed:15758953, PubMed:35076389). Interacts with HJURP (PubMed:17823411). Interacts with INTS3 (PubMed:19683501). Interacts with KPNA2 (PubMed:16188882). Interacts with TERF2; interaction is disrupted upon NBN phosphorylation by CDK2 (PubMed:10888888, PubMed:28216226). Interacts with (phosphorylated) RBBP8/CtIP; the interaction links the role of the MRN complex in DNA double-strand break sensing to resection (PubMed:19759395, PubMed:27814491, PubMed:27889449, PubMed:30787182, PubMed:33836577). Interacts with SP100; recruits NBN to PML bodies (PubMed:12470659). Interacts with ATF2 (PubMed:15916964). Interacts with MTOR, MAPKAP1 isoform 2 and RICTOR; indicative for an association with the mTORC2 complex (PubMed:23762398). Interacts with MRNIP (PubMed:27568553). Interacts with UFL1; promoting UFL1 recruitment to double-strand breaks following DNA damage (PubMed:30886146). Interacts with CYREN (via XLF motif) (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9R207, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10783165, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10888888, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11238951, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12419185, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12470659, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15758953, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15916964, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16188882, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17823411, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18411307, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18582474, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18583988, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18678890, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19338747, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19683501, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19759395, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23762398, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26215093, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27568553, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27814491, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27889449, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28216226, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28867292, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30787182, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30886146, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33836577, ECO:0000269|PubMed:35076389, ECO:0000269|PubMed:36577401, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9590181, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9705271}.; SUBUNIT: (Microbial infection) Interacts with herpes simplex virus 1 protein UL12. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20943970}. |
| Post-translational modification PTM: Phosphorylated by ATM in response of ionizing radiation, and such phosphorylation is responsible intra-S phase checkpoint control and telomere maintenance (PubMed:10766245, PubMed:10802669, PubMed:10839544, PubMed:10839545). Phosphorylated at Ser-432 by CDK2 in S/G2 phases abolishes interaction with TERF2, enabling DCLRE1B/Apollo recruitment to telomeres (PubMed:28216226). Phosphorylation at Ser-432 in response to dysfunctional telomeres promotes non-homologous end joining repair at telomeres, while dephosphorylation by PPP1CA promotes microhomology-mediated end-joining (MMEJ) repair (PubMed:28216226). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10766245, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10802669, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10839544, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10839545, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28216226}.; PTM: Ubiquitinated at Lys-435 via 'Lys-6'-linked ubiquitin chains by RNF8, promoting NBN recruitment to DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) (PubMed:23115235). Ubiquitinated at Lys-686 and Lys-689 via 'Lys-63'-linked ubiquitin chains by PELI1: ubiquitination takes place following PELI1 phosphorylation and promotes ATM activation and DNA repair (PubMed:30952868). Ubiquitinated at Lys-735 via 'Lys-63'-linked ubiquitin chains by the SCF(SKP2) complex: ubiquitination takes place following SKP2 phosphorylation and promotes ATM activation and DNA repair (PubMed:22464731). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22464731, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23115235, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30952868}.; PTM: Lactylation at Lys-388 by KAT5 in response to DNA damage promotes recruitment of the MRN complex to DNA damage sites (PubMed:38961290). Delactylated by HDAC3 (PubMed:38961290). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:38961290}. |
| Domain DOMAIN: The FHA and BRCT domains specifically recognize and bind phosphorylated proteins. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19804756}.; DOMAIN: The C-terminal domain contains a MRE11-binding site, and this interaction is required for the nuclear localization of the MRN complex. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15758953}.; DOMAIN: The FxF/Y motif (also named EEXXXDDL motif) is required for the interaction with ATM and its recruitment to sites of DNA damage and promote the phosphorylation of ATM substrates, leading to the events of DNA damage response. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15758953, ECO:0000269|PubMed:35076389}. |
| Involvement in disease DISEASE: Nijmegen breakage syndrome (NBS) [MIM:251260]: A disorder characterized by chromosomal instability, radiation sensitivity, microcephaly, growth retardation, immunodeficiency and predisposition to cancer, particularly to lymphoid malignancies. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9590180}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Breast cancer (BC) [MIM:114480]: A common malignancy originating from breast epithelial tissue. Breast neoplasms can be distinguished by their histologic pattern. Invasive ductal carcinoma is by far the most common type. Breast cancer is etiologically and genetically heterogeneous. Important genetic factors have been indicated by familial occurrence and bilateral involvement. Mutations at more than one locus can be involved in different families or even in the same case. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:14684699}. Note=Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Aplastic anemia (AA) [MIM:609135]: A form of anemia in which the bone marrow fails to produce adequate numbers of peripheral blood elements. It is characterized by peripheral pancytopenia and marrow hypoplasia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15338273}. Note=Disease susceptibility may be associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Note=Defects in NBN might play a role in the pathogenesis of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11325820}. |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: O60934 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
| Western blot IHC ICC |
Documents
| # | SDS | Certificate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | |||
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.








Reviews
There are no reviews yet.