| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| host | mouse |
| isotype | IgG1 |
| clonality | monoclonal |
| concentration | concentrate, predilute |
| applications | IHC |
| reactivity | human |
| available size | 0.1 mL, 0.5 mL, 1 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted |
mouse anti-Cytokeratin 5 monoclonal antibody (ZM186) 6146
Price range: $160.00 through $528.00
Antibody summary
- Mouse monoclonal to Cytokeratin 5
- Suitable for: Immunohistochemistry (formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues)
- Reacts with: Human
- Isotype:IgG1
- Control: Prostate
- Visualization: Cytoplasmic
- 0.1, 0.5, 1.0 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted
mouse anti-Cytokeratin 5 monoclonal antibody ZM186 6146
| target relevance |
|---|
| Protein names Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 5 (58 kDa cytokeratin) (Cytokeratin-5) (CK-5) (Keratin-5) (K5) (Type-II keratin Kb5) |
| Gene names KRT5,KRT5 |
| Protein family Intermediate filament family |
| Mass 62378Da |
| Function FUNCTION: Required for the formation of keratin intermediate filaments in the basal epidermis and maintenance of the skin barrier in response to mechanical stress (By similarity). Regulates the recruitment of Langerhans cells to the epidermis, potentially by modulation of the abundance of macrophage chemotactic cytokines, macrophage inflammatory cytokines and CTNND1 localization in keratinocytes (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q922U2}. |
| Subellular location SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: Cytoplasm {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20128788}. |
| Tissues TISSUE SPECIFICITY: Expressed in corneal epithelium (at protein level) (PubMed:26758872). Expressed in keratinocytes (at protein level) (PubMed:20128788, PubMed:31302245). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20128788, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26758872, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31302245}. |
| Structure SUBUNIT: Heterodimer of a type I and a type II keratin (PubMed:22705788, PubMed:31995743). Heterodimer with type I keratin KRT25 leading to the formation of keratin intermediate filament (KIF) network (PubMed:28899683). Forms a heterodimer (via 2B domains) with KRT14 (via 2B domains) (PubMed:22705788, PubMed:24940650, PubMed:31995743). Interacts with PLEC isoform 1C, when in a heterodimer with KRT14 (PubMed:24940650). Interacts with TCHP (PubMed:15731013). Interacts with EPPK1 (By similarity). Interacts with AMELX (By similarity). Interacts with PKP1 (via N-terminus) and PKP2 (PubMed:10852826). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q922U2, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10852826, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15731013, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22705788, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24940650, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28899683, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31995743}. |
| Post-translational modification PTM: Phosphorylated by CDK1, AURKB and Rho-kinase, phosphorylation is regulated by the cell cycle (By similarity). Thr-24 phosphorylation, mediated by CDK1, peaks during prometaphase or metaphase cells with phosphorylated filamentous structures evident throughout the cytoplasm during early mitosis (By similarity). CDK1 phosphorylates Thr-24 in mitotic cells at the site of injury (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q922U2}.; PTM: O-glycosylated. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q922U2}. |
| Involvement in disease DISEASE: Epidermolysis bullosa simplex 2A, generalized severe (EBS2A) [MIM:619555]: A form of epidermolysis bullosa simplex, a group of skin fragility disorders characterized by skin blistering due to cleavage within the basal layer of keratinocytes, and erosions caused by minor mechanical trauma. There is a broad spectrum of clinical severity ranging from minor blistering on the feet, to subtypes with extracutaneous involvement and a lethal outcome. EBS2A is an autosomal dominant, severe form characterized by extensive intraepidermal blistering from the time of birth with herpetiform marginal spreading and central healing. Oral mucosal involvement, nail dystrophy, onychogryposis, formation of milia, and palmoplantar hyperkeratosis are common features. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10730767, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12655565, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1372711, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16786515, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16882168, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19691749, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20128788, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21375516, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21623745, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26432462, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8757772, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9036937, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9406827, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9989794, ECO:0000269|Ref.22}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Epidermolysis bullosa simplex 2B, generalized intermediate (EBS2B) [MIM:619588]: A form of epidermolysis bullosa simplex, a group of skin fragility disorders characterized by skin blistering due to cleavage within the basal layer of keratinocytes, and erosions caused by minor mechanical trauma. There is a broad spectrum of clinical severity ranging from minor blistering on the feet, to subtypes with extracutaneous involvement and a lethal outcome. EBS2B is an autosomal dominant form characterized by generalized blistering manifesting at birth. The tendency to blistering diminishes in adolescence, when it may become localized to hands and feet. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11407988, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16882168, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17855059, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21375516, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21623745, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23450297, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26432462, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7534039, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7686424, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9740251, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9989794}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Epidermolysis bullosa simplex 2C, localized (EBS2C) [MIM:619594]: A form of epidermolysis bullosa simplex, a group of skin fragility disorders characterized by skin blistering due to cleavage within the basal layer of keratinocytes, and erosions caused by minor mechanical trauma. There is a broad spectrum of clinical severity ranging from minor blistering on the feet, to subtypes with extracutaneous involvement and a lethal outcome. EBS2C is an autosomal dominant form with intraepidermal blistering mainly restricted to hands and feet beginning in infancy. Nails may be thick and dystrophic. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10782015, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11973334, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12655565, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12707098, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14723728, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15140024, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15347343, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16786515, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16882168, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19220453, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21375516, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21623745, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26432462, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30240119, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7506097, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7520042, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7688477, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8595431, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8807337, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9804357}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Epidermolysis bullosa simplex 2D, generalized, intermediate or severe, autosomal recessive (EBS2D) [MIM:619599]: A form of epidermolysis bullosa simplex, a group of skin fragility disorders characterized by skin blistering due to cleavage within the basal layer of keratinocytes, and erosions caused by minor mechanical trauma. There is a broad spectrum of clinical severity ranging from minor blistering on the feet, to subtypes with extracutaneous involvement and a lethal outcome. EBS2D is an autosomal recessive form characterized by widespread intraepidermal skin blistering and erosions from birth. Death may occur in the neonatal period. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11973334, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22832485, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31302245}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Epidermolysis bullosa simplex 2E, with migratory circinate erythema (EBS2E) [MIM:609352]: A form of epidermolysis bullosa simplex, a group of skin fragility disorders characterized by skin blistering due to cleavage within the basal layer of keratinocytes, and erosions caused by minor mechanical trauma. There is a broad spectrum of clinical severity ranging from minor blistering on the feet, to subtypes with extracutaneous involvement and a lethal outcome. EBS2E is an autosomal dominant form in which multiple vesicles are present from birth onward and acquire over time a typical migratory circinate pattern on an erythematous background. Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation develops gradually and may have a mottled pattern. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12925204}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Epidermolysis bullosa simplex 2F, with mottled pigmentation (EBS2F) [MIM:131960]: A form of epidermolysis bullosa simplex, a group of skin fragility disorders characterized by skin blistering due to cleavage within the basal layer of keratinocytes, and erosions caused by minor mechanical trauma. There is a broad spectrum of clinical severity ranging from minor blistering on the feet, to subtypes with extracutaneous involvement and a lethal outcome. EBS2F is an autosomal dominant form characterized by generalized skin blistering of intermediate severity beginning at birth, with mottled or reticulate pigmentation developing gradually. Focal keratoses of palms and soles and dystrophic, thickened nails develop over time. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10494094, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16882168, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21375516, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21623745, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26432462, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8799157}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Dowling-Degos disease 1 (DDD1) [MIM:179850]: An autosomal dominant genodermatosis. Affected individuals develop a postpubertal reticulate hyperpigmentation that is progressive and disfiguring, and small hyperkeratotic dark brown papules that affect mainly the flexures and great skin folds. Patients usually show no abnormalities of the hair or nails. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16465624, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21569119, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22437315}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: P13647 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
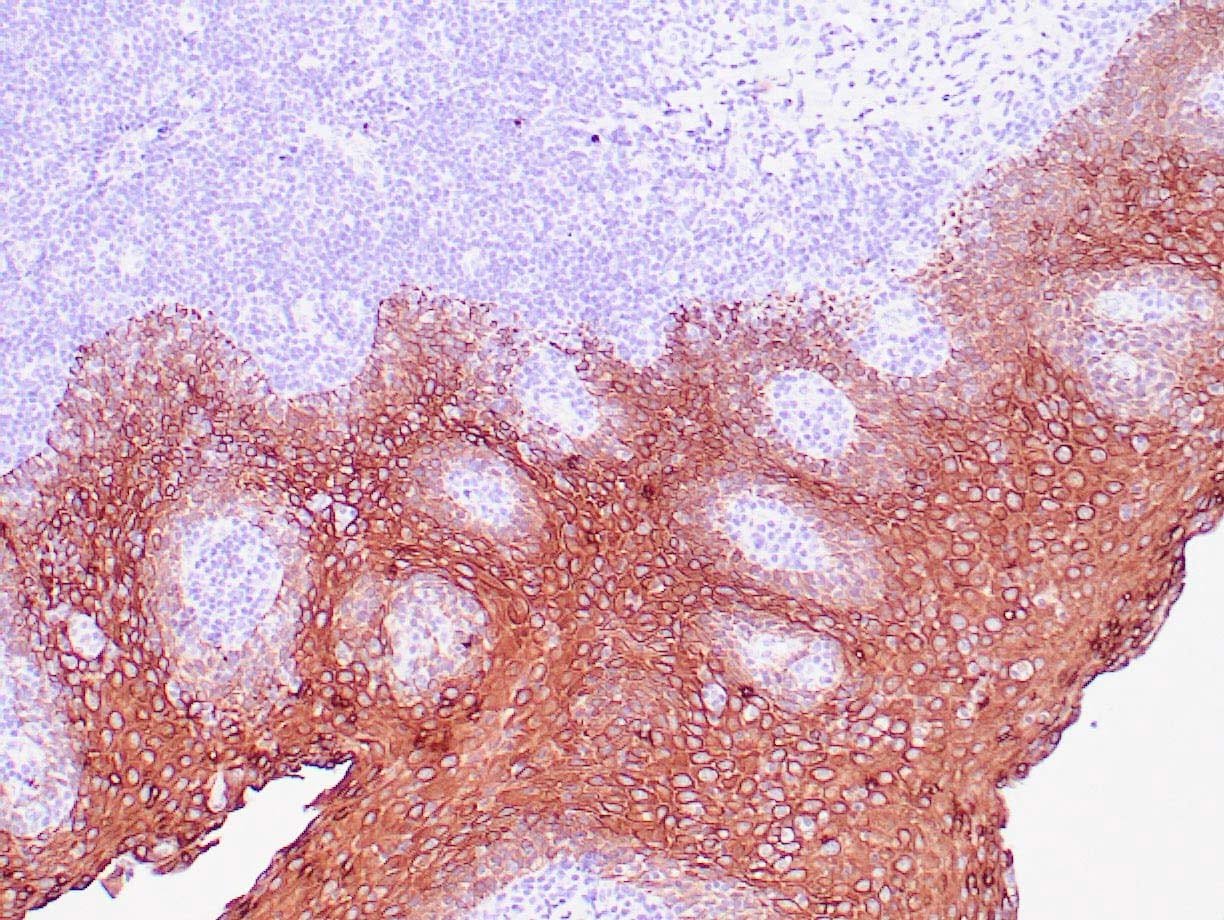 |
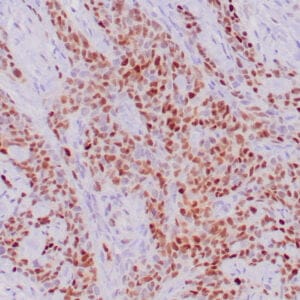
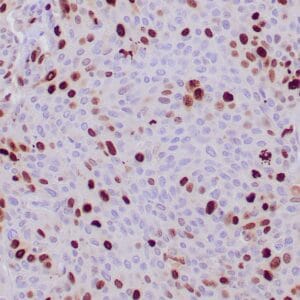
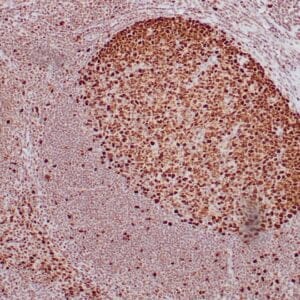
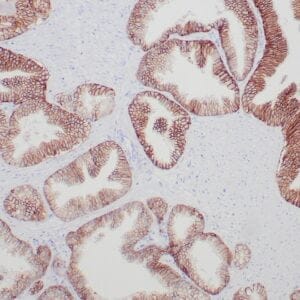
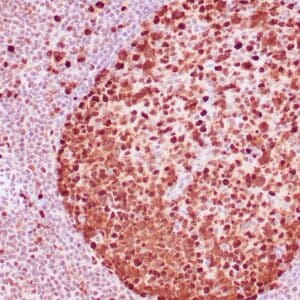
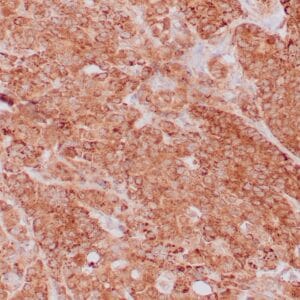
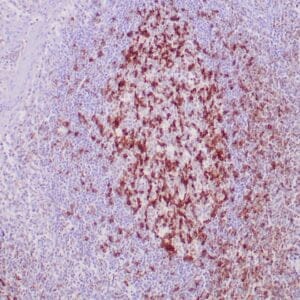
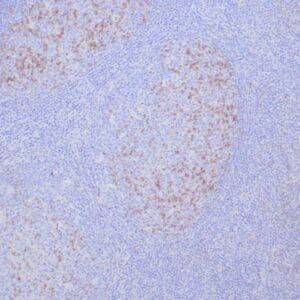
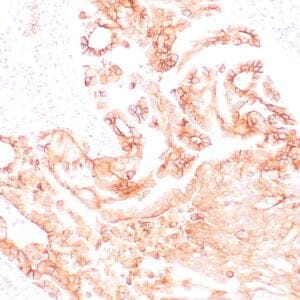
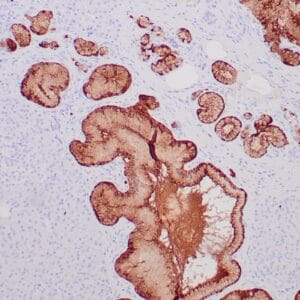
| Human tonsil with anti-Keratin 5 antibody using peroxidase-conjugate and DAB chromogen. Note the cytoplasmic staining of squamous epithelium. |
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
| IHC |
Documents
| # | SDS | Certificate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | |||
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.