| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| host | mouse |
| isotype | IgG1 |
| clonality | monoclonal |
| concentration | concentrate, predilute |
| applications | IHC |
| reactivity | human |
| available size | 0.1 mL, 0.5 mL, 1 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted |
mouse anti-BRCA-1 monoclonal antibody (MS110) 6038
Price range: $160.00 through $528.00
Antibody summary
- Mouse monoclonal to BRCA-1
- Suitable for: Immunohistochemistry (formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues)
- Reacts with: Human
- Isotype:IgG1
- Control: Breast carcinoma with BRCA-1 gene mutation
- Visualization: Nuclear
- 0.1, 0.5, 1.0 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted
mouse anti-BRCA-1 monoclonal antibody MS110 6038
| target relevance |
|---|
| Protein names Breast cancer type 1 susceptibility protein (EC 2.3.2.27) (RING finger protein 53) (RING-type E3 ubiquitin transferase BRCA1) |
| Gene names BRCA1,BRCA1 RNF53 |
| Mass 207721Da |
| Function FUNCTION: E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase that specifically mediates the formation of 'Lys-6'-linked polyubiquitin chains and plays a central role in DNA repair by facilitating cellular responses to DNA damage (PubMed:10500182, PubMed:12887909, PubMed:12890688, PubMed:14976165, PubMed:16818604, PubMed:17525340, PubMed:19261748). It is unclear whether it also mediates the formation of other types of polyubiquitin chains (PubMed:12890688). The BRCA1-BARD1 heterodimer coordinates a diverse range of cellular pathways such as DNA damage repair, ubiquitination and transcriptional regulation to maintain genomic stability (PubMed:12890688, PubMed:14976165, PubMed:20351172). Regulates centrosomal microtubule nucleation (PubMed:18056443). Required for appropriate cell cycle arrests after ionizing irradiation in both the S-phase and the G2 phase of the cell cycle (PubMed:10724175, PubMed:11836499, PubMed:12183412, PubMed:19261748). Required for FANCD2 targeting to sites of DNA damage (PubMed:12887909). Inhibits lipid synthesis by binding to inactive phosphorylated ACACA and preventing its dephosphorylation (PubMed:16326698). Contributes to homologous recombination repair (HRR) via its direct interaction with PALB2, fine-tunes recombinational repair partly through its modulatory role in the PALB2-dependent loading of BRCA2-RAD51 repair machinery at DNA breaks (PubMed:19369211). Component of the BRCA1-RBBP8 complex which regulates CHEK1 activation and controls cell cycle G2/M checkpoints on DNA damage via BRCA1-mediated ubiquitination of RBBP8 (PubMed:16818604). Acts as a transcriptional activator (PubMed:20160719). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10500182, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10724175, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11836499, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12183412, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12887909, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12890688, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14976165, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16326698, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16818604, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17525340, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18056443, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19261748, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19369211, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20160719, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20351172}. |
| Catalytic activity CATALYTIC ACTIVITY: Reaction=S-ubiquitinyl-[E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme]-L-cysteine + [acceptor protein]-L-lysine = [E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme]-L-cysteine + N(6)-ubiquitinyl-[acceptor protein]-L-lysine.; EC=2.3.2.27; Evidence={ECO:0000269|PubMed:10500182, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12887909, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12890688, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16818604, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18056443, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20351172}; |
| Pathway PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein ubiquitination. |
| Subellular location SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: Nucleus {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15133502, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17525340, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20160719, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21144835, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26778126, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9528852}. Chromosome {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23269703, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25472942, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26778126}. Cytoplasm {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20160719}. Note=Localizes at sites of DNA damage at double-strand breaks (DSBs); recruitment to DNA damage sites is mediated by ABRAXAS1 and the BRCA1-A complex (PubMed:26778126). Translocated to the cytoplasm during UV-induced apoptosis (PubMed:20160719). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20160719, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26778126}.; SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: [Isoform 3]: Cytoplasm.; SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: [Isoform 5]: Cytoplasm {ECO:0000269|PubMed:8972225}. |
| Tissues TISSUE SPECIFICITY: Isoform 1 and isoform 3 are widely expressed. Isoform 3 is reduced or absent in several breast and ovarian cancer cell lines. |
| Structure SUBUNIT: Heterodimer with BARD1 (PubMed:11573085, PubMed:12890688, PubMed:14976165). Part of the BRCA1-associated genome surveillance complex (BASC), which contains BRCA1, MSH2, MSH6, MLH1, ATM, BLM, PMS2 and the MRE11-RAD50-NBN protein (MRN) complex (PubMed:10783165). This association could be a dynamic process changing throughout the cell cycle and within subnuclear domains (PubMed:10783165). Component of the BRCA1-A complex, at least composed of BRCA1, BARD1, UIMC1/RAP80, ABRAXAS1, BRCC3/BRCC36, BABAM2 and BABAM1/NBA1 (PubMed:19261746, PubMed:19261748, PubMed:19261749, PubMed:20351172). Interacts (via the BRCT domains) with ABRAXAS1 (phosphorylated form); this is important for recruitment to sites of DNA damage (PubMed:17525340, PubMed:17643121, PubMed:17643122, PubMed:23269703, PubMed:24316840, PubMed:26778126). Can form a heterotetramer with two molecules of ABRAXAS1 (phosphorylated form) (PubMed:26778126). Component of the BRCA1-RBBP8 complex (PubMed:16101277). Interacts (via the BRCT domains) with RBBP8 ('Ser-327' phosphorylated form); the interaction ubiquitinates RBBP8, regulates CHEK1 activation, and involves RBBP8 in BRCA1-dependent G2/M checkpoint control on DNA damage (PubMed:16818604, PubMed:9811458). Associates with RNA polymerase II holoenzyme (PubMed:9662397). Interacts with SMC1A, NELFB, DCLRE1C, CLSPN (PubMed:11739404, PubMed:11877377, PubMed:15096610, PubMed:15456891). Interacts with CHEK1, CHEK2, BAP1, BRCC3, UBXN1 and PCLAF (PubMed:10724175, PubMed:11836499, PubMed:14636569, PubMed:20351172, PubMed:21673012). Interacts (via BRCT domains) with BRIP1 (phosphorylated form) (PubMed:11301010, PubMed:15133502, PubMed:21473589). Interacts with FANCD2 (ubiquitinated form) (PubMed:11239454). Interacts with H2AX (phosphorylated on 'Ser-140') (PubMed:12419185). Interacts (via the BRCT domains) with ACACA (phosphorylated form); the interaction prevents dephosphorylation of ACACA (PubMed:12360400, PubMed:16326698, PubMed:16698035, PubMed:18452305). Part of a BRCA complex containing BRCA1, BRCA2 and PALB2 (PubMed:19369211). Interacts directly with PALB2; the interaction is essential for its function in HRR (PubMed:19369211, PubMed:28319063). Interacts directly with BRCA2; the interaction occurs only in the presence of PALB2 which serves as the bridging protein (PubMed:19369211). Interacts (via the BRCT domains) with LMO4; the interaction represses the transcriptional activity of BRCA1 (PubMed:11751867). Interacts (via the BRCT domains) with CCAR2 (via N-terminus); the interaction represses the transcriptional activator activity of BRCA1 (PubMed:20160719). Interacts with EXD2 (PubMed:26807646). Interacts (via C-terminus) with DHX9; this interaction is direct and links BRCA1 to the RNA polymerase II holoenzyme (PubMed:9662397). Interacts with DNA helicase ZGRF1; the interaction is increased following DNA damage induction (PubMed:34552057). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10724175, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10783165, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11239454, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11301010, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11573085, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11739404, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11751867, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11836499, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11877377, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12360400, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12419185, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12890688, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14636569, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14976165, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15096610, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15133502, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15456891, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16101277, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16326698, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16698035, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16818604, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17525340, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17643121, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17643122, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18452305, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19261746, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19261748, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19261749, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19369211, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20159462, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20160719, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20351172, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21473589, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21673012, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23269703, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24316840, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26778126, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26807646, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28319063, ECO:0000269|PubMed:34552057, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9528852, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9662397, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9811458}. |
| Post-translational modification PTM: Phosphorylated in response to IR, UV, and various stimuli that cause checkpoint activation, probably by ATM or ATR (PubMed:11114888, PubMed:12183412, PubMed:21144835). Phosphorylation at Ser-988 by CHEK2 regulates mitotic spindle assembly (PubMed:10724175, PubMed:20364141). Phosphorylation by AURKA regulates centrosomal microtubule nucleation (PubMed:18056443). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10724175, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11114888, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12183412, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18056443, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20364141, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21144835}.; PTM: Autoubiquitinated, undergoes 'Lys-6'-linked polyubiquitination. 'Lys-6'-linked polyubiquitination does not promote degradation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12890688, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20351172}. |
| Domain DOMAIN: The BRCT domains recognize and bind phosphorylated pSXXF motif on proteins. The interaction with the phosphorylated pSXXF motif of ABRAXAS1, recruits BRCA1 at DNA damage sites. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20159462}.; DOMAIN: The RING-type zinc finger domain interacts with BAP1. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20159462}. |
| Involvement in disease DISEASE: Breast cancer (BC) [MIM:114480]: A common malignancy originating from breast epithelial tissue. Breast neoplasms can be distinguished by their histologic pattern. Invasive ductal carcinoma is by far the most common type. Breast cancer is etiologically and genetically heterogeneous. Important genetic factors have been indicated by familial occurrence and bilateral involvement. Mutations at more than one locus can be involved in different families or even in the same case. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10323242, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11114888, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11301010, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12427738, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12442275, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12938098, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14722926, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15133502, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18285836, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21473589, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23867111, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28364669, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7545954, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7894491, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7894493, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7939630, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8554067, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8723683, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8776600, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9482581, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9609997, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9760198}. Note=Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Mutations in BRCA1 are thought to be responsible for 45% of inherited breast cancer. Moreover, BRCA1 carriers have a 4-fold increased risk of colon cancer, whereas male carriers face a 3-fold increased risk of prostate cancer. Cells lacking BRCA1 show defects in DNA repair by homologous recombination.; DISEASE: Breast-ovarian cancer, familial, 1 (BROVCA1) [MIM:604370]: A condition associated with familial predisposition to cancer of the breast and ovaries. Characteristic features in affected families are an early age of onset of breast cancer (often before age 50), increased chance of bilateral cancers (cancer that develop in both breasts, or both ovaries, independently), frequent occurrence of breast cancer among men, increased incidence of tumors of other specific organs, such as the prostate. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12938098, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14722926, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17924331, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20513136, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28364669, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8968716}. Note=Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Mutations in BRCA1 are thought to be responsible for more than 80% of inherited breast-ovarian cancer.; DISEASE: Ovarian cancer (OC) [MIM:167000]: The term ovarian cancer defines malignancies originating from ovarian tissue. Although many histologic types of ovarian tumors have been described, epithelial ovarian carcinoma is the most common form. Ovarian cancers are often asymptomatic and the recognized signs and symptoms, even of late-stage disease, are vague. Consequently, most patients are diagnosed with advanced disease. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10196379, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10486320, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14746861, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28364669}. Note=Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Pancreatic cancer 4 (PNCA4) [MIM:614320]: A malignant neoplasm of the pancreas. Tumors can arise from both the exocrine and endocrine portions of the pancreas, but 95% of them develop from the exocrine portion, including the ductal epithelium, acinar cells, connective tissue, and lymphatic tissue. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18762988}. Note=Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Fanconi anemia, complementation group S (FANCS) [MIM:617883]: A form of Fanconi anemia, a disorder affecting all bone marrow elements and resulting in anemia, leukopenia and thrombopenia. It is associated with cardiac, renal and limb malformations, dermal pigmentary changes, and a predisposition to the development of malignancies. At the cellular level it is associated with hypersensitivity to DNA-damaging agents, chromosomal instability (increased chromosome breakage) and defective DNA repair. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23269703, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25472942, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29133208}. Note=Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: P38398 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
 |
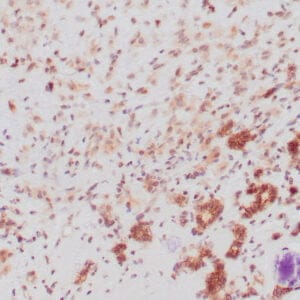
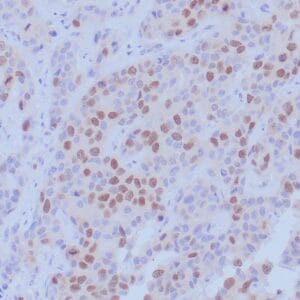
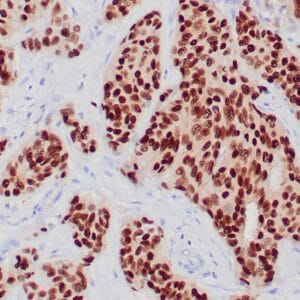
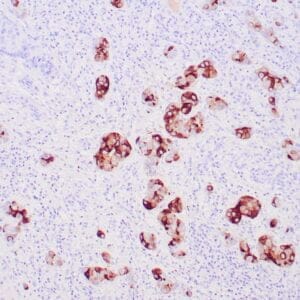
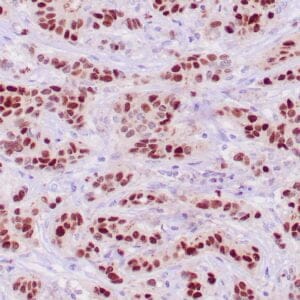
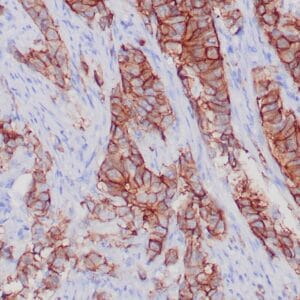
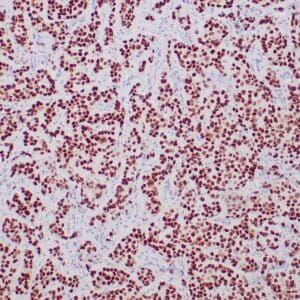
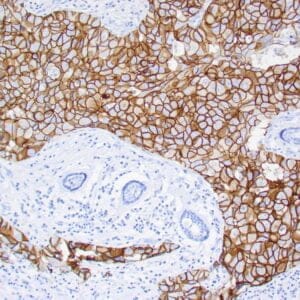
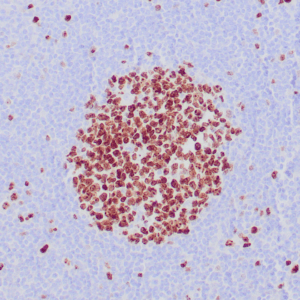
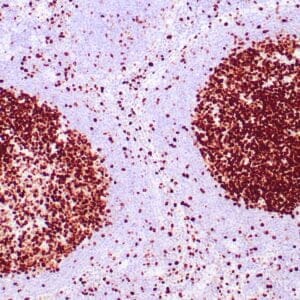
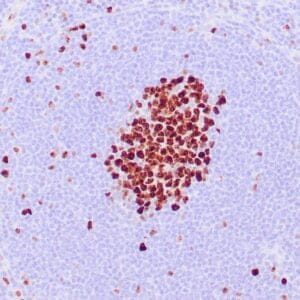
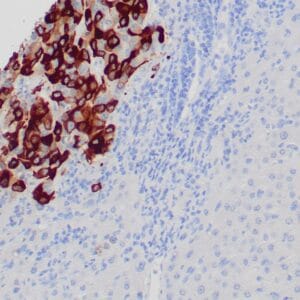
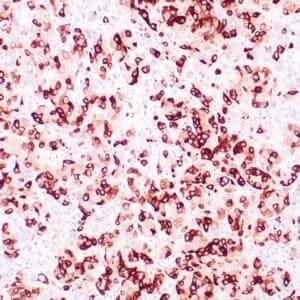
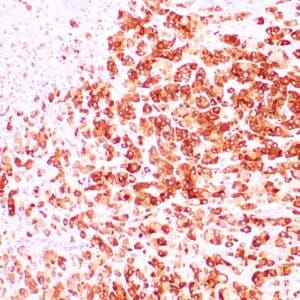
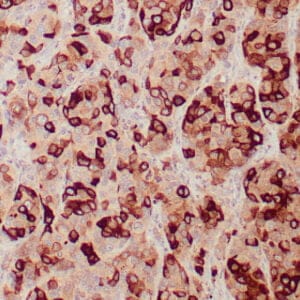
| Human breast carcinoma stained with anti-BRCA-1 antibody using peroxidase-conjugate and DAB chromogen. Note nuclear staining of some breast carcinoma cells. |
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
| IHC |
Documents
| # | SDS | Certificate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | |||
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.