| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| host | mouse |
| isotype | IgG2b |
| clonality | monoclonal |
| concentration | 1 mg/mL |
| applications | ICC/IF, WB |
| reactivity | p84 |
| available sizes | 100 µg |
mouse anti-p84 monoclonal antibody (5E9) 9573
$503.00
Antibody summary
- Mouse monoclonal to p84
- Suitable for: WB,ICC/IF,IHC-P,IP,ChIP,IHC
- Isotype: IgG2b
- 100 µg
mouse anti-p84 monoclonal antibody (5E9) 9573
| antibody |
|---|
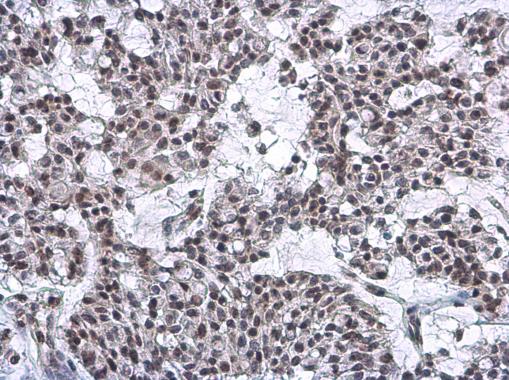
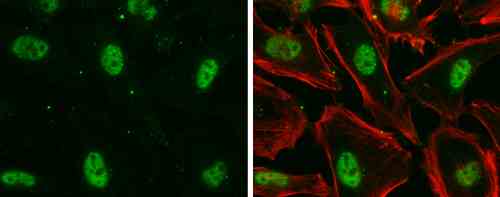
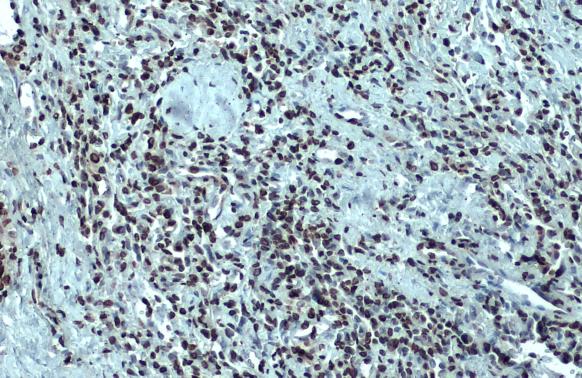
| Tested applications WB,IHC,IHC,ICC/IF |
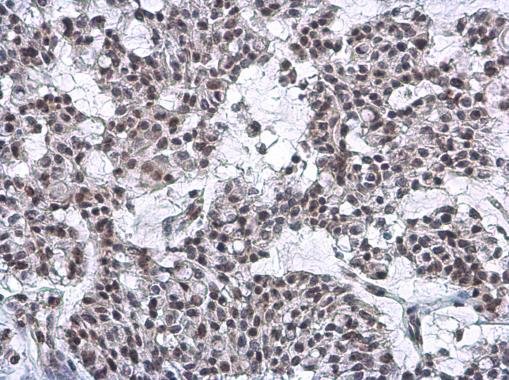
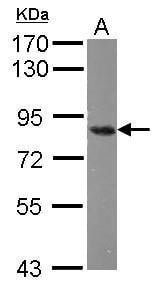
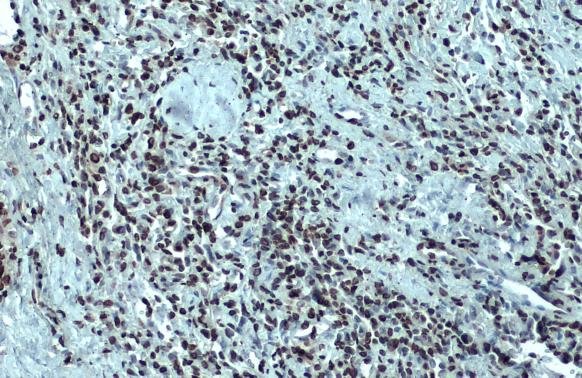
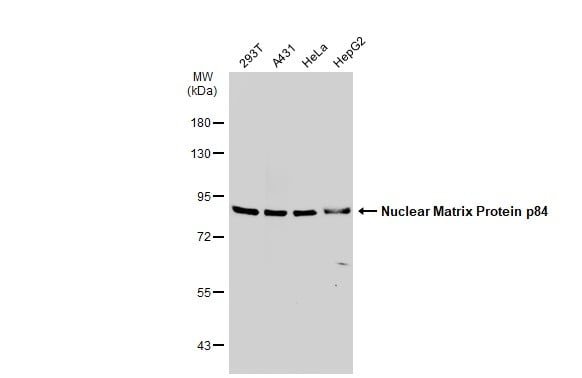
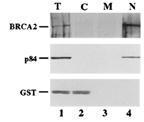
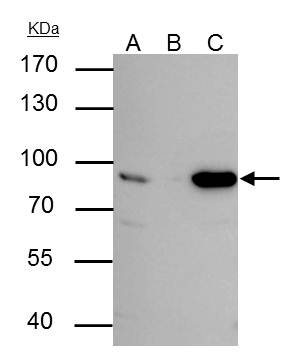
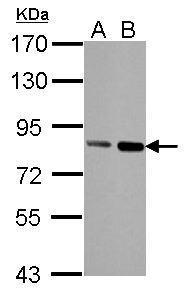
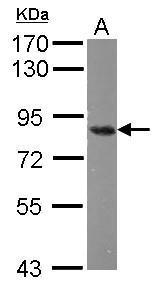
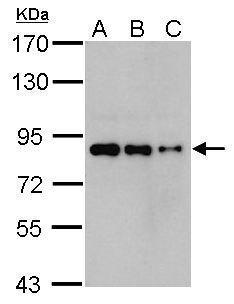
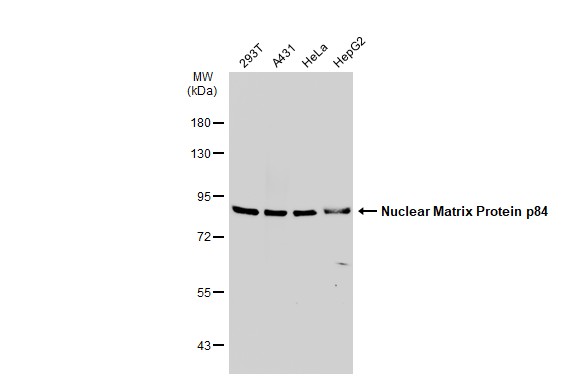
| Recommended dilutions Immunoblotting, immunoprecipitation, and Immunofluorescence: use at 0.5-2 ug/mL.In immunoblots, a band of 84 kD is detected. Positive controls: Lysates of Molt 4, HeLa, or Raji cells. |
| Immunogen Fusion protein containing amino acids 15-374 of human p84 expressed in E. coli. |
| Size and concentration 100µg and lot specific |
| Form liquid |
| Storage Instructions This antibody is stable for at least one (1) year at -70°C. Avoid multiple freeze- thaw cycles. |
| Storage buffer PBS, pH 7.4. |
| Purity protein affinity purification |
| Clonality monoclonal |
| Isotype IgG2b |
| Compatible secondaries goat anti-mouse IgG, H&L chain specific, peroxidase conjugated polyclonal antibody 5486 goat anti-mouse IgG, H&L chain specific, biotin conjugated, Conjugate polyclonal antibody 2685 goat anti-mouse IgG, H&L chain specific, FITC conjugated polyclonal antibody 7854 goat anti-mouse IgG, H&L chain specific, peroxidase conjugated polyclonal antibody, crossabsorbed 1706 goat anti-mouse IgG, H&L chain specific, biotin conjugated polyclonal antibody, crossabsorbed 1716 goat anti-mouse IgG, H&L chain specific, FITC conjugated polyclonal antibody, crossabsorbed 1721 |
| Isotype control Mouse monocolonal IgG2b - Isotype Control |
| target relevance |
|---|
| Protein names THO complex subunit 1 (Nuclear matrix protein p84) (p84N5) (hTREX84) |
| Gene names THOC1,THOC1 HPR1 |
| Protein family THOC1 family |
| Mass 75666Da |
| Function FUNCTION: Component of the THO subcomplex of the TREX complex which is thought to couple mRNA transcription, processing and nuclear export, and which specifically associates with spliced mRNA and not with unspliced pre-mRNA (PubMed:15833825, PubMed:15998806, PubMed:17190602). Required for efficient export of polyadenylated RNA (PubMed:23222130). The THOC1-THOC2-THOC3 core complex alone is sufficient to bind export factor NXF1-NXT1 and promote ATPase activity of DDX39B/UAP56 (PubMed:33191911). TREX is recruited to spliced mRNAs by a transcription-independent mechanism, binds to mRNA upstream of the exon-junction complex (EJC) and is recruited in a splicing- and cap-dependent manner to a region near the 5' end of the mRNA where it functions in mRNA export to the cytoplasm via the TAP/NXF1 pathway (PubMed:15833825, PubMed:15998806, PubMed:17190602). Regulates transcriptional elongation of a subset of genes (PubMed:22144908). Involved in genome stability by preventing co-transcriptional R-loop formation (By similarity). May play a role in hair cell formation, hence may be involved in hearing (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q7SYB2, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15833825, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15998806, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17190602, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22144908, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23222130, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33191911}.; FUNCTION: Participates in an apoptotic pathway which is characterized by activation of caspase-6, increases in the expression of BAK1 and BCL2L1 and activation of NF-kappa-B. This pathway does not require p53/TP53, nor does the presence of p53/TP53 affect the efficiency of cell killing. Activates a G2/M cell cycle checkpoint prior to the onset of apoptosis. Apoptosis is inhibited by association with RB1.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) The TREX complex is essential for the export of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) intronless mRNAs and infectious virus production. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18974867}. |
| Subellular location SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: [Isoform 1]: Nucleus speckle. Nucleus, nucleoplasm. Nucleus matrix. Cytoplasm. Note=Can shuttle between the nucleus and cytoplasm. Nuclear localization is required for induction of apoptotic cell death. Translocates to the cytoplasm during the early phase of apoptosis execution.; SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: [Isoform 2]: Cytoplasm. |
| Tissues TISSUE SPECIFICITY: Ubiquitous. Expressed in various cancer cell lines. Expressed at very low levels in normal breast epithelial cells and highly expressed in breast tumors. Expression is strongly associated with an aggressive phenotype of breast tumors and expression correlates with tumor size and the metastatic state of the tumor progression. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15358532, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15833825}. |
| Structure SUBUNIT: Component of the THO subcomplex, which is composed of THOC1, THOC2, THOC3, THOC5, THOC6 and THOC7 (PubMed:33191911, PubMed:37020021). The THO subcomplex interacts with DDX39B to form the THO-DDX39B complex which multimerizes into a 28-subunit tetrameric assembly (PubMed:33191911, PubMed:37020021). Component of the transcription/export (TREX) complex at least composed of ALYREF/THOC4, DDX39B, SARNP/CIP29, CHTOP and the THO subcomplex; in the complex interacts with THOC2, THOC5 and THOC7 (PubMed:33191911, PubMed:37020021). TREX seems to have a dynamic structure involving ATP-dependent remodeling (PubMed:23222130, PubMed:37020021). Binds to the hypophosphorylated form of RB1. Interacts with RNA polymerase II. Interacts with LUZP4. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11979277, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15833825, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15870275, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15998806, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23222130, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25662211, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33191911, ECO:0000269|PubMed:37020021, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7525595}. |
| Post-translational modification PTM: Expression is altered specifically during apoptosis and is accompanied by the appearance of novel forms with smaller apparent molecular mass.; PTM: Polyubiquitinated, leading to proteasomal degradation; probably involves NEDD4. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23460917}. |
| Domain DOMAIN: An intact death domain is needed for apoptosis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10512864}. |
| Involvement in disease DISEASE: Deafness, autosomal dominant, 86 (DFNA86) [MIM:620280]: A form of non-syndromic, sensorineural hearing loss. Sensorineural hearing loss results from damage to the neural receptors of the inner ear, the nerve pathways to the brain, or the area of the brain that receives sound information. DFNA86 is characterized by progressive, bilateral hearing loss that is most predominant in the high frequencies, begins mildly during the fourth decade and gradually progresses to severe-to-profound deafness in the seventh and eighth decades. Affected subjects have tinnitus, while vestibular dysfunction or other clinical abnormalities are not present. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:32776944}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: Q96FV9 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 37885910 | A Knock-In Mouse Model of the Gcm2 Variant p.Y392S Develops Normal Parathyroid Glands. | Vaishali I Parekh, Lauren R Brinster, Bin Guan, William F Simonds, Lee S Weinstein, Sunita K Agarwal | J Endocr Soc 7:bvad126 |
| 37790327 | Increased AID Results in Mutations at the CRLF2 Locus Implicated in Latin American ALL Health Disparities. | Nicholas Pannunzio, Valeria Rangel, Jason Sterrenberg, Aya Garawi, Vyanka Mezcord, Melissa Folkerts, Sabrina Caulderon, Jinglong Wang, Eli Soyfer, Oliver Eng, Jennifer Valerin, Sora Tanjasiri, Fabiola Quintero-Rivera, Selma Masri, Marcus Seldin, Richard Frock, Angela Fleischman | Res Sq N/A:N/A |
| 37267101 | Liver and muscle circadian clocks cooperate to support glucose tolerance in mice. | Jacob G Smith, Kevin B Koronowski, Thomas Mortimer, Tomoki Sato, Carolina M Greco, Paul Petrus, Amandine Verlande, Siwei Chen, Muntaha Samad, Ekaterina Deyneka, Lavina Mathur, Ronnie Blazev, Jeffrey Molendijk, Arun Kumar, Oleg Deryagin, Mireia Vaca-Dempere, Valentina Sica, Peng Liu, Valerio Orlando, Benjamin L Parker, Pierre Baldi, Patrick-Simon Welz, Cholsoon Jang, Selma Masri, Salvador Aznar Benitah, Pura Muñoz-Cánoves, Paolo Sassone-Corsi | Cell Rep 42:112588 |
| 36973248 | Time-of-day defines NAD(+) efficacy to treat diet-induced metabolic disease by synchronizing the hepatic clock in mice. | Quetzalcoatl Escalante-Covarrubias, Lucía Mendoza-Viveros, Mirna González-Suárez, Román Sitten-Olea, Laura A Velázquez-Villegas, Fernando Becerril-Pérez, Ignacio Pacheco-Bernal, Erick Carreño-Vázquez, Paola Mass-Sánchez, Marcia Bustamante-Zepeda, Ricardo Orozco-Solís, Lorena Aguilar-Arnal | Nat Commun 14:1685 |
| 36646704 | Expansion of interferon inducible gene pool via USP18 inhibition promotes cancer cell pyroptosis. | Kei-Ichiro Arimoto, Sayuri Miyauchi, Ty D Troutman, Yue Zhang, Mengdan Liu, Samuel A Stoner, Amanda G Davis, Jun-Bao Fan, Yi-Jou Huang, Ming Yan, Christopher K Glass, Dong-Er Zhang | Nat Commun 14:251 |
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
| Western blot IHC ICC |
Documents
| # | SDS | Certificate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | |||
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.












Reviews
There are no reviews yet.