| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| host | mouse |
| isotype | IgG1 |
| clonality | monoclonal |
| concentration | 1 mg/mL |
| applications | ICC/IF, WB |
| reactivity | SRC-1 |
| available sizes | 100 µg |
mouse anti-SRC-1 monoclonal antibody (H4) 5818
$503.00
Antibody summary
- Mouse monoclonal to SRC-1
- Suitable for: WB,IP,ChIP
- Isotype: IgG1
- 100 µg
mouse anti-SRC-1 monoclonal antibody (H4) 5818
| target relevance |
|---|
| Protein names Nuclear receptor coactivator 1 (NCoA-1) (EC 2.3.1.48) (Class E basic helix-loop-helix protein 74) (bHLHe74) (Protein Hin-2) (RIP160) (Renal carcinoma antigen NY-REN-52) (Steroid receptor coactivator 1) (SRC-1) |
| Gene names NCOA1,NCOA1 BHLHE74 SRC1 |
| Protein family SRC/p160 nuclear receptor coactivator family |
| Mass 156757Da |
| Function FUNCTION: Nuclear receptor coactivator that directly binds nuclear receptors and stimulates the transcriptional activities in a hormone-dependent fashion. Involved in the coactivation of different nuclear receptors, such as for steroids (PGR, GR and ER), retinoids (RXRs), thyroid hormone (TRs) and prostanoids (PPARs). Also involved in coactivation mediated by STAT3, STAT5A, STAT5B and STAT6 transcription factors. Displays histone acetyltransferase activity toward H3 and H4; the relevance of such activity remains however unclear. Plays a central role in creating multisubunit coactivator complexes that act via remodeling of chromatin, and possibly acts by participating in both chromatin remodeling and recruitment of general transcription factors. Required with NCOA2 to control energy balance between white and brown adipose tissues. Required for mediating steroid hormone response. Isoform 2 has a higher thyroid hormone-dependent transactivation activity than isoform 1 and isoform 3. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10449719, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12954634, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7481822, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9223281, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9223431, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9296499, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9427757}. |
| Catalytic activity CATALYTIC ACTIVITY: Reaction=L-lysyl-[protein] + acetyl-CoA = N(6)-acetyl-L-lysyl-[protein] + CoA + H(+); Xref=Rhea:RHEA:45948, Rhea:RHEA-COMP:9752, Rhea:RHEA-COMP:10731, ChEBI:CHEBI:15378, ChEBI:CHEBI:29969, ChEBI:CHEBI:57287, ChEBI:CHEBI:57288, ChEBI:CHEBI:61930; EC=2.3.1.48; |
| Subellular location SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: Nucleus {ECO:0000255|PROSITE-ProRule:PRU00981}. |
| Tissues TISSUE SPECIFICITY: Widely expressed. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15313887, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9427757}. |
| Structure SUBUNIT: Interacts with PPARA; the interaction is direct (PubMed:11698662). Interacts with PPARG; the interaction is direct (PubMed:11698662, PubMed:9744270). Interacts with ESRRG; the interaction is direct (PubMed:11864604). Interacts with STAT5A (via FDL motif) (PubMed:12954634). Interacts with STAT5B (via FDL motif) (PubMed:12954634). Interacts with STAT6 (via LXXLL motif) (PubMed:12138096). Interacts (via LXXLL 1, 2 and 3 motifs) with RORC (via AF-2 motif) (By similarity). Interacts with ASXL1 (PubMed:16606617). Interacts with the methyltransferase CARM1 (By similarity). Interacts with COPS5 (PubMed:10722692). Interacts with the histone acetyltransferase CREBBP (By similarity). Interacts with DDX5 (PubMed:11250900). Interacts with the histone acetyltransferase EP300 (By similarity). Interacts with ESR1 (PubMed:7481822). Interacts with GCCR (PubMed:7481822). Interacts with the basal transcription factor GTF2B (PubMed:8754792). Interacts with NCOA6 (PubMed:10567404). Interacts with NCOA2 (PubMed:10594042). Interacts with NR3C1 (PubMed:12917342). Interacts with NR4A1/Nur77 (PubMed:18690216). Interacts with NR4A3 (By similarity). Interacts with PCAF (PubMed:9296499). Interacts with PGR (PubMed:7481822). Interacts with PRMT2 (PubMed:12039952). Interacts with PRMT6 (PubMed:20047962). Interacts with PSMB9 (PubMed:16957778). Interacts with RXRA, the interaction is ligand-dependent (PubMed:19786558, PubMed:7481822). Interacts with STAT3 following IL-6 stimulation (PubMed:11773079). Interacts with TRA (PubMed:7481822). Interacts with TRIP4 (PubMed:25219498). Interacts with TTLL5/STAMP (PubMed:17116691). Interacts with UBE2L3; they functionally interact to regulate progesterone receptor transcriptional activity (PubMed:15367689). Interacts with VDR (PubMed:28698609). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P70365, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10567404, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10594042, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10722692, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11250900, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11698662, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11773079, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11864604, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12039952, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12138096, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12917342, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12954634, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15367689, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16606617, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16957778, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17116691, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18690216, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19786558, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20047962, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25219498, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28698609, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7481822, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8754792, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9296499, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9744270}. |
| Post-translational modification PTM: Sumoylated; sumoylation increases its interaction with PGR and prolongs its retention in the nucleus. It does not prevent its ubiquitination and does not exert a clear effect on the stability of the protein. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12529333}.; PTM: Ubiquitinated; leading to proteasome-mediated degradation. Ubiquitination and sumoylation take place at different sites. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12529333}. |
| Domain DOMAIN: The C-terminal (1107-1441) part mediates the histone acetyltransferase (HAT) activity.; DOMAIN: Contains 7 Leu-Xaa-Xaa-Leu-Leu (LXXLL) motifs. LXXLL motifs 3, 4 and 5 are essential for the association with nuclear receptors. LXXLL motif 7, which is not present in isoform 2, increases the affinity for steroid receptors in vitro. |
| Involvement in disease DISEASE: Note=A chromosomal aberration involving NCOA1 is a cause of rhabdomyosarcoma. Translocation t(2;2)(q35;p23) with PAX3 generates the NCOA1-PAX3 oncogene consisting of the N-terminus part of PAX3 and the C-terminus part of NCOA1. The fusion protein acts as a transcriptional activator. Rhabdomyosarcoma is the most common soft tissue carcinoma in childhood, representing 5-8% of all malignancies in children. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15313887}. |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: Q15788 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
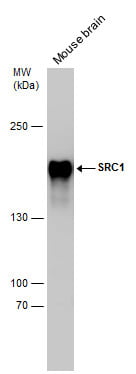
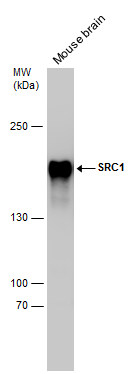 |
| Mouse tissue (50 µg) was separated by 5% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with SRC1 antibody [1135] (5818) diluted at 1:2000. |
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
| Western blot |
Documents
| # | SDS | Certificate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | |||
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.







Reviews
There are no reviews yet.