| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| host | mouse |
| isotype | IgG1 |
| clonality | monoclonal |
| concentration | 1 mg/mL |
| applications | ICC/IF, WB |
| reactivity | CD46/Membrane Cofactor Protein |
| available sizes | 100 µg |
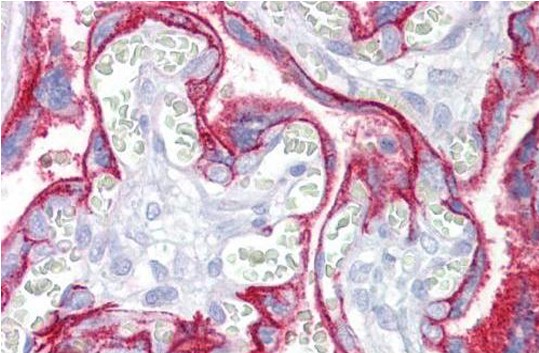
mouse anti-CD46/Membrane Cofactor Protein monoclonal antibody (3F1) 7171
$520.00
Antibody summary
- Mouse monoclonal to CD46/Membrane Cofactor Protein
- Suitable for: WB,IHC,ELISA
- Isotype: IgG1
- 100 µg
mouse anti-CD46/Membrane Cofactor Protein monoclonal antibody (3F1) 7171
| antibody |
|---|
| Tested applications WB,IHC,IHC,ELISA |
| Recommended dilutions Immunohistochemistry: use at 1- 10ug/ml. Immunoblotting: use at 0.5-1ug/ml. A band of ~44kDa is detected. Additional bands due to glycosylation of CD46 may be detected.ELISA: use at 0.1-1ug/ml with human CD46 on the solid phase. These are recommended concentrations. |
| Immunogen Recombinant human CD46. |
| Size and concentration 100µg and |
| Form lyophilized |
| Storage Instructions This product is stable for at least one (1) year at -20°C to -70°C. Reconstituted product should be stored in appropriate aliquots to avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Storage buffer Lyophilized in PBS. |
| Purity protein affinity purification |
| Clonality monoclonal |
| Isotype IgG1 |
| Compatible secondaries goat anti-mouse IgG, H&L chain specific, peroxidase conjugated polyclonal antibody 5486 goat anti-mouse IgG, H&L chain specific, biotin conjugated, Conjugate polyclonal antibody 2685 goat anti-mouse IgG, H&L chain specific, FITC conjugated polyclonal antibody 7854 goat anti-mouse IgG, H&L chain specific, peroxidase conjugated polyclonal antibody, crossabsorbed 1706 goat anti-mouse IgG, H&L chain specific, biotin conjugated polyclonal antibody, crossabsorbed 1716 goat anti-mouse IgG, H&L chain specific, FITC conjugated polyclonal antibody, crossabsorbed 1721 |
| Isotype control Mouse monocolonal IgG1 - Isotype Control |
| target relevance |
|---|
| Protein names Membrane cofactor protein (TLX) (Trophoblast leukocyte common antigen) (CD antigen CD46) |
| Gene names CD46,CD46 MCP MIC10 |
| Mass 43747Da |
| Function FUNCTION: Acts as a cofactor for complement factor I, a serine protease which protects autologous cells against complement-mediated injury by cleaving C3b and C4b deposited on host tissue. May be involved in the fusion of the spermatozoa with the oocyte during fertilization. Also acts as a costimulatory factor for T-cells which induces the differentiation of CD4+ into T-regulatory 1 cells. T-regulatory 1 cells suppress immune responses by secreting interleukin-10, and therefore are thought to prevent autoimmunity. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10843656, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12540904}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) A number of viral and bacterial pathogens seem to bind MCP in order to exploit its immune regulation property and directly induce an immunosuppressive phenotype in T-cells.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Acts as a receptor for Adenovirus subgroup B2 and Ad3. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12915534, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14566335, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15047806, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15078926, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15919905, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16254377}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Acts as a receptor for cultured Measles virus. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10972291, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20010840, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7534417, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8371352, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8402913}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Acts as a receptor for Herpesvirus 6/HHV-6. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12663806, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12724329}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) May act as a receptor for pathogenic bacteria Neisseria and Streptococcus pyogenes (PubMed:11260136, PubMed:11971006, PubMed:7708671, PubMed:9379894). |
| Subellular location SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: Cytoplasmic vesicle, secretory vesicle, acrosome inner membrane {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12112588, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14597734, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15307194}; Single-pass type I membrane protein {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12112588, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14597734, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15307194}. Note=Inner acrosomal membrane of spermatozoa. Internalized upon binding of Measles virus, Herpesvirus 6 or Neisseria gonorrhoeae, which results in an increased susceptibility of infected cells to complement-mediated injury. In cancer cells or cells infected by Neisseria, shedding leads to a soluble peptide. |
| Tissues TISSUE SPECIFICITY: Expressed by all cells except erythrocytes. |
| Structure SUBUNIT: Interacts with C3b (PubMed:1717583, PubMed:3260937). Interacts with C4b (PubMed:1717583). Interacts with moesin/MSN (PubMed:7884872). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:1717583, ECO:0000269|PubMed:3260937, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7884872}.; SUBUNIT: (Microbial infection) Interacts (via N-terminus) with measles virus H protein; this interaction allows attachment and viral entry of vaccine and laboratory-adapted strains. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10972291, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20010840}.; SUBUNIT: (Microbial infection) Interacts with human herpesvirus 6 GH protein (PubMed:12663806, PubMed:12724329). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12663806, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12724329}.; SUBUNIT: (Microbial infection) Interacts with human adenovirus B/D fiber protein (PubMed:12915534, PubMed:14566335, PubMed:15047806, PubMed:15078926, PubMed:15919905, PubMed:16254377). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12915534, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14566335, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15047806, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15078926, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15919905, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16254377}.; SUBUNIT: (Microbial infection) Binds to Streptococcus pyogenes M protein and to type IV pili from Neisseria (PubMed:11260136, PubMed:11971006, PubMed:7708671, PubMed:9379894). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11260136, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11971006, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7708671, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9379894}. |
| Post-translational modification PTM: N-glycosylated on Asn-83; Asn-114 and Asn-273 in most tissues, but probably less N-glycosylated in testis. N-glycosylation on Asn-114 and Asn-273 is required for cytoprotective function. N-glycosylation on Asn-114 is required for Measles virus binding. N-glycosylation on Asn-273 is required for Neisseria binding. N-glycosylation is not required for human adenovirus binding.; PTM: Extensively O-glycosylated in the Ser/Thr-rich domain. O-glycosylation is required for Neisseria binding but not for Measles virus or human adenovirus binding.; PTM: In epithelial cells, isoforms B/D/F/H/J/L/3 are phosphorylated by YES1 in response to infection by Neisseria gonorrhoeae; which promotes infectivity. In T-cells, these isoforms may be phosphorylated by LCK. |
| Domain DOMAIN: Sushi domains 1 and 2 are required for interaction with human adenovirus B PIV/FIBER protein and with Measles virus H protein. Sushi domains 2 and 3 are required for Herpesvirus 6 binding. Sushi domain 3 is required for Neisseria binding. Sushi domains 3 and 4 are required for interaction with Streptococcus pyogenes M protein and are the most important for interaction with C3b and C4b. |
| Involvement in disease DISEASE: Hemolytic uremic syndrome, atypical, 2 (AHUS2) [MIM:612922]: An atypical form of hemolytic uremic syndrome. It is a complex genetic disease characterized by microangiopathic hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, renal failure and absence of episodes of enterocolitis and diarrhea. In contrast to typical hemolytic uremic syndrome, atypical forms have a poorer prognosis, with higher death rates and frequent progression to end-stage renal disease. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:14566051, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16386793, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16621965, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20513133}. Note=Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Other genes may play a role in modifying the phenotype. Patients with CD46 mutations seem to have an overall better prognosis compared to patients carrying CFH mutations. |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: P15529 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
| Western blot IHC |
Documents
| # | SDS | Certificate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | |||
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.








Reviews
There are no reviews yet.