| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| host | mouse |
| isotype | IgG1 |
| clonality | monoclonal |
| concentration | concentrate, predilute |
| applications | IHC |
| reactivity | human |
| available size | 0.1 mL, 0.5 mL, 1 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted |
mouse anti-Caldesmon monoclonal antibody (ZM79) 6418
Price range: $160.00 through $528.00
Antibody summary
- Mouse monoclonal to Caldesmon
- Suitable for: Immunohistochemistry (formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues)
- Reacts with: Human
- Isotype:IgG1
- Control: Uterus, colon carcinoma
- Visualization: Cytoplasmic
- 0.1, 0.5, 1.0 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted
mouse anti-Caldesmon monoclonal antibody ZM79 6418
| target relevance |
|---|
| Protein names Caldesmon (CDM) |
| Gene names CALD1,CALD1 CAD CDM |
| Protein family Caldesmon family |
| Mass 93231Da |
| Function FUNCTION: Actin- and myosin-binding protein implicated in the regulation of actomyosin interactions in smooth muscle and nonmuscle cells (could act as a bridge between myosin and actin filaments). Stimulates actin binding of tropomyosin which increases the stabilization of actin filament structure. In muscle tissues, inhibits the actomyosin ATPase by binding to F-actin. This inhibition is attenuated by calcium-calmodulin and is potentiated by tropomyosin. Interacts with actin, myosin, two molecules of tropomyosin and with calmodulin. Also plays an essential role during cellular mitosis and receptor capping. Involved in Schwann cell migration during peripheral nerve regeneration (By similarity). {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8227296}. |
| Subellular location SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P13505}. Cytoplasm, myofibril {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P13505}. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, stress fiber {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P13505}. Note=On thin filaments in smooth muscle and on stress fibers in fibroblasts (nonmuscle). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P13505}. |
| Tissues TISSUE SPECIFICITY: High-molecular-weight caldesmon (isoform 1) is predominantly expressed in smooth muscles, whereas low-molecular-weight caldesmon (isoforms 2, 3, 4 and 5) are widely distributed in non-muscle tissues and cells. Not expressed in skeletal muscle or heart. |
| Post-translational modification PTM: In non-muscle cells, phosphorylation by CDK1 during mitosis causes caldesmon to dissociate from microfilaments. Phosphorylation reduces caldesmon binding to actin, myosin, and calmodulin as well as its inhibition of actomyosin ATPase activity. Phosphorylation also occurs in both quiescent and dividing smooth muscle cells with similar effects on the interaction with actin and calmodulin and on microfilaments reorganization. CDK1-mediated phosphorylation promotes Schwann cell migration during peripheral nerve regeneration (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
| Domain DOMAIN: The N-terminal part seems to be a myosin/calmodulin-binding domain, and the C-terminal a tropomyosin/actin/calmodulin-binding domain. These two domains are separated by a central helical region in the smooth-muscle form. |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: Q05682 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
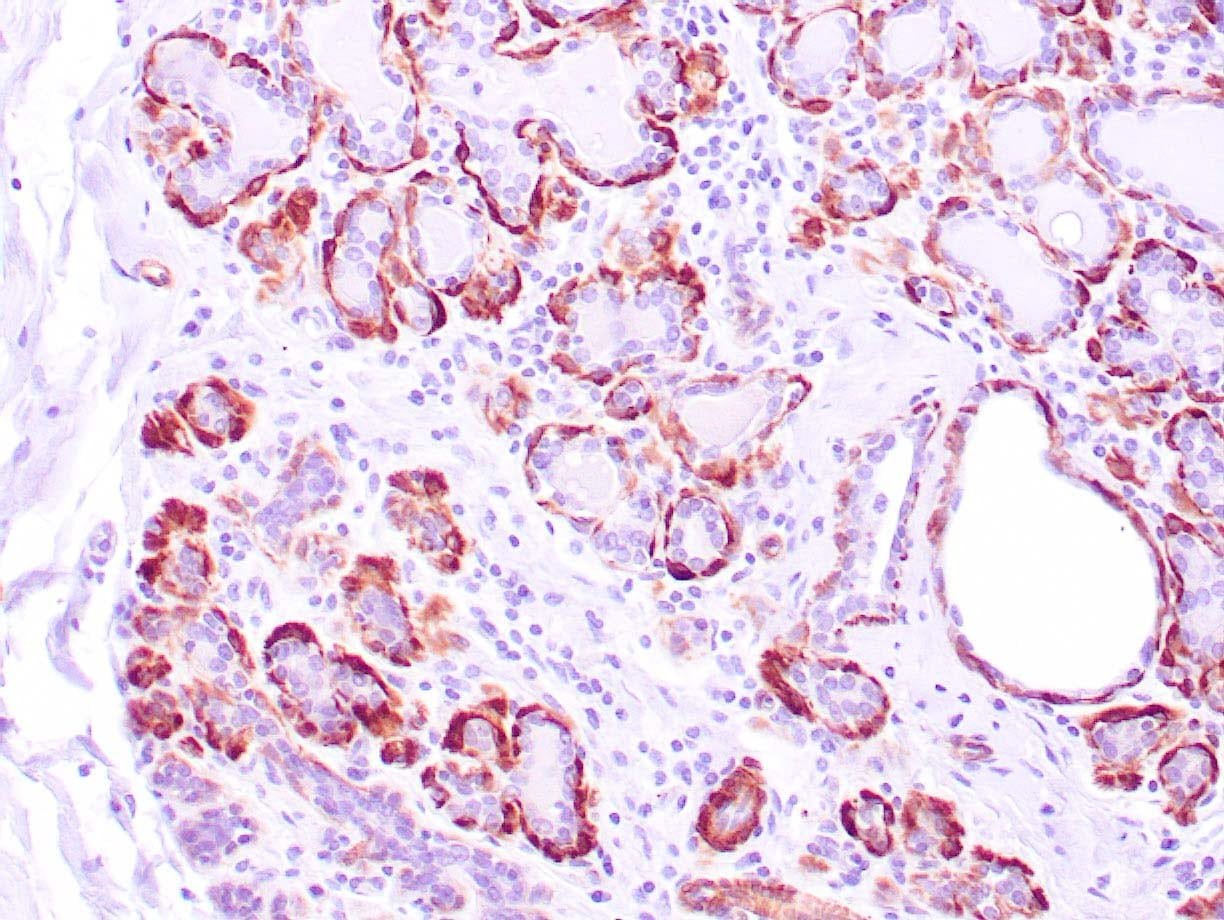 |
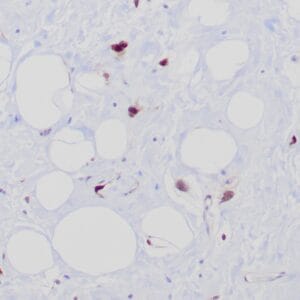
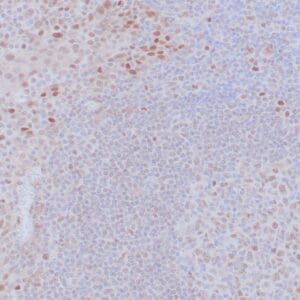
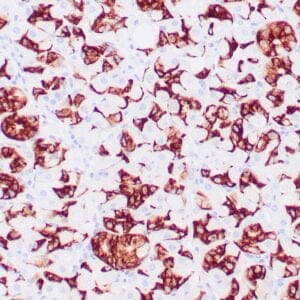
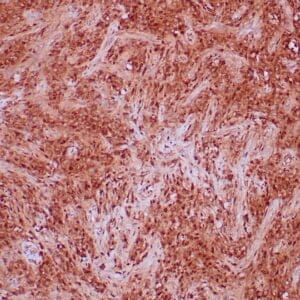
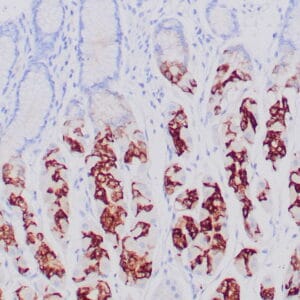
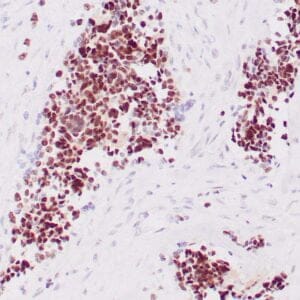
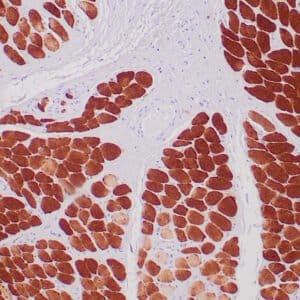
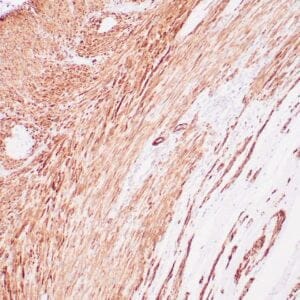
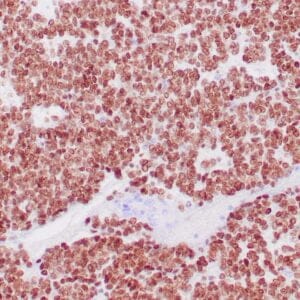
| Human breast tissue stained with anti-caldesmon antibody using peroxidase-conjugate and DAB chromogen. Note cytoplasmic staining of myoepithelial cells. |
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
| IHC |
Documents
| # | SDS | Certificate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | |||
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.